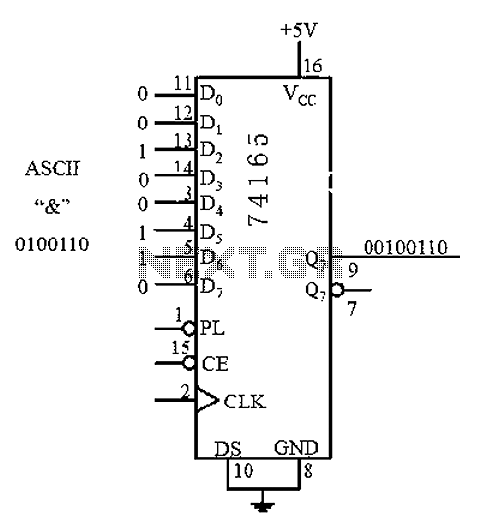
Fluorescent Tube Light Circuit
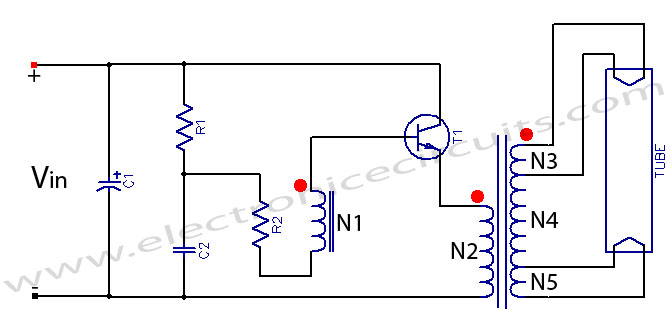
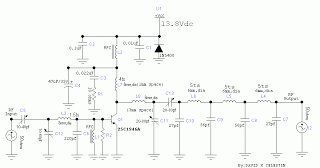
Fluorescent tube light circuit of an inverter that uses a single transistor and a single transformer. This type of inverter can be made in various configurations.
The fluorescent tube light circuit described utilizes a basic inverter design that incorporates a single transistor and a transformer to drive the lamp. The inverter operates by converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which is necessary for the operation of fluorescent tubes.
In this circuit, the transistor acts as a switch, controlling the flow of current through the primary winding of the transformer. When the transistor is turned on, current flows through the primary winding, creating a magnetic field in the transformer. This magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary winding, which is connected to the fluorescent tube. The oscillation of the transistor can be achieved through feedback mechanisms, often utilizing a resistor and capacitor to establish a resonant circuit that enables the inverter to operate efficiently.
The design can be adapted to different power ratings and fluorescent tube sizes by selecting appropriate values for the transformer and the transistor. Additionally, safety features such as fuses or current-limiting resistors may be included to protect the circuit from overload conditions. This inverter circuit is known for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for various applications where fluorescent lighting is required.
Overall, the implementation of a single transistor and transformer in the inverter circuit provides a compact solution for driving fluorescent tube lights, allowing for easy integration into existing lighting systems.Fluorescent Tube Light Circuit of an inverter that uses a single transistor and a single transformer. This type inverter can be made in various.. 🔗 External reference
The fluorescent tube light circuit described utilizes a basic inverter design that incorporates a single transistor and a transformer to drive the lamp. The inverter operates by converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which is necessary for the operation of fluorescent tubes.
In this circuit, the transistor acts as a switch, controlling the flow of current through the primary winding of the transformer. When the transistor is turned on, current flows through the primary winding, creating a magnetic field in the transformer. This magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary winding, which is connected to the fluorescent tube. The oscillation of the transistor can be achieved through feedback mechanisms, often utilizing a resistor and capacitor to establish a resonant circuit that enables the inverter to operate efficiently.
The design can be adapted to different power ratings and fluorescent tube sizes by selecting appropriate values for the transformer and the transistor. Additionally, safety features such as fuses or current-limiting resistors may be included to protect the circuit from overload conditions. This inverter circuit is known for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for various applications where fluorescent lighting is required.
Overall, the implementation of a single transistor and transformer in the inverter circuit provides a compact solution for driving fluorescent tube lights, allowing for easy integration into existing lighting systems.Fluorescent Tube Light Circuit of an inverter that uses a single transistor and a single transformer. This type inverter can be made in various.. 🔗 External reference