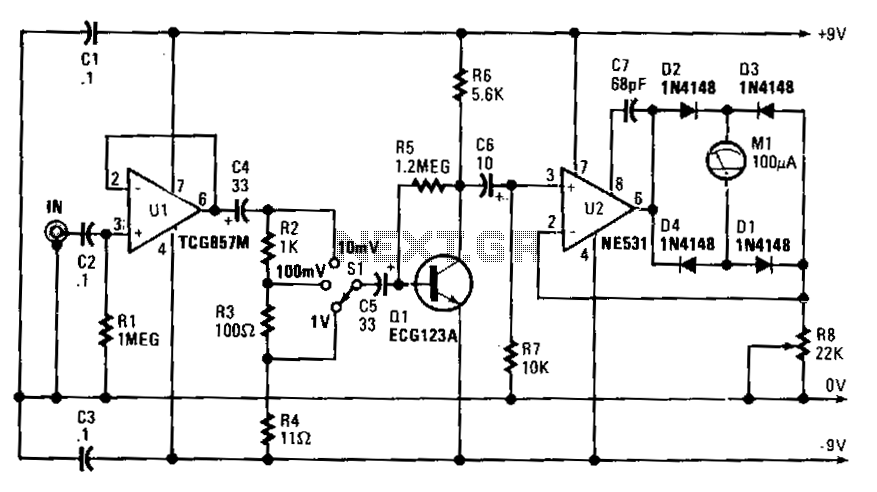
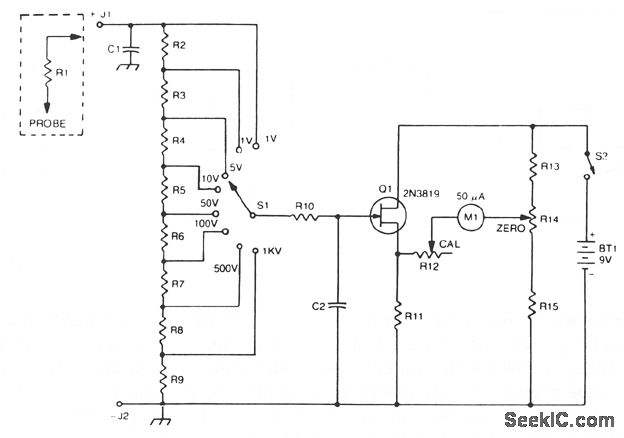
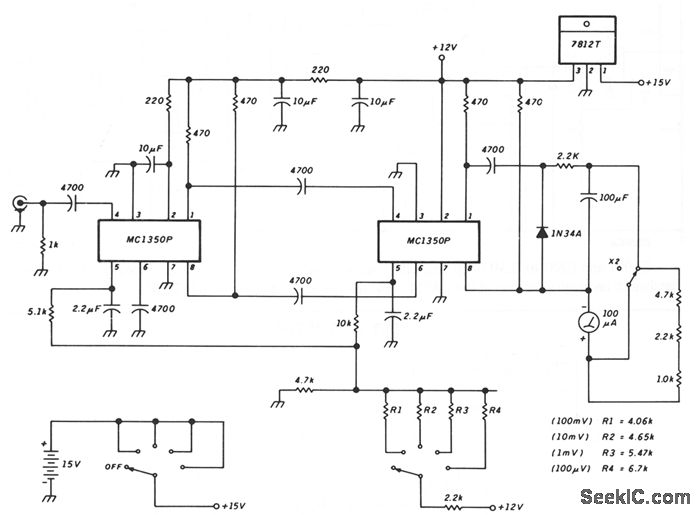
FETVM-FET Voltmeter
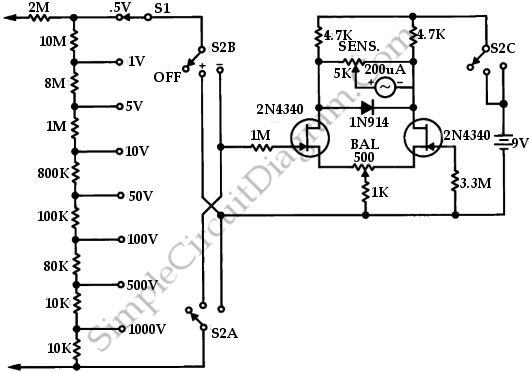
This is a circuit of a FETVM (Field Effect Transistor Voltmeter). The function of the VTVM (Vacuum Tube Voltmeter) is replaced by the FETVM while eliminating the conventional line cord instrument.
The FETVM circuit employs field effect transistors (FETs) to measure voltage levels with high impedance and accuracy. The primary advantage of using FETs in this application is their high input impedance, which minimizes the loading effect on the circuit being tested. This characteristic allows the FETVM to measure voltages without significantly altering the circuit's behavior.
The circuit typically includes an input stage that consists of a FET configured as a voltage follower, which provides isolation between the input and the subsequent stages. The output from this stage is then fed into an amplifier that further processes the signal. The gain of the amplifier can be adjusted to accommodate various voltage ranges, ensuring versatility in measurement.
In addition to the input and amplification stages, the FETVM circuit may incorporate a display mechanism, such as an analog meter or a digital readout, to present the measured voltage. The choice of display technology can affect the circuit's overall design, particularly in terms of power requirements and signal conditioning.
Power supply considerations are also crucial in the design of the FETVM. The circuit may utilize battery power to enhance portability and eliminate the need for a line cord, aligning with the goal of providing a more convenient and flexible measurement tool.
Overall, the FETVM circuit represents a modern approach to voltage measurement, leveraging the advantages of field effect transistors to achieve high precision and minimal impact on the circuit under test.This is a circuit of FETVM-FET Volmeter. The function of the VTVM is replaced by the FTEVM while at the same time ridding the usual line cord instrument. This.. 🔗 External reference
The FETVM circuit employs field effect transistors (FETs) to measure voltage levels with high impedance and accuracy. The primary advantage of using FETs in this application is their high input impedance, which minimizes the loading effect on the circuit being tested. This characteristic allows the FETVM to measure voltages without significantly altering the circuit's behavior.
The circuit typically includes an input stage that consists of a FET configured as a voltage follower, which provides isolation between the input and the subsequent stages. The output from this stage is then fed into an amplifier that further processes the signal. The gain of the amplifier can be adjusted to accommodate various voltage ranges, ensuring versatility in measurement.
In addition to the input and amplification stages, the FETVM circuit may incorporate a display mechanism, such as an analog meter or a digital readout, to present the measured voltage. The choice of display technology can affect the circuit's overall design, particularly in terms of power requirements and signal conditioning.
Power supply considerations are also crucial in the design of the FETVM. The circuit may utilize battery power to enhance portability and eliminate the need for a line cord, aligning with the goal of providing a more convenient and flexible measurement tool.
Overall, the FETVM circuit represents a modern approach to voltage measurement, leveraging the advantages of field effect transistors to achieve high precision and minimal impact on the circuit under test.This is a circuit of FETVM-FET Volmeter. The function of the VTVM is replaced by the FTEVM while at the same time ridding the usual line cord instrument. This.. 🔗 External reference