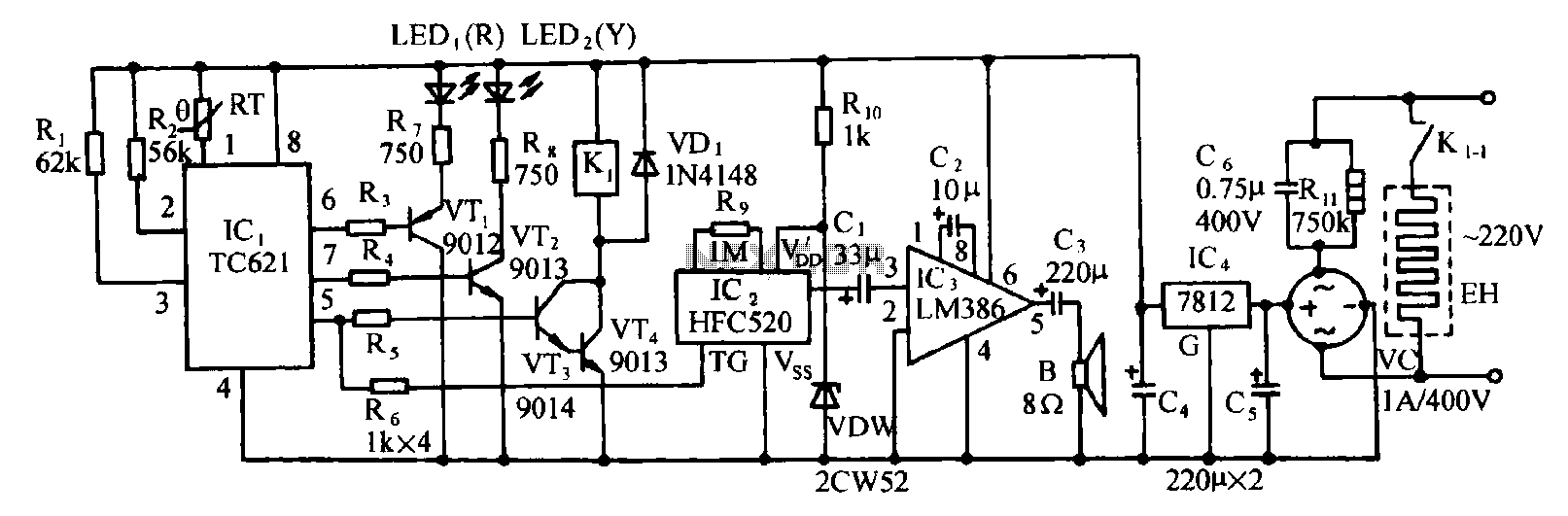
High-Voltage Supply Circuit
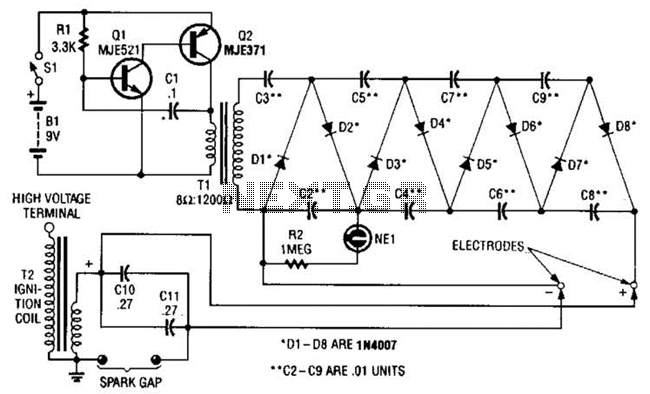
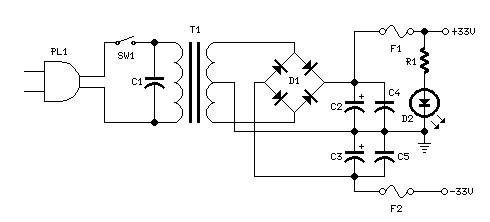
This circuit employs a transistor oscillator and a voltage multiplier to charge capacitors CIO and CI1 to a high voltage. When the spark gap breaks down, T2 generates a high-voltage pulse through the discharge of capacitors CIO and CI1 into its primary winding. T2 functions as an auto ignition coil.
The circuit operates by utilizing a transistor oscillator to create a high-frequency signal, which is then used to drive a voltage multiplier circuit. This voltage multiplier consists of diodes and capacitors arranged in a manner that effectively increases the input voltage to a significantly higher level. Capacitors CIO and CI1 are charged to this elevated voltage, storing substantial electrical energy.
When the spark gap, a crucial component in this circuit, reaches its breakdown voltage, it allows the stored energy in capacitors CIO and CI1 to discharge rapidly. This discharge occurs through the primary winding of the auto ignition coil, T2. The rapid collapse of the magnetic field in the coil generates a high-voltage pulse in the secondary winding, which can be utilized to ignite fuel in an internal combustion engine or for other applications requiring a brief, high-voltage spark.
The design of this circuit is particularly effective for applications requiring ignition systems, as it can deliver the necessary high-voltage pulses reliably and efficiently. The use of an auto ignition coil as T2 ensures that the circuit can handle the high voltages involved while maintaining durability and performance over time. This circuit uses a transistor oscillator and a voltage multiplier to charge CIO and CI 1 to a high voltage. When the spark gap breaks down, T2 produces a high-voltage pulse via the capacitance discharge of CIO and Cll into its primary.
T2 is an auto ignition coil.
The circuit operates by utilizing a transistor oscillator to create a high-frequency signal, which is then used to drive a voltage multiplier circuit. This voltage multiplier consists of diodes and capacitors arranged in a manner that effectively increases the input voltage to a significantly higher level. Capacitors CIO and CI1 are charged to this elevated voltage, storing substantial electrical energy.
When the spark gap, a crucial component in this circuit, reaches its breakdown voltage, it allows the stored energy in capacitors CIO and CI1 to discharge rapidly. This discharge occurs through the primary winding of the auto ignition coil, T2. The rapid collapse of the magnetic field in the coil generates a high-voltage pulse in the secondary winding, which can be utilized to ignite fuel in an internal combustion engine or for other applications requiring a brief, high-voltage spark.
The design of this circuit is particularly effective for applications requiring ignition systems, as it can deliver the necessary high-voltage pulses reliably and efficiently. The use of an auto ignition coil as T2 ensures that the circuit can handle the high voltages involved while maintaining durability and performance over time. This circuit uses a transistor oscillator and a voltage multiplier to charge CIO and CI 1 to a high voltage. When the spark gap breaks down, T2 produces a high-voltage pulse via the capacitance discharge of CIO and Cll into its primary.
T2 is an auto ignition coil.