Help with Laser Alarm Circuit
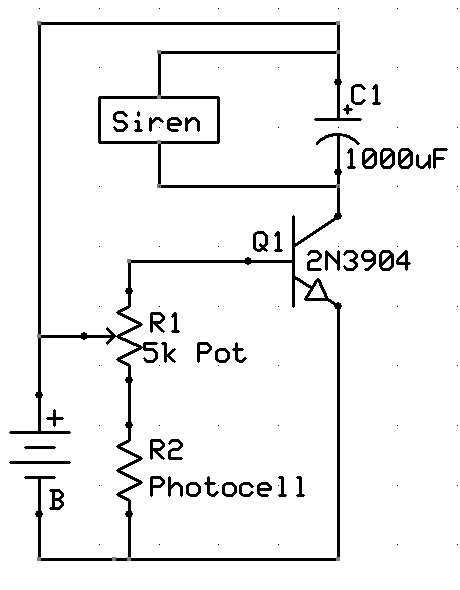
A new user has recently discovered a Laser Alarm System and has decided to explore this project.
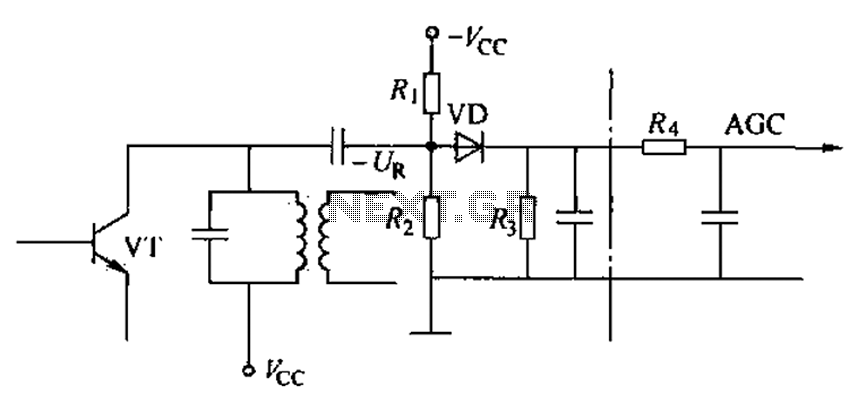
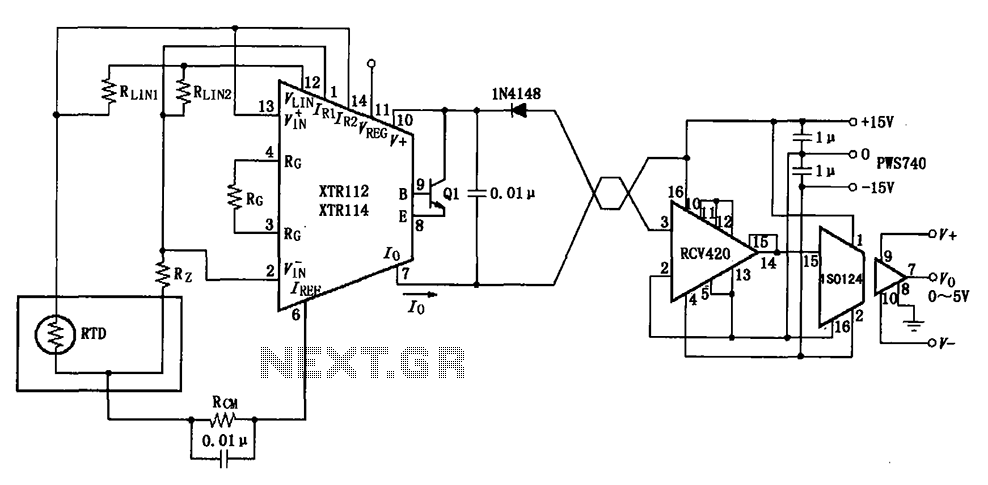
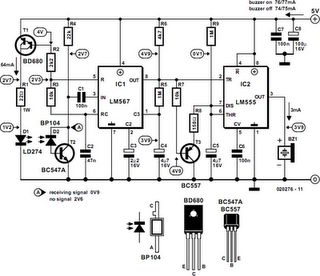
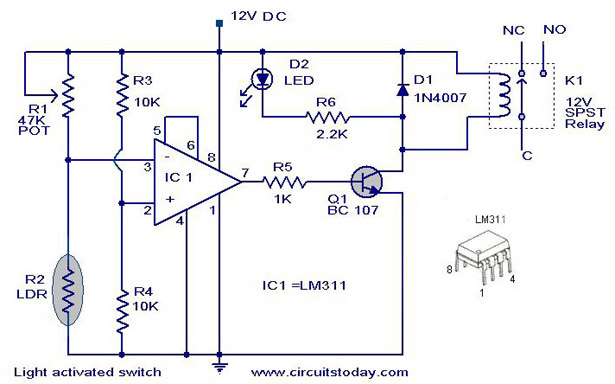
The Laser Alarm System is a security device that utilizes laser beams to detect unauthorized entry or movement within a designated area. The fundamental operation of this system involves a laser source, a photodetector, and a microcontroller or alarm module.
The laser source, typically a laser diode, emits a focused beam of light across the area to be monitored. This beam is directed toward a photodetector, which can be a photodiode or a phototransistor. When an intruder or an object interrupts the laser beam, the photodetector senses the absence of light and triggers an alert.
The microcontroller or alarm module processes the signal from the photodetector. Upon detecting a break in the laser beam, the microcontroller can activate an alarm, send a notification, or execute other programmed responses. The system may include additional features such as adjustable sensitivity, delay timers to prevent false alarms, and integration with other security systems.
Power supply considerations are crucial in the design of a Laser Alarm System. The laser diode typically requires a specific voltage and current, which must be supplied through a regulated power source. Similarly, the photodetector and microcontroller will have their own power requirements that need to be met.
In terms of circuit design, the layout should minimize interference and ensure that the laser beam is properly aligned with the photodetector. Proper shielding may be necessary to protect sensitive components from environmental factors.
Overall, the Laser Alarm System is an effective and versatile project for those interested in electronics, providing hands-on experience with optical sensors, microcontrollers, and alarm systems.Hey all I`m new to both the forums and electronics. Recently I chanced upon a Laser Alarm System and decided to give it a go.. 🔗 External reference
The Laser Alarm System is a security device that utilizes laser beams to detect unauthorized entry or movement within a designated area. The fundamental operation of this system involves a laser source, a photodetector, and a microcontroller or alarm module.
The laser source, typically a laser diode, emits a focused beam of light across the area to be monitored. This beam is directed toward a photodetector, which can be a photodiode or a phototransistor. When an intruder or an object interrupts the laser beam, the photodetector senses the absence of light and triggers an alert.
The microcontroller or alarm module processes the signal from the photodetector. Upon detecting a break in the laser beam, the microcontroller can activate an alarm, send a notification, or execute other programmed responses. The system may include additional features such as adjustable sensitivity, delay timers to prevent false alarms, and integration with other security systems.
Power supply considerations are crucial in the design of a Laser Alarm System. The laser diode typically requires a specific voltage and current, which must be supplied through a regulated power source. Similarly, the photodetector and microcontroller will have their own power requirements that need to be met.
In terms of circuit design, the layout should minimize interference and ensure that the laser beam is properly aligned with the photodetector. Proper shielding may be necessary to protect sensitive components from environmental factors.
Overall, the Laser Alarm System is an effective and versatile project for those interested in electronics, providing hands-on experience with optical sensors, microcontrollers, and alarm systems.Hey all I`m new to both the forums and electronics. Recently I chanced upon a Laser Alarm System and decided to give it a go.. 🔗 External reference