FM Booster~Active FM Antenna Amplifier
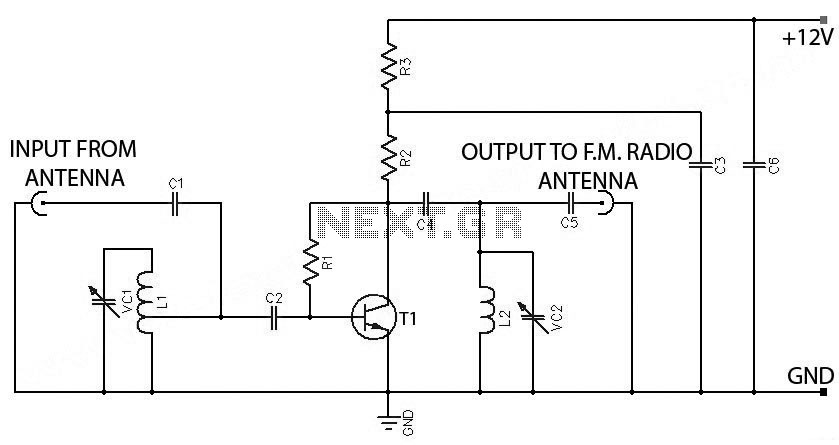
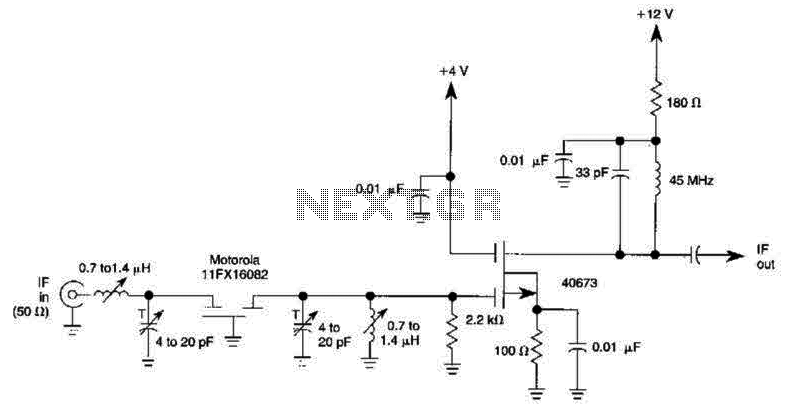
FM Booster, Active FM Antenna Amplifier. This FM booster can be used to listen to programs from distant FM stations clearly. The circuit comprises a common-emitter tuned RF preamplifier wired around VHF/UHF transistor 2SC2570.
The FM booster circuit is designed to enhance the reception of FM signals from distant stations by amplifying weak radio frequency signals. The primary component of this circuit is the VHF/UHF transistor 2SC2570, which operates in a common-emitter configuration. This configuration is advantageous for RF amplification as it provides a good balance of gain and bandwidth.
The circuit typically includes several key components: an input matching network, a tuned circuit for frequency selection, and a power supply circuit. The input matching network is designed to optimize the impedance seen by the antenna to maximize signal capture. The tuned circuit, often consisting of an inductor and a variable capacitor, allows for selective amplification of the desired FM frequency while filtering out unwanted signals.
Power supply requirements for the 2SC2570 transistor should be carefully considered, as it operates efficiently within a specific voltage range. The circuit may also incorporate bypass capacitors to stabilize the power supply and improve performance by reducing noise.
Additionally, it is essential to ensure proper grounding and shielding of the circuit to minimize interference from external sources. The layout should be compact to reduce losses and maintain signal integrity. The output of the amplifier can be connected directly to an FM receiver or a further processing stage, depending on the application.
Overall, the FM booster circuit utilizing the 2SC2570 transistor is a robust solution for improving FM radio reception, particularly in areas with weak signal strength.FM Booster, Active FM Antenna Amplifier This FM booster that can be used to listen to programmes from distant FM stations clearly. The circuit comprises a common-emitter tuned RF preamplifier wired around VHF/UHF transistor 2SC2570.
(Only C.. 🔗 External reference
The FM booster circuit is designed to enhance the reception of FM signals from distant stations by amplifying weak radio frequency signals. The primary component of this circuit is the VHF/UHF transistor 2SC2570, which operates in a common-emitter configuration. This configuration is advantageous for RF amplification as it provides a good balance of gain and bandwidth.
The circuit typically includes several key components: an input matching network, a tuned circuit for frequency selection, and a power supply circuit. The input matching network is designed to optimize the impedance seen by the antenna to maximize signal capture. The tuned circuit, often consisting of an inductor and a variable capacitor, allows for selective amplification of the desired FM frequency while filtering out unwanted signals.
Power supply requirements for the 2SC2570 transistor should be carefully considered, as it operates efficiently within a specific voltage range. The circuit may also incorporate bypass capacitors to stabilize the power supply and improve performance by reducing noise.
Additionally, it is essential to ensure proper grounding and shielding of the circuit to minimize interference from external sources. The layout should be compact to reduce losses and maintain signal integrity. The output of the amplifier can be connected directly to an FM receiver or a further processing stage, depending on the application.
Overall, the FM booster circuit utilizing the 2SC2570 transistor is a robust solution for improving FM radio reception, particularly in areas with weak signal strength.FM Booster, Active FM Antenna Amplifier This FM booster that can be used to listen to programmes from distant FM stations clearly. The circuit comprises a common-emitter tuned RF preamplifier wired around VHF/UHF transistor 2SC2570.
(Only C.. 🔗 External reference