High and low frequency signal generator circuit diagram
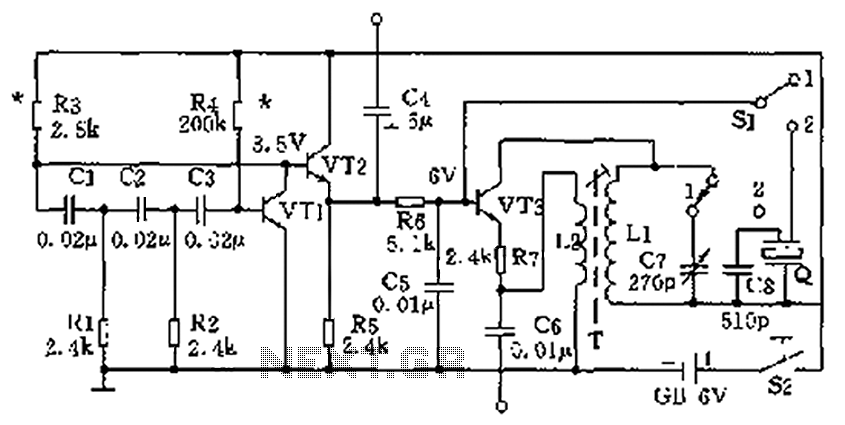
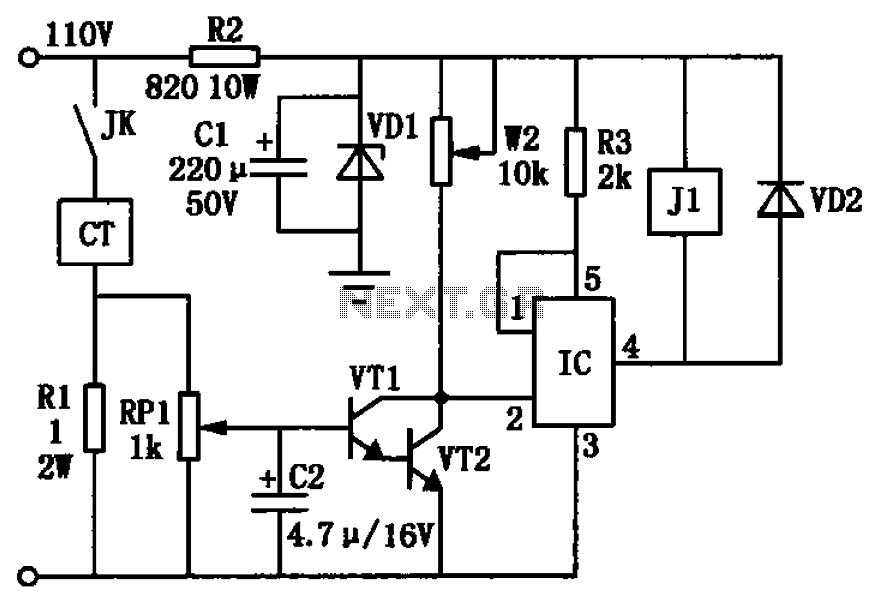
The high-frequency signal generator is designed to produce a low frequency of 1 kHz, an intermediate frequency (IF) signal of 465 kHz, and high frequencies ranging from 525 kHz to 1605 kHz. This device is particularly useful for radio repair and circuit debugging, making it an excellent tool for beginners in electronics. The transistors used in the circuit are VT1 to VT3, which can be selected from models such as 3DGl00 or 3DG201, both of which are high-frequency, low-power silicon transistors with a transition frequency (fT) of 100 MHz and current gain (hFE) values between 50 and 100. Capacitor C7 can be a 7/270 pF radio capacitor, which can be configured with either a double or single row of capacitors. The oscillation transformer T can be constructed using a high-strength wire of 0.08 mm diameter wound around the core, with L1 consisting of 100 turns and L2 consisting of 35 turns. Capacitor C8 is a 510 pF mica capacitor. The circuit includes a three-stage selection of 465 kHz IF ceramic filters. The switch S1 is an optional DPDT type switch. Additional component values are indicated in the figure labels.
The high-frequency signal generator circuit operates by utilizing a combination of transistors, capacitors, and inductors to create oscillations at specified frequencies. The transistors (VT1 to VT3) serve as the main amplification elements, allowing for the generation of the desired frequency signals. The choice of transistors such as the 3DGl00 or 3DG201 ensures that the circuit can operate efficiently at high frequencies while maintaining low power consumption.
The capacitors play a critical role in determining the frequency response of the circuit. C7, with its dual configuration options, allows for fine-tuning of the oscillation frequency. The oscillation transformer, constructed with L1 and L2, is essential for coupling the generated signal and ensuring stability in the oscillation process. The specified number of turns in the inductors (100 for L1 and 35 for L2) is crucial for achieving the desired inductance values, which directly influence the frequency characteristics of the circuit.
Capacitor C8, being a mica capacitor, is chosen for its stability and low loss characteristics, which are important for maintaining signal integrity at high frequencies. The inclusion of three-stage ceramic filters for the 465 kHz IF signal enhances the selectivity and minimizes interference from unwanted signals, ensuring that the output is clean and usable for radio applications.
The optional DPDT switch (S1) provides versatility in circuit operation, allowing users to toggle between different modes or outputs as needed. This feature is particularly beneficial for experimentation and debugging purposes, enabling users to assess the performance of various configurations without the need for extensive rewiring. Overall, this high-frequency signal generator is an invaluable tool for both novice and experienced electronics enthusiasts, facilitating the exploration and repair of radio frequency circuits. As shown in the high-frequency signal generator capable of generating a low frequency 1kHz, 465kHz IF signal and the high frequency of 525 ~ 1605kHz, to repair radios or other circuit debugging very helpful for beginners production. Transistor VTl ~ VT3: choice 3DGl00,3DG201 other high-frequency low-power silicon tube, fT 100MHz, values between 50 and 100. C7 can be used 7/270pF radio with double or single row of capacitors connected capacitors. Oscillation transformer T can be carried out in radio in the week on the restructuring, on the core with a high strength wire 0.08mm around Ll, 100 turns, L2,35 turns.
C8 510pF available mica capacitors. Q three-stage selection of 465kHz IF ceramic filters. Sl optional DPDT type switch. Other component values shown in Figure labels.
The high-frequency signal generator circuit operates by utilizing a combination of transistors, capacitors, and inductors to create oscillations at specified frequencies. The transistors (VT1 to VT3) serve as the main amplification elements, allowing for the generation of the desired frequency signals. The choice of transistors such as the 3DGl00 or 3DG201 ensures that the circuit can operate efficiently at high frequencies while maintaining low power consumption.
The capacitors play a critical role in determining the frequency response of the circuit. C7, with its dual configuration options, allows for fine-tuning of the oscillation frequency. The oscillation transformer, constructed with L1 and L2, is essential for coupling the generated signal and ensuring stability in the oscillation process. The specified number of turns in the inductors (100 for L1 and 35 for L2) is crucial for achieving the desired inductance values, which directly influence the frequency characteristics of the circuit.
Capacitor C8, being a mica capacitor, is chosen for its stability and low loss characteristics, which are important for maintaining signal integrity at high frequencies. The inclusion of three-stage ceramic filters for the 465 kHz IF signal enhances the selectivity and minimizes interference from unwanted signals, ensuring that the output is clean and usable for radio applications.
The optional DPDT switch (S1) provides versatility in circuit operation, allowing users to toggle between different modes or outputs as needed. This feature is particularly beneficial for experimentation and debugging purposes, enabling users to assess the performance of various configurations without the need for extensive rewiring. Overall, this high-frequency signal generator is an invaluable tool for both novice and experienced electronics enthusiasts, facilitating the exploration and repair of radio frequency circuits. As shown in the high-frequency signal generator capable of generating a low frequency 1kHz, 465kHz IF signal and the high frequency of 525 ~ 1605kHz, to repair radios or other circuit debugging very helpful for beginners production. Transistor VTl ~ VT3: choice 3DGl00,3DG201 other high-frequency low-power silicon tube, fT 100MHz, values between 50 and 100. C7 can be used 7/270pF radio with double or single row of capacitors connected capacitors. Oscillation transformer T can be carried out in radio in the week on the restructuring, on the core with a high strength wire 0.08mm around Ll, 100 turns, L2,35 turns.
C8 510pF available mica capacitors. Q three-stage selection of 465kHz IF ceramic filters. Sl optional DPDT type switch. Other component values shown in Figure labels.