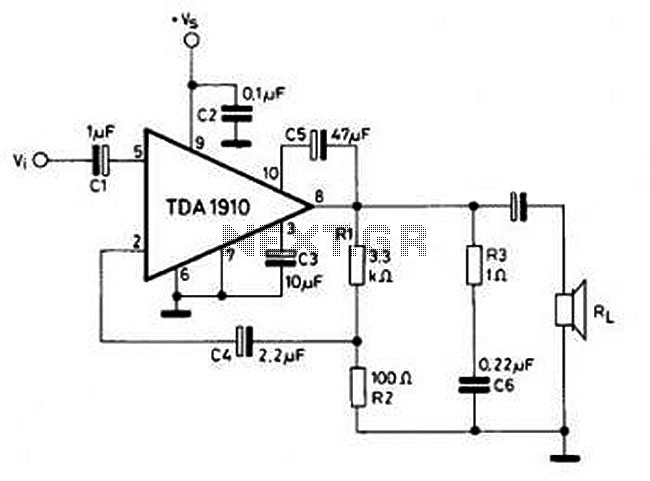
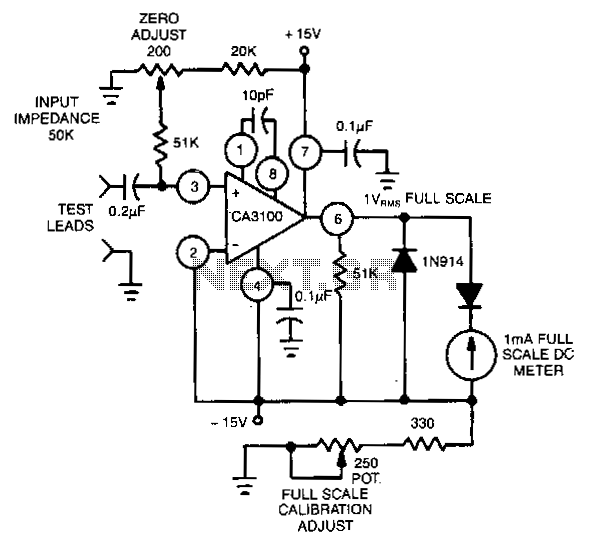
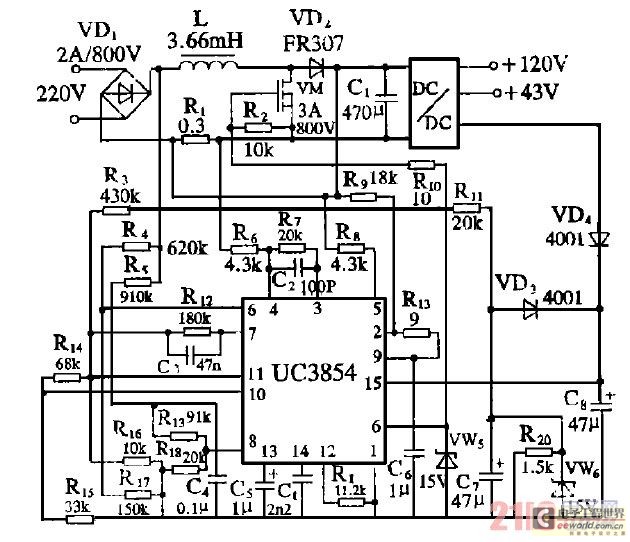
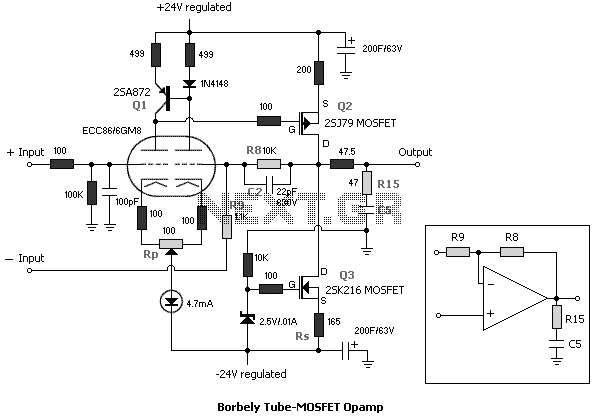
High-frequency signal output amplifier
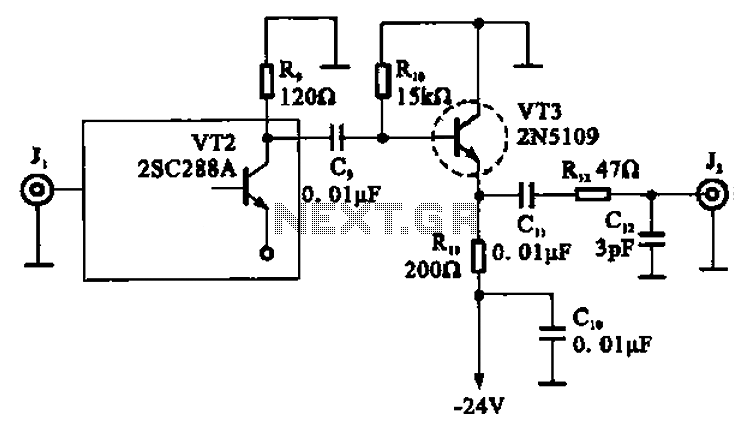
A high-frequency signal is displayed in the output amplifier. The circuit consists of a VI3 common collector amplifier (emitter follower) designed to enhance the child-band. It is a high-frequency amplifier (1-250 MHz) that increases the output voltage and boosts the power output stage circuit. This circuit utilizes an emitter, with a signal from high-frequency wideband amplifiers, where VT3 is applied to the base of the circuit in the first stage of the wideband high-frequency amplifier. The design employs a negative power supply, thereby improving the capacity of the pre-wideband high-frequency amplifier.
The described circuit utilizes a common collector configuration, also known as an emitter follower, to achieve impedance matching and provide a high input impedance while maintaining a low output impedance. This configuration is particularly beneficial in high-frequency applications, as it minimizes signal distortion and maximizes bandwidth. The VI3 amplifier is specifically tailored for high-frequency operations, capable of handling frequencies ranging from 1 MHz to 250 MHz, making it suitable for a variety of communication and signal processing applications.
The output stage of the circuit is designed to amplify the voltage signal while ensuring that the power output is significantly increased. This is crucial for applications requiring strong signal transmission over longer distances or through lossy mediums. The use of a negative power supply enhances the performance of the amplifier by allowing for a wider dynamic range and improved linearity, which is essential in high-frequency signal amplification.
In this specific design, the emitter follower configuration allows for the direct application of the output from the high-frequency wideband amplifier (VT3) to the base of the common collector amplifier. This connection facilitates efficient signal transfer and minimizes losses, ensuring that the high-frequency characteristics of the signal are preserved. Additionally, the circuit is optimized for low noise operation, which is a critical factor in high-frequency applications where signal integrity is paramount.
Overall, the combination of a common collector amplifier with a negative power supply and high-frequency design principles results in a robust circuit capable of delivering enhanced performance in various electronic applications.A high frequency signal is shown in the output amplifier, the circuit is constituted by a VI3 common collector amplifier (emitter follower), in order to improve the child-band high-frequency amplifier (1-250 MHz) of the output voltage, increasing the power output stage circuit. This circuit uses emitter, a signal from the high-frequency wideband amplifiers, VT3 applied to the base of the circuit with the first stage of a wideband high frequency amplifier, are performed using negative power supply, thus improving pre-wideband high-frequency amplifier capacity.
The described circuit utilizes a common collector configuration, also known as an emitter follower, to achieve impedance matching and provide a high input impedance while maintaining a low output impedance. This configuration is particularly beneficial in high-frequency applications, as it minimizes signal distortion and maximizes bandwidth. The VI3 amplifier is specifically tailored for high-frequency operations, capable of handling frequencies ranging from 1 MHz to 250 MHz, making it suitable for a variety of communication and signal processing applications.
The output stage of the circuit is designed to amplify the voltage signal while ensuring that the power output is significantly increased. This is crucial for applications requiring strong signal transmission over longer distances or through lossy mediums. The use of a negative power supply enhances the performance of the amplifier by allowing for a wider dynamic range and improved linearity, which is essential in high-frequency signal amplification.
In this specific design, the emitter follower configuration allows for the direct application of the output from the high-frequency wideband amplifier (VT3) to the base of the common collector amplifier. This connection facilitates efficient signal transfer and minimizes losses, ensuring that the high-frequency characteristics of the signal are preserved. Additionally, the circuit is optimized for low noise operation, which is a critical factor in high-frequency applications where signal integrity is paramount.
Overall, the combination of a common collector amplifier with a negative power supply and high-frequency design principles results in a robust circuit capable of delivering enhanced performance in various electronic applications.A high frequency signal is shown in the output amplifier, the circuit is constituted by a VI3 common collector amplifier (emitter follower), in order to improve the child-band high-frequency amplifier (1-250 MHz) of the output voltage, increasing the power output stage circuit. This circuit uses emitter, a signal from the high-frequency wideband amplifiers, VT3 applied to the base of the circuit with the first stage of a wideband high frequency amplifier, are performed using negative power supply, thus improving pre-wideband high-frequency amplifier capacity.