High Volt LED Flasher
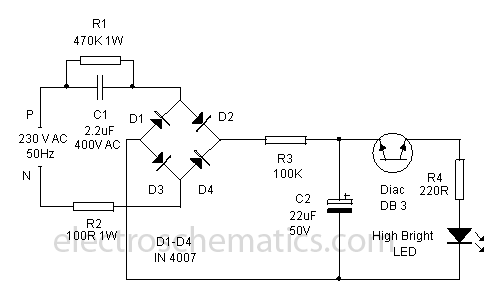
This is a flasher circuit that directly derives power from AC to produce brilliant flashes at a rate of one flash per second. It utilizes a DIAC as the main element.
The flasher circuit operates by converting alternating current (AC) into a pulsed output that generates visible flashes of light. The circuit typically consists of a few key components: a DIAC, a resistor, a capacitor, and a light-emitting diode (LED) or another type of lamp.
When the AC voltage is applied, the capacitor begins to charge through the resistor. Once the voltage across the capacitor reaches the breakover voltage of the DIAC, the DIAC conducts and allows current to flow through the load—typically an LED. This causes the LED to flash brightly. After the capacitor discharges, the DIAC turns off, cutting off the current flow, and the cycle repeats, resulting in a flash rate of approximately one flash per second.
The choice of resistor and capacitor values is crucial, as they determine the charging time of the capacitor and thus the flash rate. For instance, a larger capacitance or resistance will slow down the charging process, leading to a longer flash interval, while smaller values will speed it up. The circuit is efficient and straightforward, making it suitable for various applications, including decorative lighting and signaling devices.
Overall, this flasher circuit design effectively utilizes AC power to create a visually appealing flashing effect, with the DIAC playing a pivotal role in controlling the timing of the flashes.Here is a Flasher circuit that directly derives power from AC to give brilliant flashes at the rate of one flash per second. It uses a Diac as the main ele. 🔗 External reference
The flasher circuit operates by converting alternating current (AC) into a pulsed output that generates visible flashes of light. The circuit typically consists of a few key components: a DIAC, a resistor, a capacitor, and a light-emitting diode (LED) or another type of lamp.
When the AC voltage is applied, the capacitor begins to charge through the resistor. Once the voltage across the capacitor reaches the breakover voltage of the DIAC, the DIAC conducts and allows current to flow through the load—typically an LED. This causes the LED to flash brightly. After the capacitor discharges, the DIAC turns off, cutting off the current flow, and the cycle repeats, resulting in a flash rate of approximately one flash per second.
The choice of resistor and capacitor values is crucial, as they determine the charging time of the capacitor and thus the flash rate. For instance, a larger capacitance or resistance will slow down the charging process, leading to a longer flash interval, while smaller values will speed it up. The circuit is efficient and straightforward, making it suitable for various applications, including decorative lighting and signaling devices.
Overall, this flasher circuit design effectively utilizes AC power to create a visually appealing flashing effect, with the DIAC playing a pivotal role in controlling the timing of the flashes.Here is a Flasher circuit that directly derives power from AC to give brilliant flashes at the rate of one flash per second. It uses a Diac as the main ele. 🔗 External reference