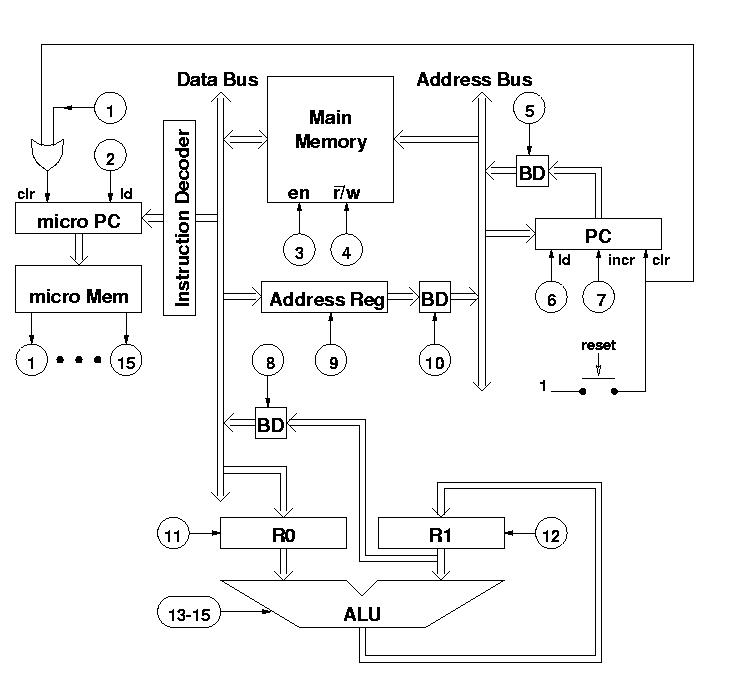
Game Circuits
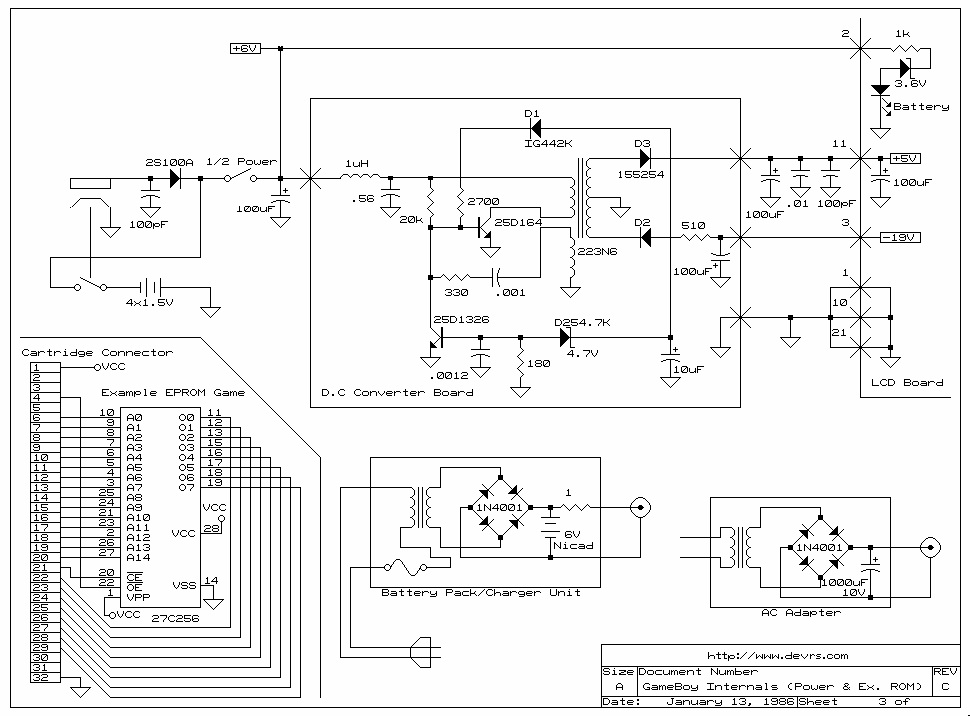
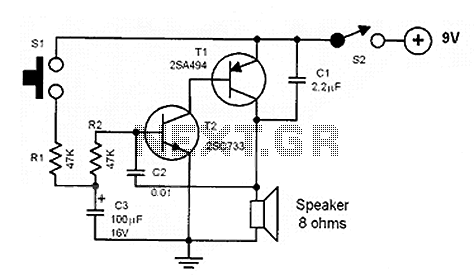
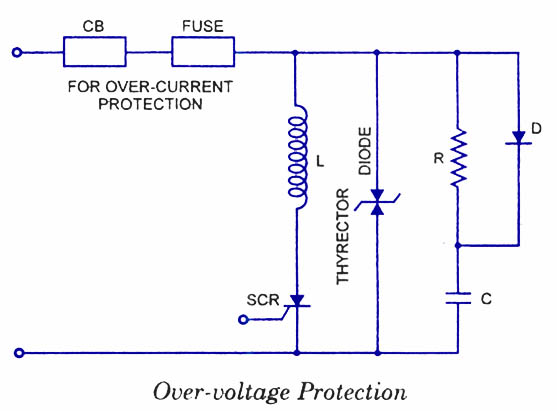
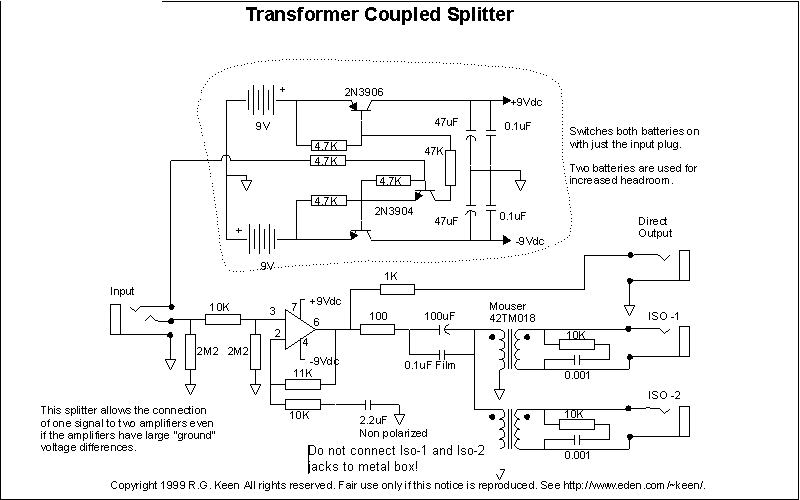
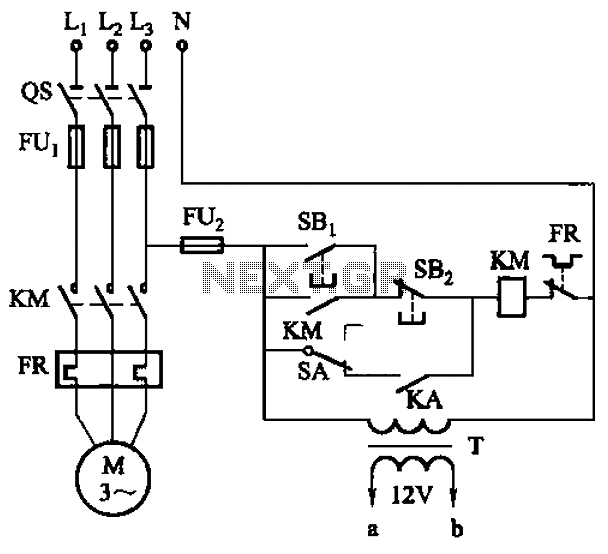
The circuits in Figure 1 and Figure 2 demonstrate specific advantages over the circuit presented in the Design Idea in EDN, titled "Circuit detects first event," published on May 3, 2001, page 89. The n-player first-event detection circuit provides several enhancements: it requires fewer passive components and only needs n diodes instead of (n^2+n)/2 for three or more players.
The n-player first-event detection circuit is designed to efficiently identify the first event among multiple players with minimal component usage. In traditional designs, the complexity increases significantly as the number of players increases, leading to a quadratic growth in the number of required components. However, this innovative circuit reduces the number of diodes needed to just n, where n represents the number of players involved in the detection process.
This reduction in component count not only simplifies the circuit layout but also enhances reliability and reduces the overall cost of the design. Each diode in the circuit plays a critical role in signal routing, ensuring that the first event is accurately detected without interference from subsequent events. The architecture typically incorporates a combination of logic gates to process the signals received from the diodes, allowing for a quick and efficient determination of the first event.
The operational principle relies on the concept of prioritizing signals from the players. When an event occurs, the corresponding diode conducts, allowing the signal to propagate through the circuit. The configuration is such that only the first signal to reach a designated output will be recognized, effectively ignoring any subsequent signals until the circuit is reset. This feature is particularly advantageous in applications such as gaming, where it is crucial to determine the first player to act.
In conclusion, the n-player first-event detection circuit offers a streamlined solution for event detection in multi-player scenarios, showcasing significant improvements in component efficiency and operational performance over traditional designs.The circuits in Figure1 and Figure 2 exhibit certain advantages over the circuit shown in the Design Idea in EDN, "Circuit detects first event, " May 3, 2001, pg 89. The n-player first-event-detection circuit offers several improvements: It has fewer passive components.
It needs only n diodes instead of (n2+n)/2 for three or more players. 🔗 External reference
The n-player first-event detection circuit is designed to efficiently identify the first event among multiple players with minimal component usage. In traditional designs, the complexity increases significantly as the number of players increases, leading to a quadratic growth in the number of required components. However, this innovative circuit reduces the number of diodes needed to just n, where n represents the number of players involved in the detection process.
This reduction in component count not only simplifies the circuit layout but also enhances reliability and reduces the overall cost of the design. Each diode in the circuit plays a critical role in signal routing, ensuring that the first event is accurately detected without interference from subsequent events. The architecture typically incorporates a combination of logic gates to process the signals received from the diodes, allowing for a quick and efficient determination of the first event.
The operational principle relies on the concept of prioritizing signals from the players. When an event occurs, the corresponding diode conducts, allowing the signal to propagate through the circuit. The configuration is such that only the first signal to reach a designated output will be recognized, effectively ignoring any subsequent signals until the circuit is reset. This feature is particularly advantageous in applications such as gaming, where it is crucial to determine the first player to act.
In conclusion, the n-player first-event detection circuit offers a streamlined solution for event detection in multi-player scenarios, showcasing significant improvements in component efficiency and operational performance over traditional designs.The circuits in Figure1 and Figure 2 exhibit certain advantages over the circuit shown in the Design Idea in EDN, "Circuit detects first event, " May 3, 2001, pg 89. The n-player first-event-detection circuit offers several improvements: It has fewer passive components.
It needs only n diodes instead of (n2+n)/2 for three or more players. 🔗 External reference