Mathematical approch to measuring current voltage and resistance of mixed series and parallel
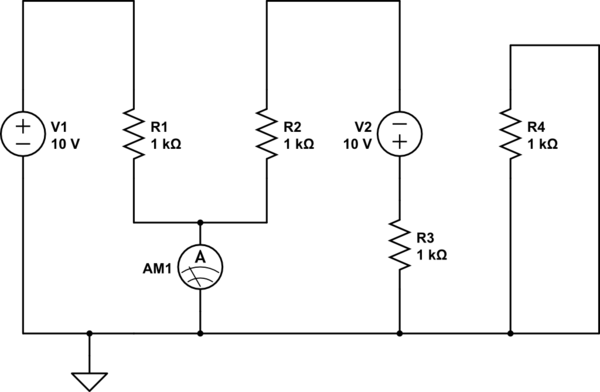
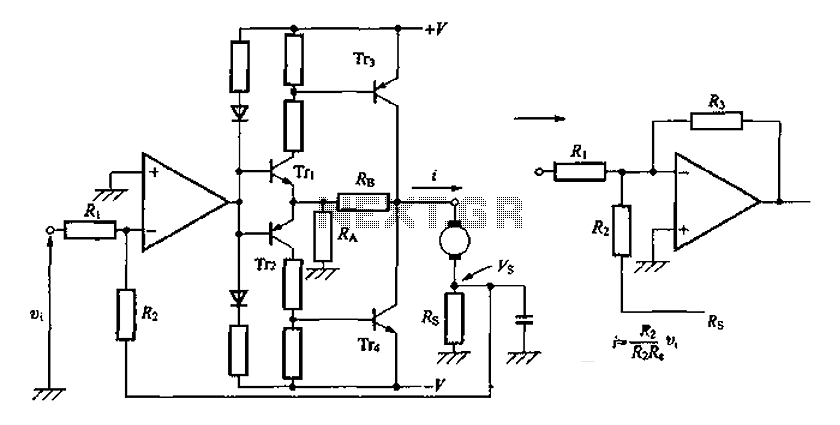
There is one significant low-impedance node in the entire circuit, referred to as 0V, located at the frame and the intersection in the middle. The upper voltage source is connected to this midpoint through a 1kΩ resistor, indicating that the lower voltage source takes precedence. The two resistors in the upper section create a potential divider between 0V and 0V, which may lead to the assumption that the upper voltage source is also at approximately 0V. However, since it is generating a voltage, the upper side will be at 5V, while the lower side will be at -5V.
The circuit features a low-impedance node that plays a crucial role in defining the reference point for the entire system. This node, designated as 0V, serves as a common ground for the circuit's operation. The connection of the upper voltage source to this node through a 1kΩ resistor establishes a pathway for current flow, enabling the lower voltage source to exert its influence over the circuit dynamics.
The two resistors positioned in the upper half of the circuit form a potential divider. In a potential divider configuration, the voltage across each resistor is determined by the ratio of their resistances. While it might initially appear that both sides of the divider are at 0V, the active voltage generation from the upper source alters this perception. The upper voltage source, supplying 5V, elevates the potential on its side of the divider, while the lower voltage source, at -5V, pulls the potential down on the opposite side.
This configuration creates a balanced yet dynamic voltage distribution across the circuit. It is essential to consider the effects of these voltage levels on the overall circuit behavior, particularly in applications where precise voltage references are critical. The interaction between the upper and lower voltage sources, mediated by the resistive components, establishes a stable operating environment for connected devices or circuits, ensuring reliable performance across a range of operational conditions.There is one important low-impedance node in the whole circuit. That`s the frame and the cross in the middle. Let`s call that 0v. The top voltage source is connected to the middle via that 1k resistor, that means the lower voltage source has priority. the two resistors in the top half form a potential divider between 0v and 0v, so you might think of the top voltage source as sitting at about 0v too. However, since it`s generating a voltage, then the top side will be at 5v, and the bottom side at -5v. 🔗 External reference
The circuit features a low-impedance node that plays a crucial role in defining the reference point for the entire system. This node, designated as 0V, serves as a common ground for the circuit's operation. The connection of the upper voltage source to this node through a 1kΩ resistor establishes a pathway for current flow, enabling the lower voltage source to exert its influence over the circuit dynamics.
The two resistors positioned in the upper half of the circuit form a potential divider. In a potential divider configuration, the voltage across each resistor is determined by the ratio of their resistances. While it might initially appear that both sides of the divider are at 0V, the active voltage generation from the upper source alters this perception. The upper voltage source, supplying 5V, elevates the potential on its side of the divider, while the lower voltage source, at -5V, pulls the potential down on the opposite side.
This configuration creates a balanced yet dynamic voltage distribution across the circuit. It is essential to consider the effects of these voltage levels on the overall circuit behavior, particularly in applications where precise voltage references are critical. The interaction between the upper and lower voltage sources, mediated by the resistive components, establishes a stable operating environment for connected devices or circuits, ensuring reliable performance across a range of operational conditions.There is one important low-impedance node in the whole circuit. That`s the frame and the cross in the middle. Let`s call that 0v. The top voltage source is connected to the middle via that 1k resistor, that means the lower voltage source has priority. the two resistors in the top half form a potential divider between 0v and 0v, so you might think of the top voltage source as sitting at about 0v too. However, since it`s generating a voltage, then the top side will be at 5v, and the bottom side at -5v. 🔗 External reference