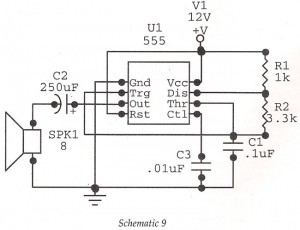
Frequency comparator circuit
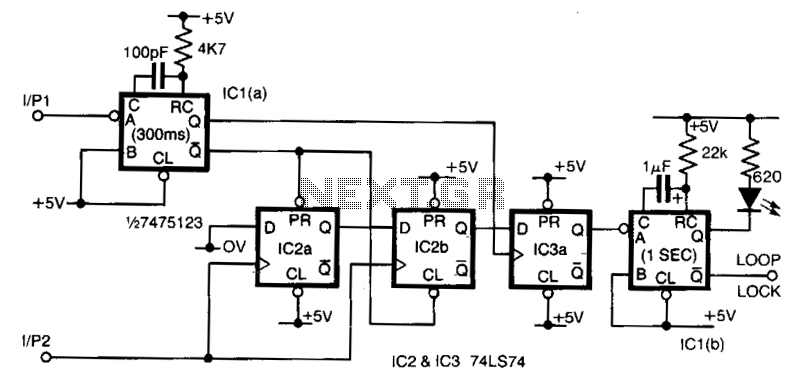
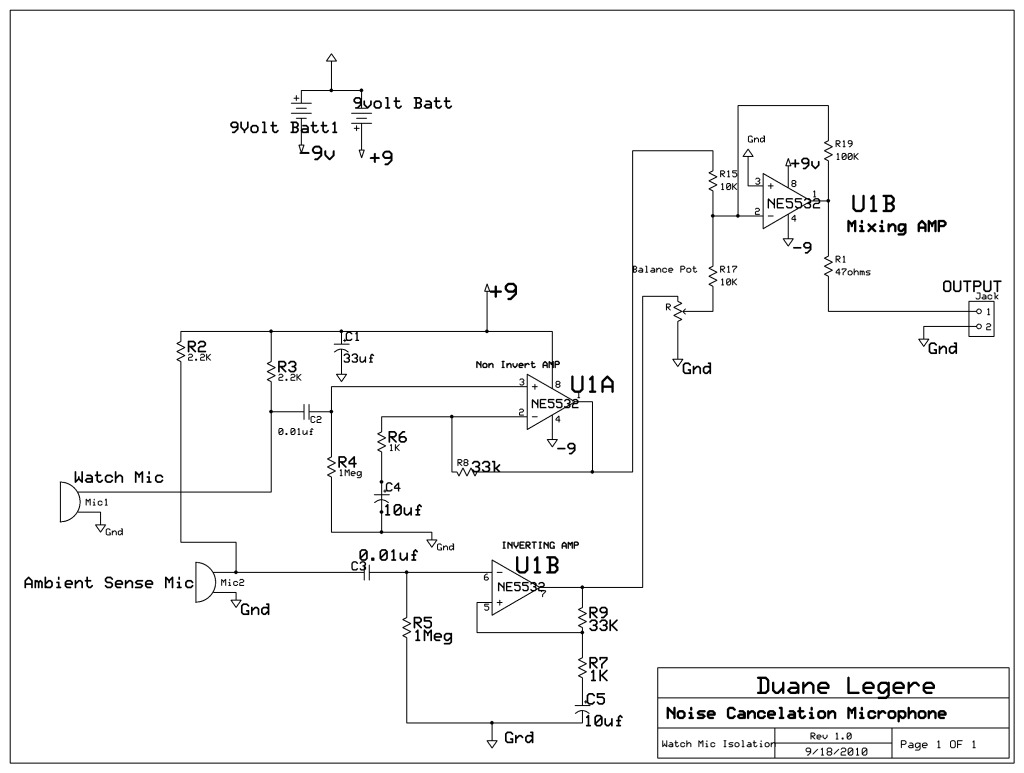
Input 1 functions as a gating period, during which a single rising edge on input 2 produces a logic 1 output. Any other input that indicates non-identical frequencies results in a logic 0 output. IC1a converts input 1 into a narrow pulse, which initializes IC2, a two-stage shift register that is clocked by input 2. Upon the first edge of input 2, a logic 1 is generated at the output of IC2b, while subsequent inputs yield a logic 0. At the conclusion of the gating period, this output is latched by IC3, resulting in the lock output. Additionally, since this is only valid for one input period, a monostable circuit is incorporated at the output to allow for visual monitoring. Depending on which state is deemed most critical, either output from IC3 can be utilized. The current configuration indicates a failure state.
The circuit utilizes a gating mechanism wherein Input 1 establishes a time window for valid signal detection from Input 2. The logic state of Input 2 is pivotal; a single rising edge during the gating period triggers a transition to a logic 1 output, while any other frequencies during this timeframe lead to a logic 0 output. This function is facilitated by IC1a, which processes Input 1 into a narrow pulse signal. This pulse serves as an initialization signal for IC2, which is configured as a two-stage shift register. The clocking of this shift register is directly influenced by Input 2. On the initial rising edge of Input 2, IC2b outputs a logic 1, indicating the detection of the valid signal, while all subsequent edges result in a logic 0 output, effectively creating a one-shot response to the first edge.
The output from IC2b is then latched by IC3 at the end of the gating period, establishing a lock output that signifies the successful capture of the input signal. To ensure that this output can be monitored visually, a monostable multivibrator is employed. This component generates a temporary pulse that can be observed, thus allowing for real-time monitoring of the system's state. The design allows for flexibility in output selection, enabling the user to choose between two outputs from IC3 based on the importance of the respective states. The current configuration is particularly useful for indicating a failure state, providing critical feedback for system diagnostics.Input 1 is used as a gating period, during which a single rising edge on input 2 will cause a logic 1 output-any other number, indicating non-identical frequencies causes a logic 0 output. ICla converts input 1 to a narrow pulse which initializes IC2 which forms a two-stage shift register clocked by input 2.
On the first edge of input 2 a logic 1 appears on the output of IC2b and for all subsequent inputs a logic 0 is present. At the end of the gating period this output is latched by IC3 forming the lock output. As this is only valid for one input period a monostable is added to the output to enable, for example, visual monitoring of the output. Either output from IC3 can be used depending on which state is most important. As connected the failure state is indicated.
The circuit utilizes a gating mechanism wherein Input 1 establishes a time window for valid signal detection from Input 2. The logic state of Input 2 is pivotal; a single rising edge during the gating period triggers a transition to a logic 1 output, while any other frequencies during this timeframe lead to a logic 0 output. This function is facilitated by IC1a, which processes Input 1 into a narrow pulse signal. This pulse serves as an initialization signal for IC2, which is configured as a two-stage shift register. The clocking of this shift register is directly influenced by Input 2. On the initial rising edge of Input 2, IC2b outputs a logic 1, indicating the detection of the valid signal, while all subsequent edges result in a logic 0 output, effectively creating a one-shot response to the first edge.
The output from IC2b is then latched by IC3 at the end of the gating period, establishing a lock output that signifies the successful capture of the input signal. To ensure that this output can be monitored visually, a monostable multivibrator is employed. This component generates a temporary pulse that can be observed, thus allowing for real-time monitoring of the system's state. The design allows for flexibility in output selection, enabling the user to choose between two outputs from IC3 based on the importance of the respective states. The current configuration is particularly useful for indicating a failure state, providing critical feedback for system diagnostics.Input 1 is used as a gating period, during which a single rising edge on input 2 will cause a logic 1 output-any other number, indicating non-identical frequencies causes a logic 0 output. ICla converts input 1 to a narrow pulse which initializes IC2 which forms a two-stage shift register clocked by input 2.
On the first edge of input 2 a logic 1 appears on the output of IC2b and for all subsequent inputs a logic 0 is present. At the end of the gating period this output is latched by IC3 forming the lock output. As this is only valid for one input period a monostable is added to the output to enable, for example, visual monitoring of the output. Either output from IC3 can be used depending on which state is most important. As connected the failure state is indicated.