Heart Rate Sensor
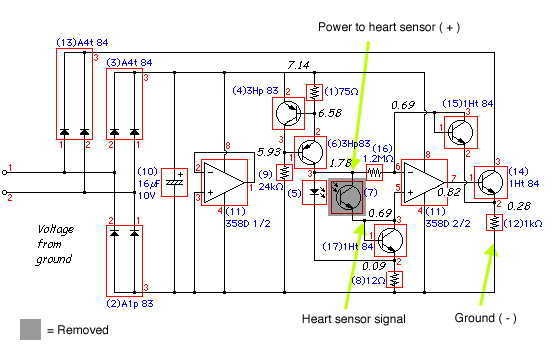
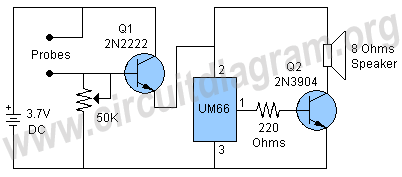
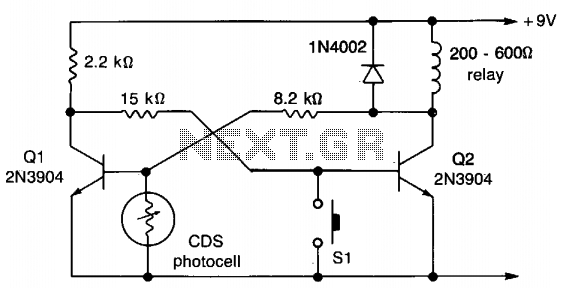
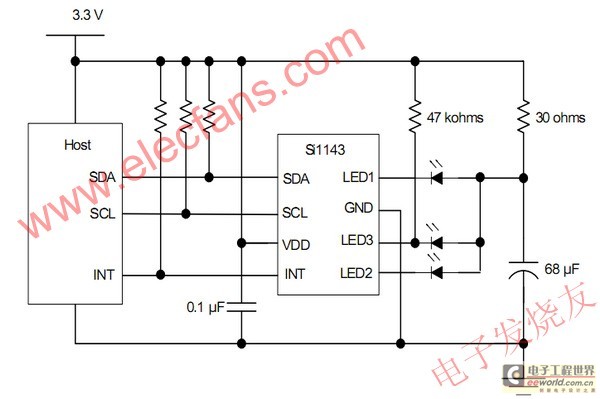
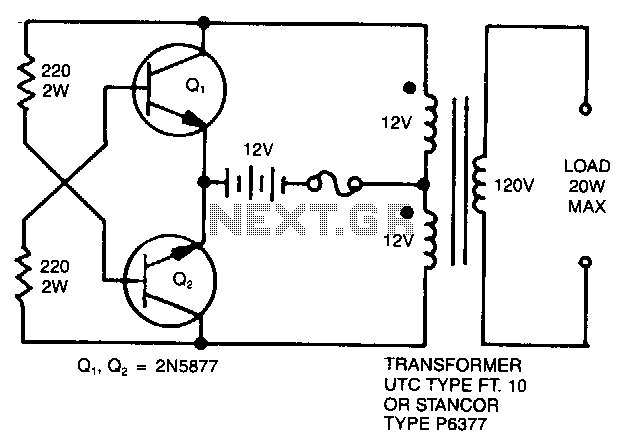
Here is the inside of the light reflectance sensor (top) and a schematic drawing of its circuitry (bottom). First, carefully remove the phototransistor as shown. Then, attach the three wires that we will connect to the heart sensor (shown in bright yellow). Hint: if you leave the leads from the phototransistor when you cut it off, you can attach the two corresponding wires directly to them, rather than to the circuit board itself.
The light reflectance sensor typically consists of a phototransistor, which is the primary component for detecting light levels. The schematic drawing illustrates the connections and layout of the circuit, emphasizing the importance of proper wiring to ensure accurate readings. The phototransistor, when exposed to light, generates a current that can be measured and interpreted by the connected heart sensor.
In the assembly process, careful removal of the phototransistor is crucial to maintain the integrity of the circuit. Once the phototransistor is detached, the three wires intended for connection to the heart sensor must be securely attached. The use of the existing leads from the phototransistor can simplify this process, allowing for a more straightforward connection without needing to solder directly onto the circuit board.
The schematic also indicates the placement of resistors and capacitors that may be present in the circuit, which can help stabilize the output signal and filter any noise that may interfere with the sensor's performance. Proper attention to these components will enhance the reliability of the light reflectance sensor in measuring light intensity, which is essential for accurate heart rate monitoring in various applications.Here is the inside of the light reflectance sensor (top) and a schematic drawing of it's circuitry (bottom). First, carefully remove the phototransistor as shown. Then, attach the three wires that we will connect to the heart sensor (show in bright yellow). Hint: if you leave the leads from the phototransistor when you cut it off, you can attach the two corresponding wires directly to them, rather than to the circuit board itself.
🔗 External reference
The light reflectance sensor typically consists of a phototransistor, which is the primary component for detecting light levels. The schematic drawing illustrates the connections and layout of the circuit, emphasizing the importance of proper wiring to ensure accurate readings. The phototransistor, when exposed to light, generates a current that can be measured and interpreted by the connected heart sensor.
In the assembly process, careful removal of the phototransistor is crucial to maintain the integrity of the circuit. Once the phototransistor is detached, the three wires intended for connection to the heart sensor must be securely attached. The use of the existing leads from the phototransistor can simplify this process, allowing for a more straightforward connection without needing to solder directly onto the circuit board.
The schematic also indicates the placement of resistors and capacitors that may be present in the circuit, which can help stabilize the output signal and filter any noise that may interfere with the sensor's performance. Proper attention to these components will enhance the reliability of the light reflectance sensor in measuring light intensity, which is essential for accurate heart rate monitoring in various applications.Here is the inside of the light reflectance sensor (top) and a schematic drawing of it's circuitry (bottom). First, carefully remove the phototransistor as shown. Then, attach the three wires that we will connect to the heart sensor (show in bright yellow). Hint: if you leave the leads from the phototransistor when you cut it off, you can attach the two corresponding wires directly to them, rather than to the circuit board itself.
🔗 External reference