Headlight Flasher
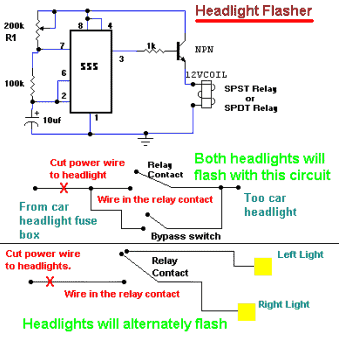
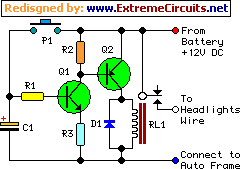
A compact and intriguing circuit designed to flash automotive headlights. It utilizes a well-known NE555 timer circuit to achieve this functionality.
The circuit operates by employing the NE555 timer in astable mode, which allows it to generate a continuous square wave output. This output is connected to a relay that controls the headlights, enabling them to turn on and off at a specified frequency. The frequency of the flashing can be adjusted by changing the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer.
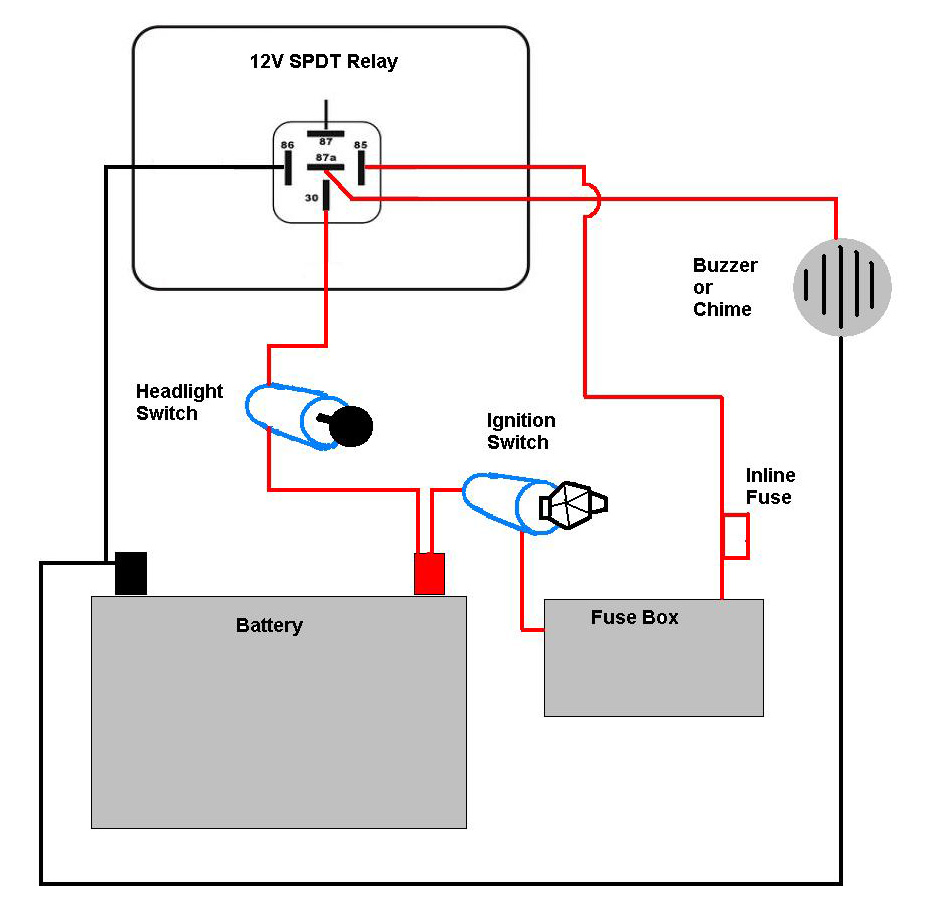
In a typical setup, the circuit includes the NE555 timer IC, a few passive components such as resistors and capacitors, and a relay capable of handling the current drawn by the headlights. The NE555 timer is powered by the vehicle's battery, ensuring that it operates effectively even when the vehicle is stationary.
The use of the relay is crucial as it isolates the low-power timer circuit from the high-power headlights, preventing any potential damage to the timer IC. The circuit can be further enhanced with additional features such as a variable resistor to adjust the flashing rate, or diodes to protect against back EMF generated by the relay.
Overall, this circuit serves as an engaging project for automotive enthusiasts, providing a practical application of the NE555 timer while enhancing vehicle visibility through the flashing headlights.Small and interesting circuit that flashes your head lights. Automotive, head lights, circuit diagram. Built around famous NE555 timer circuit.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by employing the NE555 timer in astable mode, which allows it to generate a continuous square wave output. This output is connected to a relay that controls the headlights, enabling them to turn on and off at a specified frequency. The frequency of the flashing can be adjusted by changing the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer.
In a typical setup, the circuit includes the NE555 timer IC, a few passive components such as resistors and capacitors, and a relay capable of handling the current drawn by the headlights. The NE555 timer is powered by the vehicle's battery, ensuring that it operates effectively even when the vehicle is stationary.
The use of the relay is crucial as it isolates the low-power timer circuit from the high-power headlights, preventing any potential damage to the timer IC. The circuit can be further enhanced with additional features such as a variable resistor to adjust the flashing rate, or diodes to protect against back EMF generated by the relay.
Overall, this circuit serves as an engaging project for automotive enthusiasts, providing a practical application of the NE555 timer while enhancing vehicle visibility through the flashing headlights.Small and interesting circuit that flashes your head lights. Automotive, head lights, circuit diagram. Built around famous NE555 timer circuit.. 🔗 External reference