infrared extending IR range
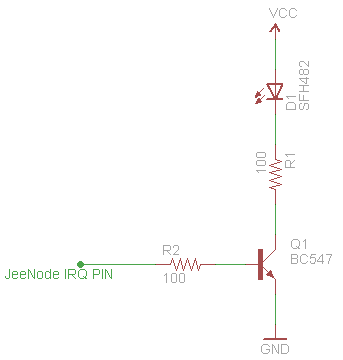
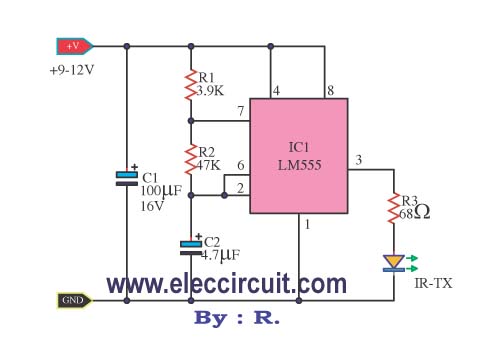
This schematic effectively doubles the range of an infrared (IR) LED, with the circuit now drawing 37mA of power. In contrast, the previous circuit, which did not utilize an NPN transistor, drew 20mA, which is the maximum current per digital pin for a JeeNode. This results in nearly double the power output. Further increases in range can be achieved by using resistors with smaller values; however, this may exceed the limits of the LED and transistor. A larger range was not necessary, as IR emitter cables are used with the devices.
The described schematic employs an NPN transistor to amplify the current supplied to the IR LED, enhancing its operational range. The circuit configuration typically includes a power source, the IR LED, an NPN transistor, and associated resistors. The NPN transistor serves as a switch or amplifier, allowing a higher current to flow through the IR LED compared to a direct connection to a microcontroller pin, which is limited in current output.
The power supply should be appropriately rated to handle the increased current draw of 37mA. The choice of resistors is critical in this design; they limit the current to the base of the NPN transistor and ensure that the IR LED operates within its safe limits. Calculating the base resistor value involves considering the transistor's current gain (beta) and the desired collector current, ensuring that the transistor operates in its active region.
Additionally, while reducing resistor values can indeed increase current and range, it is essential to monitor the thermal performance of both the LED and the transistor to prevent damage from overheating. The schematic may also include bypass capacitors to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply, further enhancing performance.
In summary, this circuit design efficiently utilizes an NPN transistor to amplify the current to an IR LED, resulting in a significant increase in range while maintaining safe operational parameters. Proper component selection and circuit design principles are crucial for achieving optimal performance.Using this schematic I doubled the range of my IR LED, the power drawn in the circuit is now 37mA. My former circuit, without using a NPN transistor drew 20mA (JeeNode max per digital pin). So that`s almost twice the power. You could increase this even further using smaller valued resistors, but that would push the boundaries of the LED and transi stor. I didn`t need any bigger range anyway as I use IR emitter cables attached to my devices. 🔗 External reference
The described schematic employs an NPN transistor to amplify the current supplied to the IR LED, enhancing its operational range. The circuit configuration typically includes a power source, the IR LED, an NPN transistor, and associated resistors. The NPN transistor serves as a switch or amplifier, allowing a higher current to flow through the IR LED compared to a direct connection to a microcontroller pin, which is limited in current output.
The power supply should be appropriately rated to handle the increased current draw of 37mA. The choice of resistors is critical in this design; they limit the current to the base of the NPN transistor and ensure that the IR LED operates within its safe limits. Calculating the base resistor value involves considering the transistor's current gain (beta) and the desired collector current, ensuring that the transistor operates in its active region.
Additionally, while reducing resistor values can indeed increase current and range, it is essential to monitor the thermal performance of both the LED and the transistor to prevent damage from overheating. The schematic may also include bypass capacitors to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply, further enhancing performance.
In summary, this circuit design efficiently utilizes an NPN transistor to amplify the current to an IR LED, resulting in a significant increase in range while maintaining safe operational parameters. Proper component selection and circuit design principles are crucial for achieving optimal performance.Using this schematic I doubled the range of my IR LED, the power drawn in the circuit is now 37mA. My former circuit, without using a NPN transistor drew 20mA (JeeNode max per digital pin). So that`s almost twice the power. You could increase this even further using smaller valued resistors, but that would push the boundaries of the LED and transi stor. I didn`t need any bigger range anyway as I use IR emitter cables attached to my devices. 🔗 External reference