FLED-based solar engines

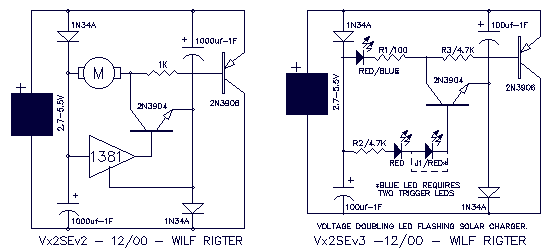
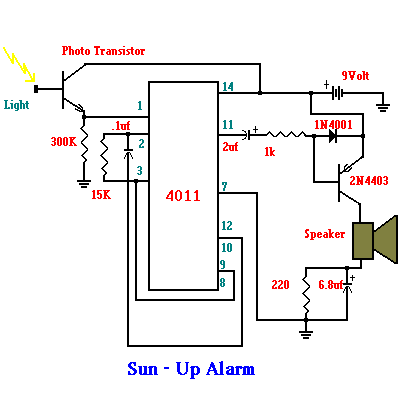
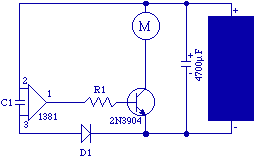
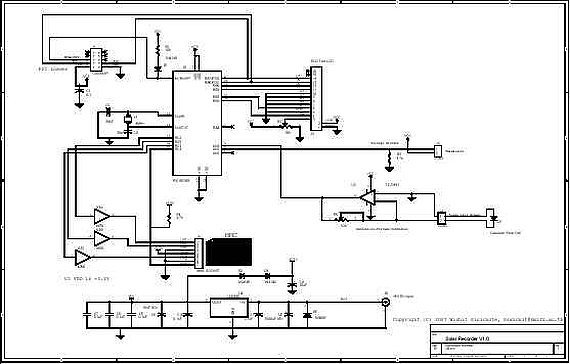
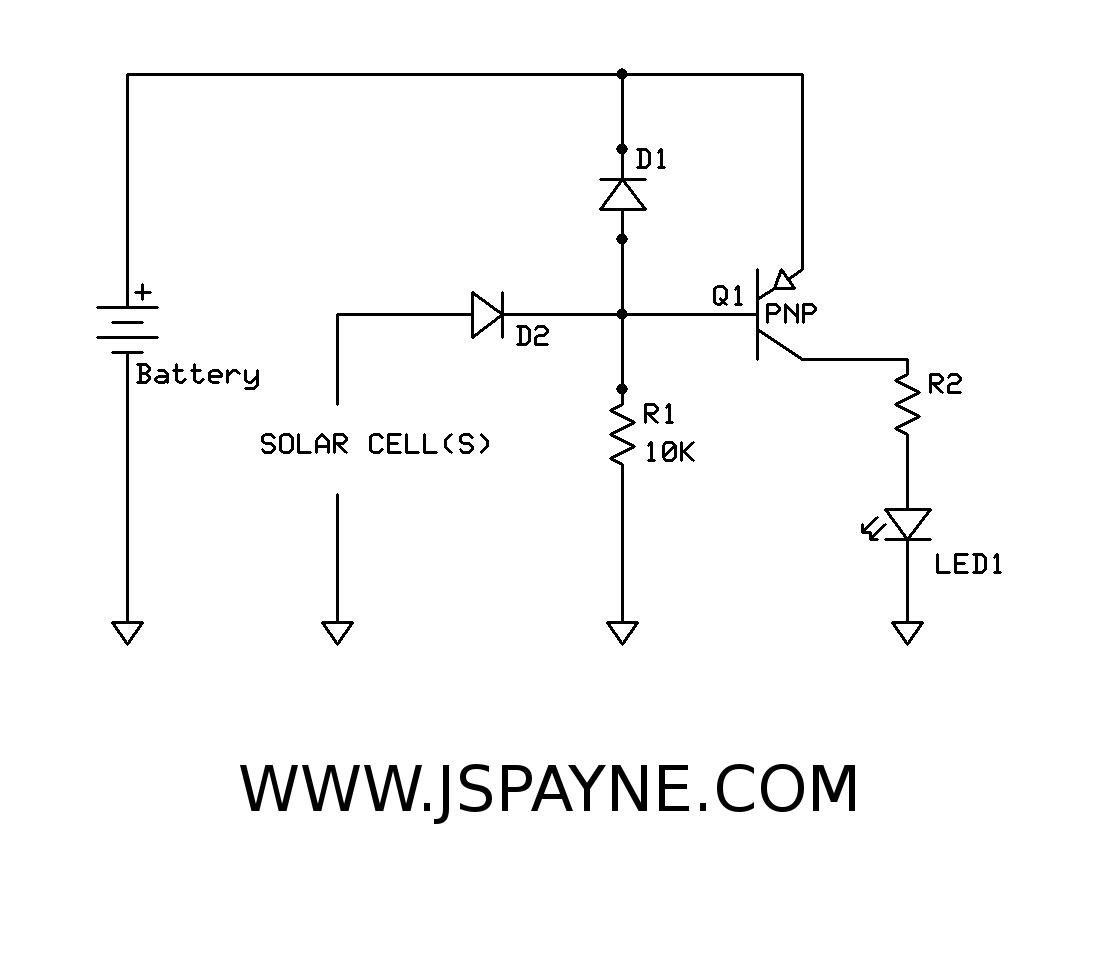
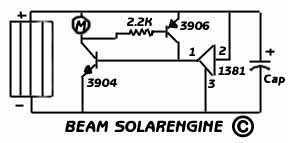
The original FLED-based SE uses a flashing LED to drive a type 1 solar engine (you'll note that it's just like the Zener-based SE, but with a FLED in the starring role). The good news is that all the parts in this solar engine are relatively easy to find; the bad news is that this solar engine design isn't particularly efficient unless you work at it.
The FLED-based solar engine (SE) circuit operates by utilizing a flashing LED (FLED) as the primary light source to charge a storage element, typically a capacitor or rechargeable battery, which is then used to power a load. The circuit design closely resembles that of a Zener-based solar engine, with the key difference being the use of the FLED, which provides a pulsing light output that can enhance the energy harvesting capabilities under certain conditions.
The components of the FLED-based solar engine include a solar panel, a FLED, a charging circuit, a storage element, and a load. The solar panel converts sunlight into electrical energy, which is used to power the FLED. The FLED flashes at a specific frequency, which can be modulated to optimize energy transfer to the storage element.
The charging circuit typically consists of a diode to prevent backflow of current and a resistor to limit the current flowing to the FLED and the storage element. The storage element accumulates energy during the periods when the FLED is illuminated. When the FLED is off, the stored energy can be discharged to power a load, such as a small motor or LED light.
To improve efficiency, careful selection of the FLED's flashing frequency and duty cycle is essential. Adjusting these parameters can maximize the energy captured from the solar panel and enhance the overall performance of the solar engine. Additionally, employing high-efficiency components and minimizing losses in the circuit can further increase the effectiveness of the design.
Overall, while the FLED-based solar engine offers a viable solution for energy harvesting in low-power applications, achieving optimal performance requires attention to design details and component selection.The original FLED-based SE uses a flashing LED to drive a type 1 solar engine (you`ll note that it`s just like the Zener-based SE, but with a FLED in the starring role). The good news is that all the parts in this solar engine are relatively easy to find; the bad news is that this solar engine design isn`t particularly efficient unless you work at it.
🔗 External reference
The FLED-based solar engine (SE) circuit operates by utilizing a flashing LED (FLED) as the primary light source to charge a storage element, typically a capacitor or rechargeable battery, which is then used to power a load. The circuit design closely resembles that of a Zener-based solar engine, with the key difference being the use of the FLED, which provides a pulsing light output that can enhance the energy harvesting capabilities under certain conditions.
The components of the FLED-based solar engine include a solar panel, a FLED, a charging circuit, a storage element, and a load. The solar panel converts sunlight into electrical energy, which is used to power the FLED. The FLED flashes at a specific frequency, which can be modulated to optimize energy transfer to the storage element.
The charging circuit typically consists of a diode to prevent backflow of current and a resistor to limit the current flowing to the FLED and the storage element. The storage element accumulates energy during the periods when the FLED is illuminated. When the FLED is off, the stored energy can be discharged to power a load, such as a small motor or LED light.
To improve efficiency, careful selection of the FLED's flashing frequency and duty cycle is essential. Adjusting these parameters can maximize the energy captured from the solar panel and enhance the overall performance of the solar engine. Additionally, employing high-efficiency components and minimizing losses in the circuit can further increase the effectiveness of the design.
Overall, while the FLED-based solar engine offers a viable solution for energy harvesting in low-power applications, achieving optimal performance requires attention to design details and component selection.The original FLED-based SE uses a flashing LED to drive a type 1 solar engine (you`ll note that it`s just like the Zener-based SE, but with a FLED in the starring role). The good news is that all the parts in this solar engine are relatively easy to find; the bad news is that this solar engine design isn`t particularly efficient unless you work at it.
🔗 External reference