IC Controlled Emergency Light With Charger Circuit
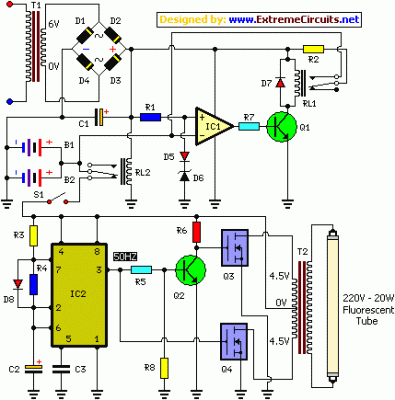
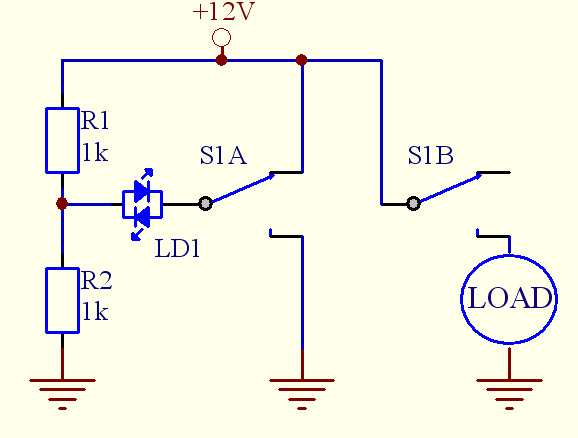
The circuit diagram presented illustrates an IC-controlled emergency light with a charger, functioning as a 12V to 220V AC inverter circuit. This emergency light circuit is designed to automatically activate in the event of a mains failure, while also incorporating a battery charger equipped with over-charge protection. In the absence of mains power, relay RL2 remains in a de-energized state, allowing battery supply to be directed to the inverter section through its normally closed (N/C) contacts and switch S1.
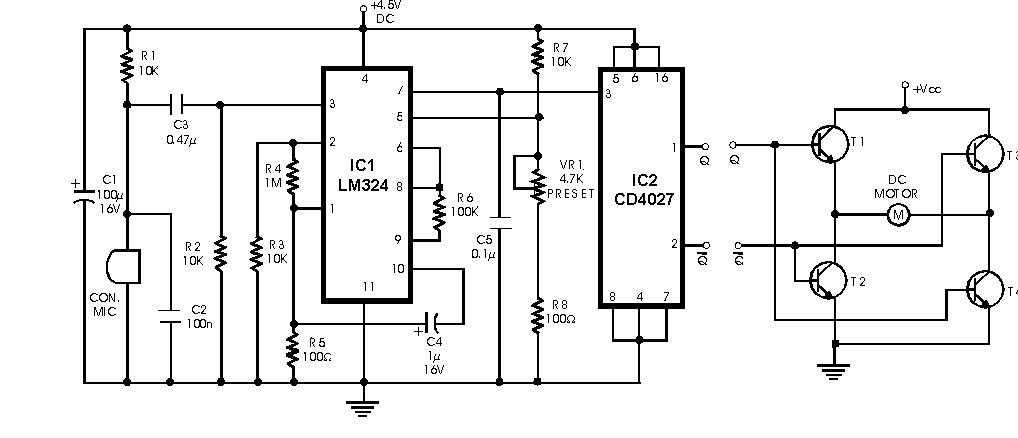
The IC-controlled emergency light circuit operates on a dual functionality principle, serving both as an emergency lighting solution and a battery charging system. The core components include an inverter circuit that converts the 12V DC battery voltage to 220V AC output, suitable for powering standard household appliances during power outages.
The operation begins with the detection of a mains failure. When the mains voltage drops below a certain threshold, the relay RL2 is triggered to switch to its de-energized state. This action connects the battery to the inverter circuit, enabling the inverter to generate 220V AC output. The inverter typically consists of a transformer and a switching mechanism, often using transistors or MOSFETs, to efficiently convert the DC voltage to AC.
Simultaneously, the circuit includes a battery charging mechanism that ensures the battery remains charged when mains power is available. The charger is designed with over-charge protection to prevent damage to the battery. This is typically achieved through a voltage regulation circuit that monitors the battery voltage and disconnects the charging current when the battery reaches its full charge capacity.
Switch S1 plays a critical role in the circuit by allowing manual intervention to enable or disable the inverter operation, providing flexibility in usage. Overall, this circuit design combines safety, efficiency, and reliability, making it an effective solution for emergency lighting needs.Here is the circuit diagram of IC Controlled Emergancy Light With Charger or simply 12V to 220V AC inverter circuit. The circuit shown here is that of the IC controlled emergency light. Its main features are: automatic switching-on of the light on mains failure and battery charger with over-charge protection.
When mains is absent, relay RL2 is in de-energized state, feeding battery supply to inverter section via its N/C contacts and switch S1 🔗 External reference
The IC-controlled emergency light circuit operates on a dual functionality principle, serving both as an emergency lighting solution and a battery charging system. The core components include an inverter circuit that converts the 12V DC battery voltage to 220V AC output, suitable for powering standard household appliances during power outages.
The operation begins with the detection of a mains failure. When the mains voltage drops below a certain threshold, the relay RL2 is triggered to switch to its de-energized state. This action connects the battery to the inverter circuit, enabling the inverter to generate 220V AC output. The inverter typically consists of a transformer and a switching mechanism, often using transistors or MOSFETs, to efficiently convert the DC voltage to AC.
Simultaneously, the circuit includes a battery charging mechanism that ensures the battery remains charged when mains power is available. The charger is designed with over-charge protection to prevent damage to the battery. This is typically achieved through a voltage regulation circuit that monitors the battery voltage and disconnects the charging current when the battery reaches its full charge capacity.
Switch S1 plays a critical role in the circuit by allowing manual intervention to enable or disable the inverter operation, providing flexibility in usage. Overall, this circuit design combines safety, efficiency, and reliability, making it an effective solution for emergency lighting needs.Here is the circuit diagram of IC Controlled Emergancy Light With Charger or simply 12V to 220V AC inverter circuit. The circuit shown here is that of the IC controlled emergency light. Its main features are: automatic switching-on of the light on mains failure and battery charger with over-charge protection.
When mains is absent, relay RL2 is in de-energized state, feeding battery supply to inverter section via its N/C contacts and switch S1 🔗 External reference