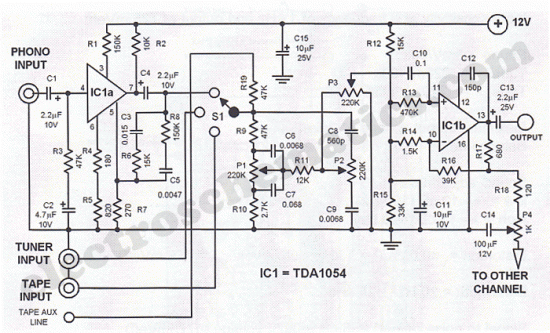
General-Purpose Preamp

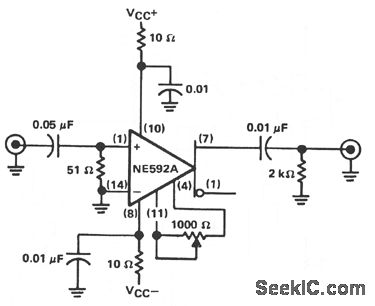
This amplifier is suitable for audio and video applications. The gain is determined by Rf, and the voltage gain of this amplifier is approximately 1 + (Rf / Rs), where Rs is in ohms. The bandwidth is influenced by the selected gain, typically reaching several MHz. With Rf set to 5.1 kOhm, a gain of 10 (20 dB) voltage is achieved.
This amplifier circuit is designed for versatility in audio and video applications, leveraging a gain configuration that allows for easy adjustment through the feedback resistor (Rf). The expression for voltage gain, approximately 1 + (Rf / Rs), indicates that the gain can be tailored by selecting appropriate resistor values, where Rs represents the source resistance.
The bandwidth of the amplifier is a critical parameter that varies with the gain setting. Generally, as the gain increases, the bandwidth decreases, adhering to the trade-off principle known as Gain-Bandwidth Product. In practical applications, this amplifier can achieve a bandwidth in the range of several MHz, making it suitable for high-frequency audio and video signals.
When Rf is set to 5.1 kOhm, the resulting gain of 10 (20 dB) is indicative of the amplifier's capability to significantly amplify input signals. This gain setting is particularly useful in scenarios where moderate amplification is required without compromising the integrity of the signal.
To implement this amplifier in a circuit, it is essential to consider the power supply requirements, input and output impedance matching, and thermal management to ensure optimal performance. Proper layout and grounding techniques should be employed to minimize noise and interference, which is critical in high-fidelity audio and video applications. The selection of additional components, such as bypass capacitors and feedback capacitors, may further enhance the stability and performance of the amplifier across its operational bandwidth. This amplifier is useful for audio and video applications. Gain is set by Rf and the voltage gain of this amplifier is approximately 1 + i//560, where R/vs, in ohms. Bandwidth depends on gain selected, but typically it is several MHz. R/= 5.1 KOhmhm, which produces a gain of 10 (20 dB) voltage. 🔗 External reference
This amplifier circuit is designed for versatility in audio and video applications, leveraging a gain configuration that allows for easy adjustment through the feedback resistor (Rf). The expression for voltage gain, approximately 1 + (Rf / Rs), indicates that the gain can be tailored by selecting appropriate resistor values, where Rs represents the source resistance.
The bandwidth of the amplifier is a critical parameter that varies with the gain setting. Generally, as the gain increases, the bandwidth decreases, adhering to the trade-off principle known as Gain-Bandwidth Product. In practical applications, this amplifier can achieve a bandwidth in the range of several MHz, making it suitable for high-frequency audio and video signals.
When Rf is set to 5.1 kOhm, the resulting gain of 10 (20 dB) is indicative of the amplifier's capability to significantly amplify input signals. This gain setting is particularly useful in scenarios where moderate amplification is required without compromising the integrity of the signal.
To implement this amplifier in a circuit, it is essential to consider the power supply requirements, input and output impedance matching, and thermal management to ensure optimal performance. Proper layout and grounding techniques should be employed to minimize noise and interference, which is critical in high-fidelity audio and video applications. The selection of additional components, such as bypass capacitors and feedback capacitors, may further enhance the stability and performance of the amplifier across its operational bandwidth. This amplifier is useful for audio and video applications. Gain is set by Rf and the voltage gain of this amplifier is approximately 1 + i//560, where R/vs, in ohms. Bandwidth depends on gain selected, but typically it is several MHz. R/= 5.1 KOhmhm, which produces a gain of 10 (20 dB) voltage. 🔗 External reference