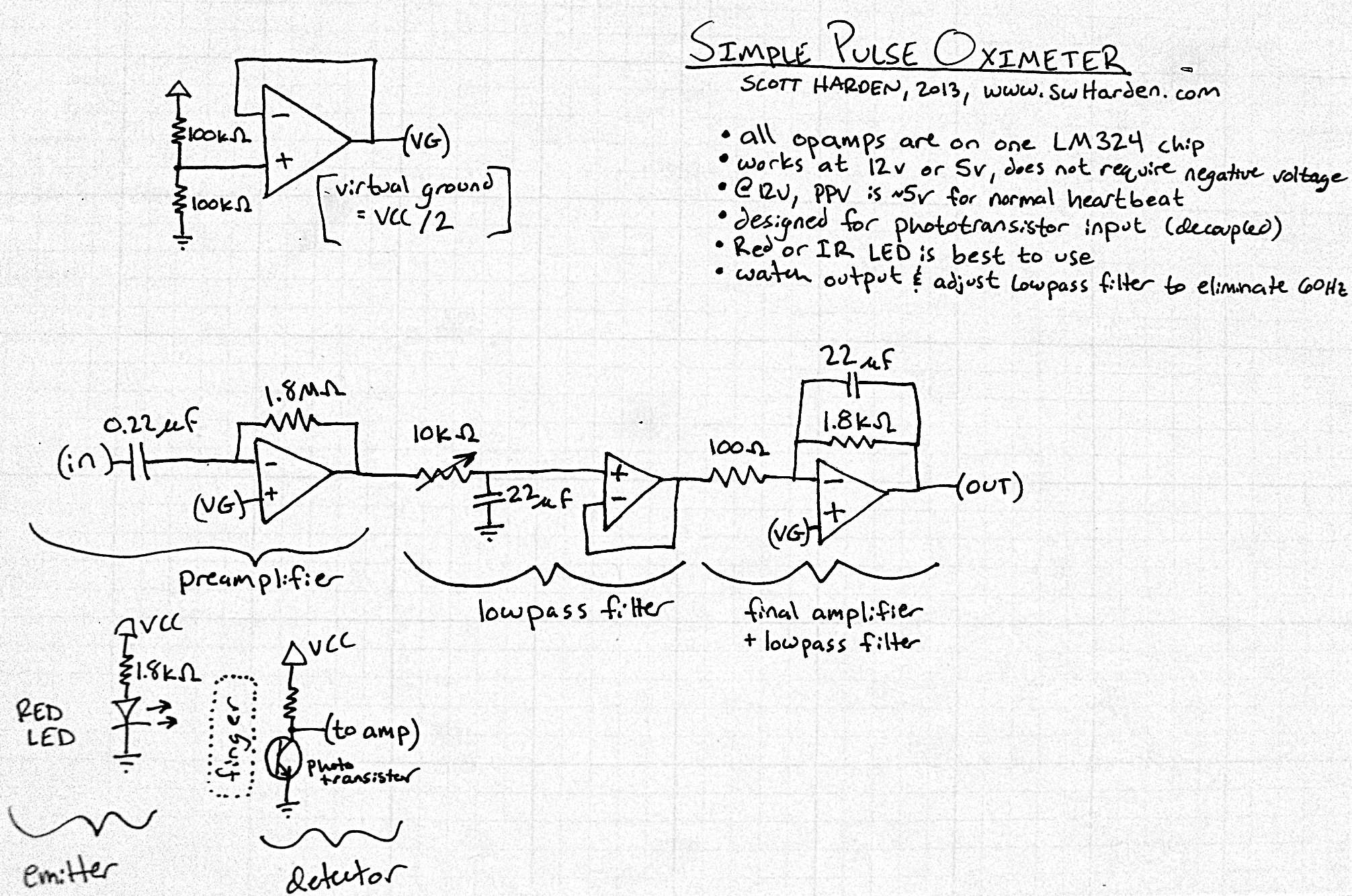
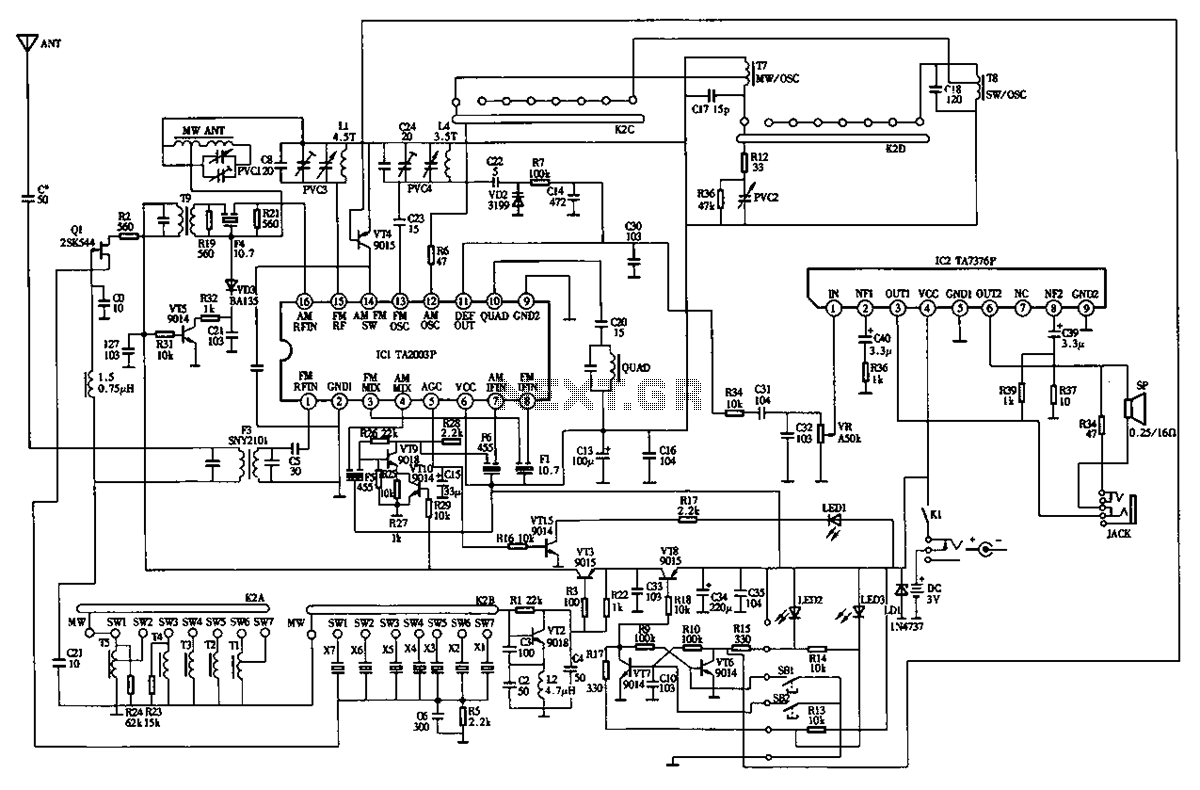
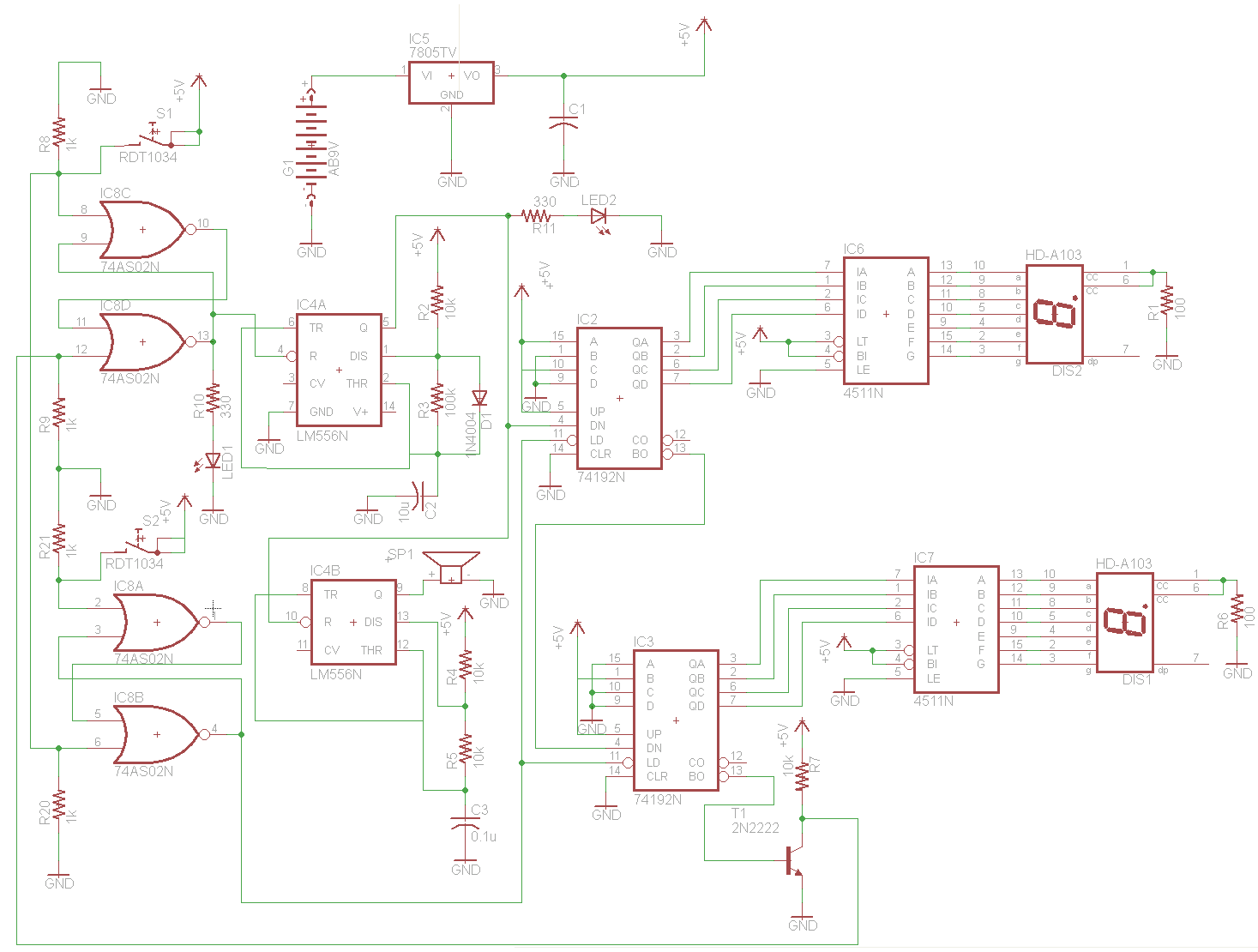
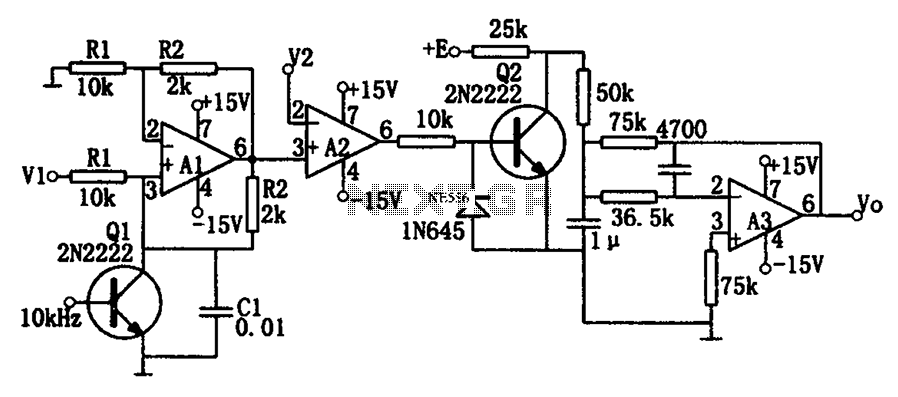
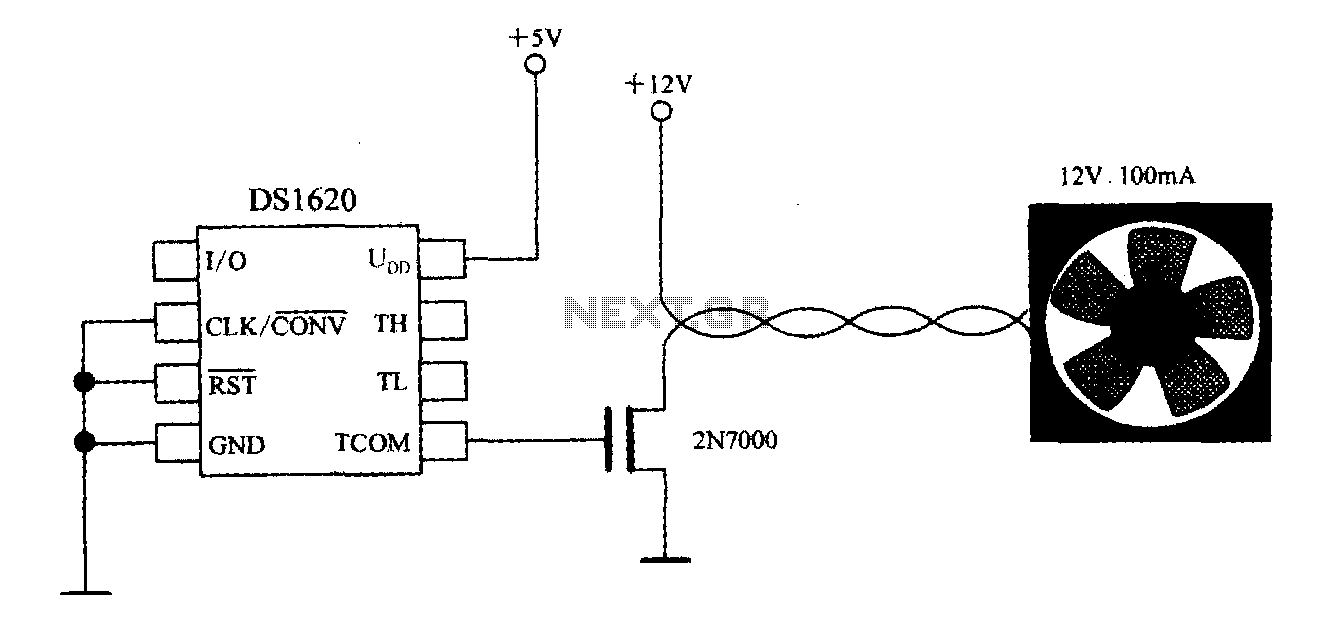
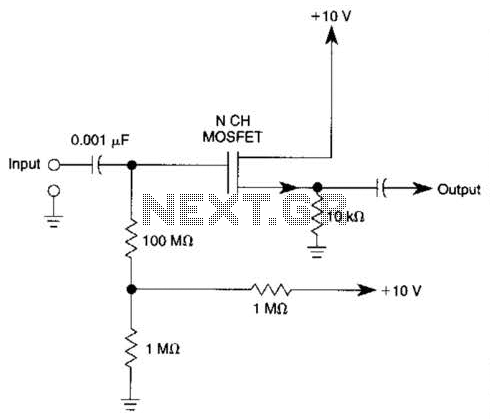
Delayed type AGC circuit diagram of principle
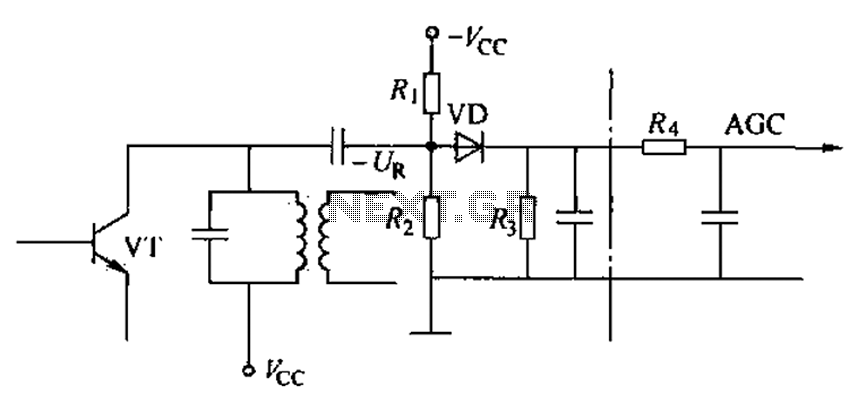
Commonly referred to as an automatic gain control (AGC) circuit, it is primarily utilized in receivers. This circuit maintains a constant output voltage amplitude despite variations in the input signal amplitude. It ensures that the receiver can effectively process radio signals of varying distances and strengths, providing approximately uniform reception. The principle of a delay-type AGC circuit is illustrated in the accompanying figure.
The automatic gain control (AGC) circuit is an essential component in various electronic communication systems, particularly in radio receivers. Its primary function is to automatically adjust the gain of the receiver to compensate for fluctuations in the amplitude of incoming signals. This capability is crucial for maintaining a consistent output level, which enhances the overall performance and reliability of the communication system.
In a typical AGC circuit, the input signal is first fed into an amplifier. The output of this amplifier is then monitored to determine the signal strength. When the input signal amplitude increases beyond a certain threshold, the AGC circuit reduces the gain of the amplifier. Conversely, if the input signal amplitude decreases, the gain is increased. This feedback mechanism ensures that the output remains relatively constant, regardless of the variations in input signal strength.
The delay-type AGC circuit operates on the principle of introducing a time delay in the feedback loop. This delay allows the circuit to respond to changes in signal amplitude without causing rapid fluctuations in the output. The delay can be implemented using capacitors and resistors, which determine the time constant of the circuit. By carefully selecting these components, the AGC circuit can be tuned to respond optimally to the dynamics of the incoming signal.
In practical applications, AGC circuits are utilized in various devices, including televisions, radios, and communication satellites, where they play a vital role in ensuring clear and stable audio and video quality. The design and implementation of AGC circuits can vary widely, depending on the specific requirements of the application, such as the desired response time, frequency range, and output characteristics. Commonly referred to as automatic amplitude control circuit AGC circuit. It is mainly used in the receiver, the machine when the input signal amplitude change to maintain the o utput voltage constant amplitude. To ensure that the receiver of the radio signals of different distance and different strength, there are approximately the same reception. Delay type AGC circuit principle of FIG.
The automatic gain control (AGC) circuit is an essential component in various electronic communication systems, particularly in radio receivers. Its primary function is to automatically adjust the gain of the receiver to compensate for fluctuations in the amplitude of incoming signals. This capability is crucial for maintaining a consistent output level, which enhances the overall performance and reliability of the communication system.
In a typical AGC circuit, the input signal is first fed into an amplifier. The output of this amplifier is then monitored to determine the signal strength. When the input signal amplitude increases beyond a certain threshold, the AGC circuit reduces the gain of the amplifier. Conversely, if the input signal amplitude decreases, the gain is increased. This feedback mechanism ensures that the output remains relatively constant, regardless of the variations in input signal strength.
The delay-type AGC circuit operates on the principle of introducing a time delay in the feedback loop. This delay allows the circuit to respond to changes in signal amplitude without causing rapid fluctuations in the output. The delay can be implemented using capacitors and resistors, which determine the time constant of the circuit. By carefully selecting these components, the AGC circuit can be tuned to respond optimally to the dynamics of the incoming signal.
In practical applications, AGC circuits are utilized in various devices, including televisions, radios, and communication satellites, where they play a vital role in ensuring clear and stable audio and video quality. The design and implementation of AGC circuits can vary widely, depending on the specific requirements of the application, such as the desired response time, frequency range, and output characteristics. Commonly referred to as automatic amplitude control circuit AGC circuit. It is mainly used in the receiver, the machine when the input signal amplitude change to maintain the o utput voltage constant amplitude. To ensure that the receiver of the radio signals of different distance and different strength, there are approximately the same reception. Delay type AGC circuit principle of FIG.