Flexible AC Transmission Systems
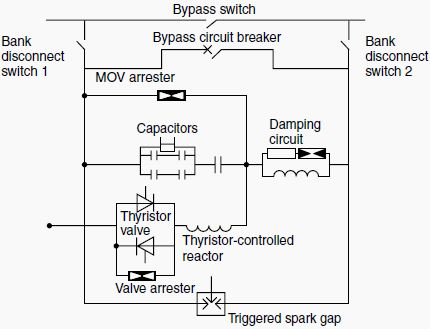
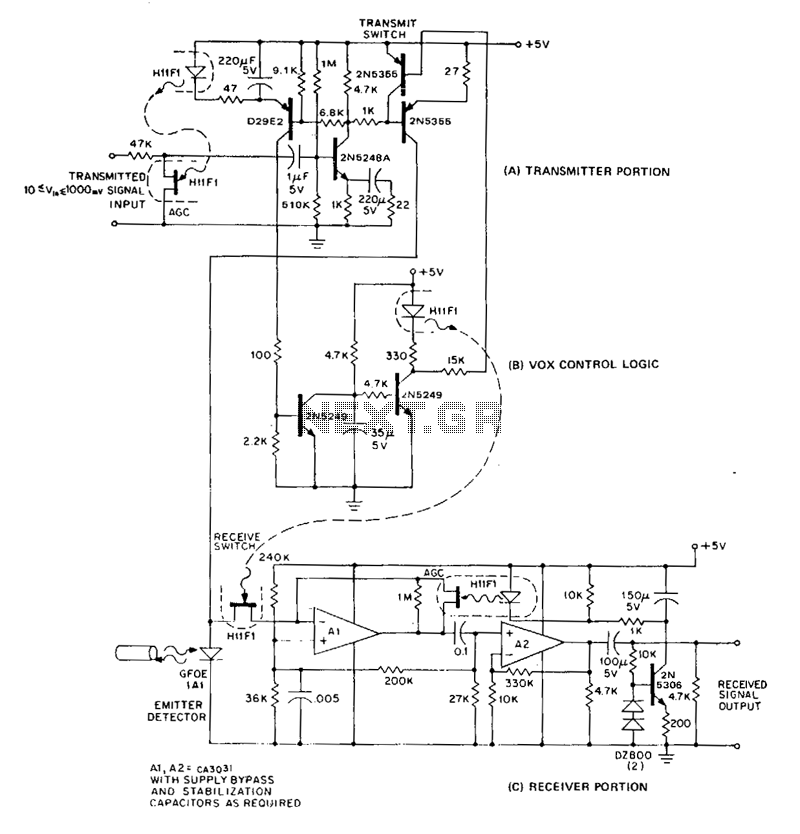
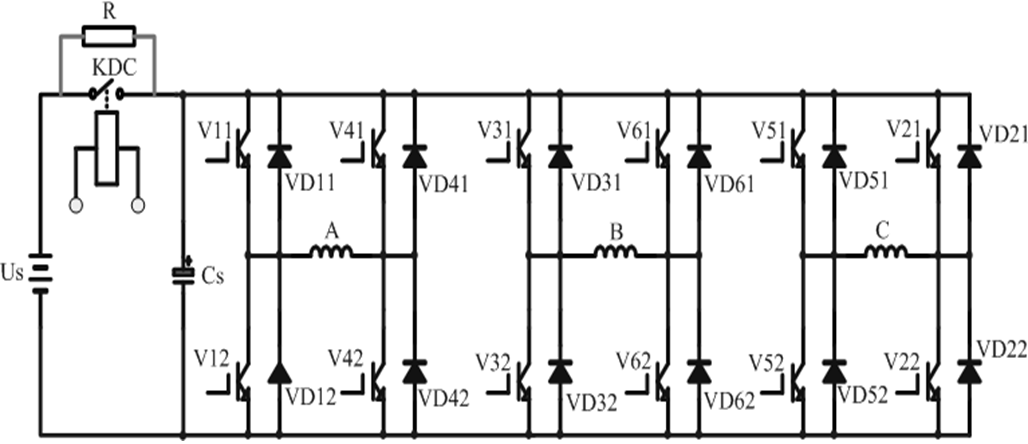
The acronym FACTS stands for "flexible AC transmission systems." These systems incorporate some advantages of direct current (DC), such as phase independence and rapid response.
Flexible AC transmission systems (FACTS) are advanced technologies designed to enhance the controllability and stability of electrical power transmission networks. By utilizing power electronics, FACTS devices can dynamically manage power flow, improve voltage stability, and increase the capacity of existing transmission lines.
Key components of FACTS include Static Synchronous Compensators (STATCOMs), Thyristor-Controlled Series Capacitors (TCSCs), and Unified Power Flow Controllers (UPFCs). STATCOMs are employed to regulate voltage levels and provide reactive power support, facilitating improved voltage stability during peak loads or disturbances. TCSCs enhance power transfer capability by dynamically controlling the reactance of transmission lines, thereby optimizing power flow. UPFCs combine the functionalities of both series and shunt compensation, allowing for simultaneous control of active and reactive power flows in the system.
The integration of FACTS into transmission systems significantly mitigates issues such as voltage fluctuations, line overloads, and oscillations, leading to a more reliable and efficient power grid. These systems are particularly advantageous in areas with high renewable energy penetration, where they help maintain grid stability amidst variable generation patterns. The deployment of FACTS technologies ultimately supports the transition towards smarter, more resilient electrical networks, enhancing the overall performance and reliability of power transmission systems.The acronym FACTS stands for “flexible ac transmission systems.â€These systems add some of the virtues of DC, i.e., phase independence and fast. 🔗 External reference
Flexible AC transmission systems (FACTS) are advanced technologies designed to enhance the controllability and stability of electrical power transmission networks. By utilizing power electronics, FACTS devices can dynamically manage power flow, improve voltage stability, and increase the capacity of existing transmission lines.
Key components of FACTS include Static Synchronous Compensators (STATCOMs), Thyristor-Controlled Series Capacitors (TCSCs), and Unified Power Flow Controllers (UPFCs). STATCOMs are employed to regulate voltage levels and provide reactive power support, facilitating improved voltage stability during peak loads or disturbances. TCSCs enhance power transfer capability by dynamically controlling the reactance of transmission lines, thereby optimizing power flow. UPFCs combine the functionalities of both series and shunt compensation, allowing for simultaneous control of active and reactive power flows in the system.
The integration of FACTS into transmission systems significantly mitigates issues such as voltage fluctuations, line overloads, and oscillations, leading to a more reliable and efficient power grid. These systems are particularly advantageous in areas with high renewable energy penetration, where they help maintain grid stability amidst variable generation patterns. The deployment of FACTS technologies ultimately supports the transition towards smarter, more resilient electrical networks, enhancing the overall performance and reliability of power transmission systems.The acronym FACTS stands for “flexible ac transmission systems.â€These systems add some of the virtues of DC, i.e., phase independence and fast. 🔗 External reference