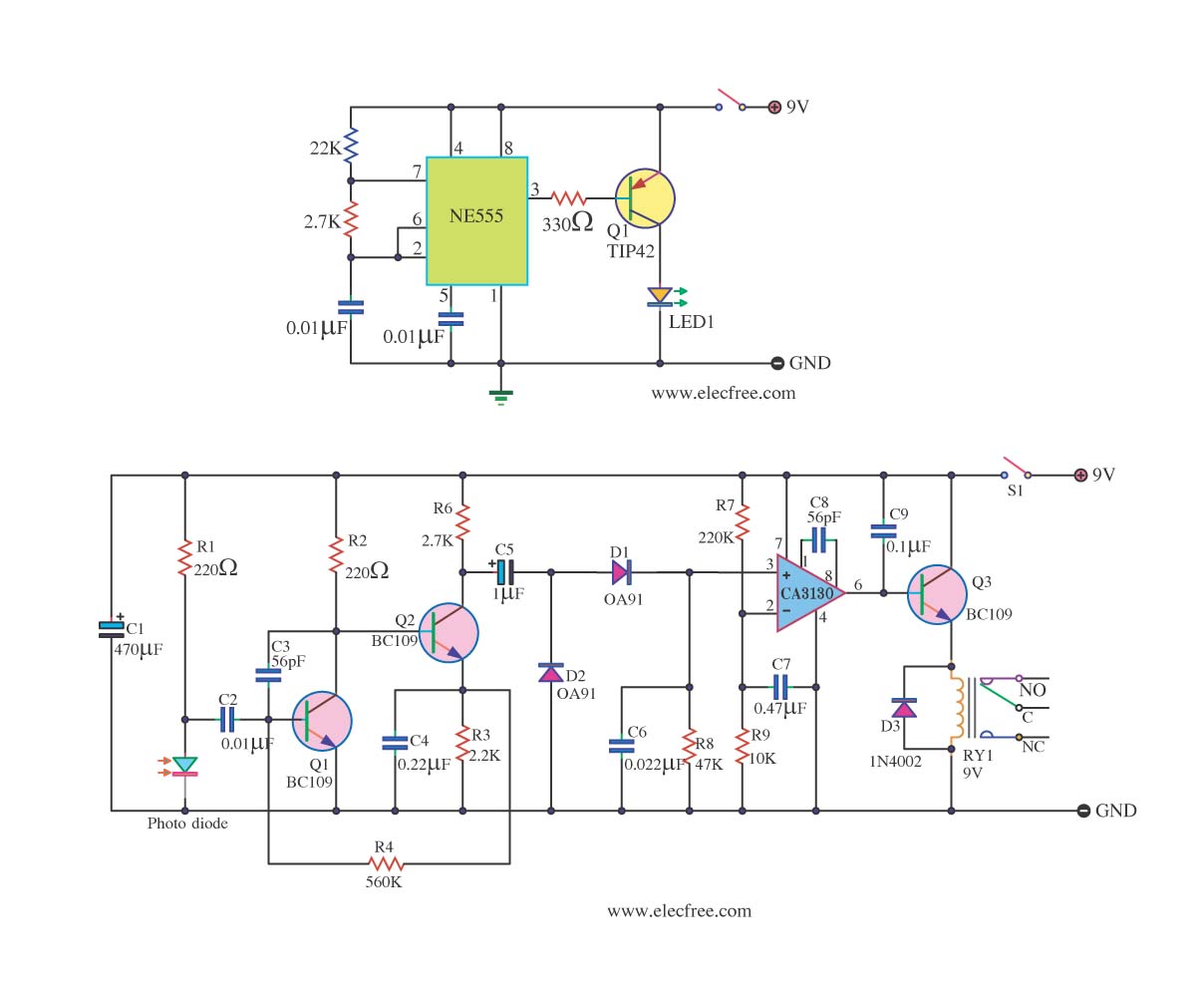
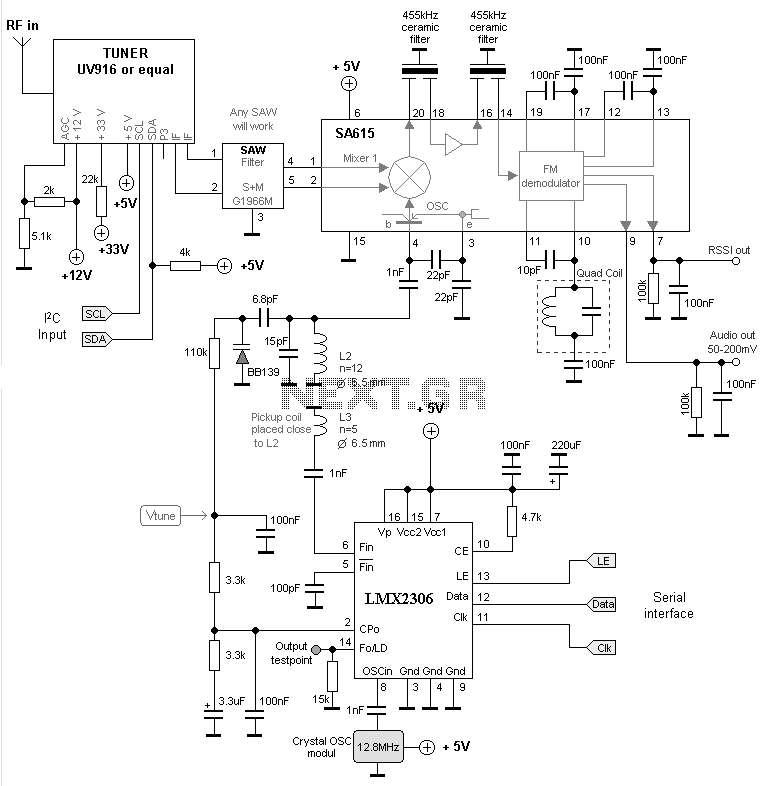
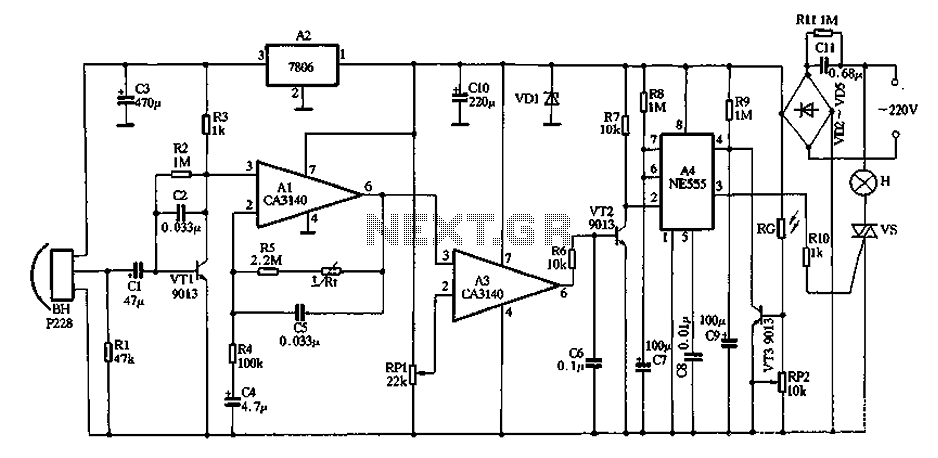
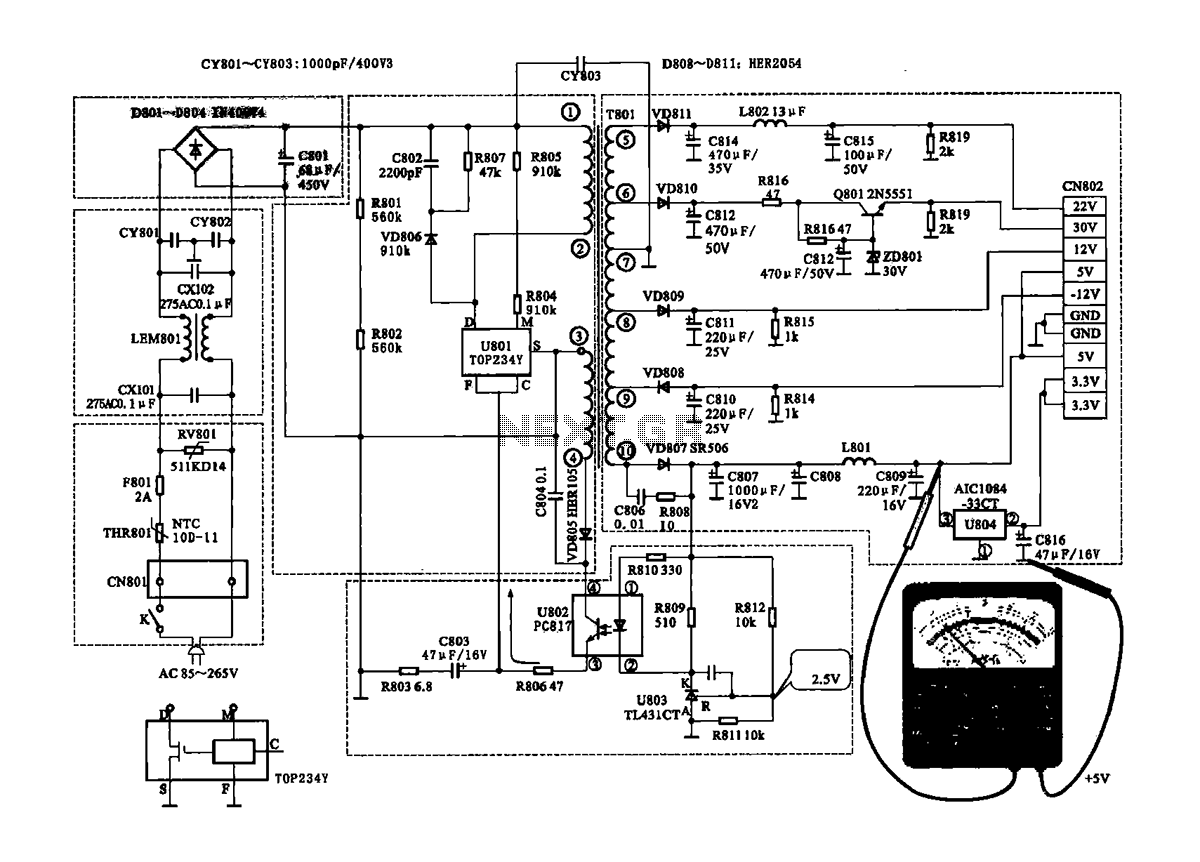
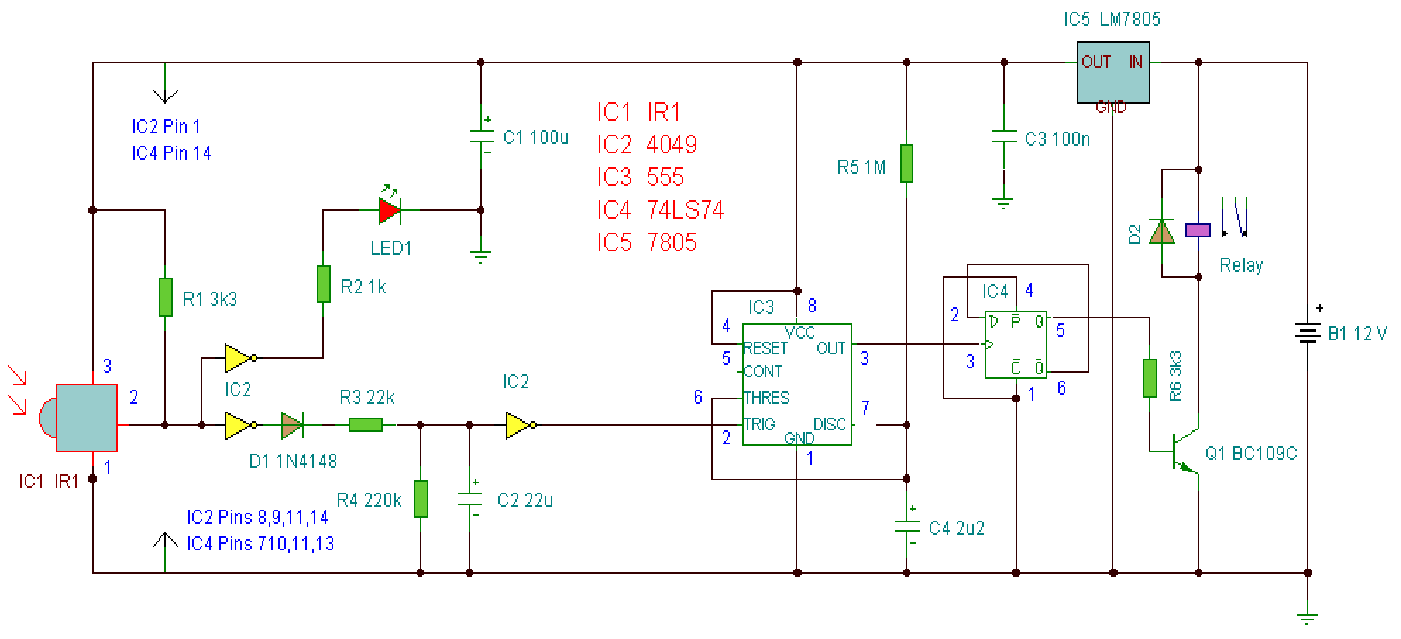
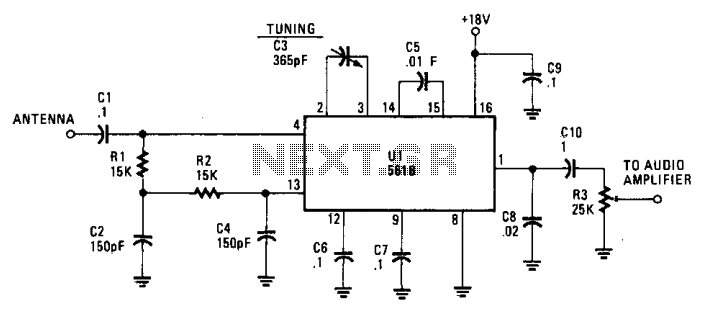
Infrared receiver
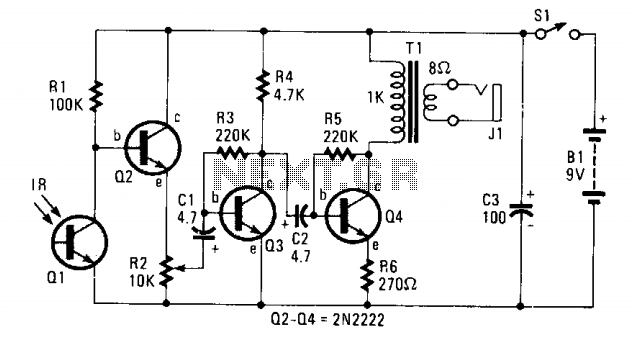
The circuit consists of Q1, a phototransistor that responds to an intensity of amplitude-modulated infrared light source, and a three-stage, high-gain audio amplifier. Transformer T1 is utilized to match the output impedance of the receiver to modern low-impedance (low-Z) headphones. However, if a set of 1000-2000 ohm magnetic (not crystal) high-impedance (high-Z) headphones is to be used, T1 should be removed, and the high-Z headphones should be connected in place of T1's primary winding, specifically the 1000-ohm winding.
The circuit design integrates a phototransistor (Q1) that is sensitive to amplitude-modulated infrared light, allowing it to effectively detect signals transmitted via infrared communication. The phototransistor acts as a light-to-voltage converter, where the intensity of the incoming infrared light modulates the collector current, producing an electrical signal that can be further amplified.
The three-stage high-gain audio amplifier is essential for boosting the low-level signals generated by the phototransistor. This amplifier configuration typically includes multiple transistor stages, each providing additional gain while maintaining signal integrity. The use of a high-gain amplifier is crucial for ensuring that the output signal is strong enough to drive headphones or other audio output devices.
Transformer T1 plays a pivotal role in impedance matching, which is necessary for optimal power transfer between the amplifier and the load (headphones). Low-impedance headphones, which are commonly used today, require a specific output impedance from the amplifier to function effectively. The transformer is designed to step down the impedance from the amplifier to match the low-Z headphones, enhancing audio quality and preventing distortion.
In scenarios where high-impedance (high-Z) headphones are employed, the circuit can be modified by removing the transformer T1. High-Z headphones typically have a higher resistance (1000-2000 ohms) and can be directly connected to the circuit. This adjustment allows for a direct interface with the amplifier output, ensuring that the audio signal is delivered effectively without the need for impedance matching.
Overall, this circuit design provides flexibility in headphone compatibility, allowing users to choose between low-impedance and high-impedance options based on their preferences and equipment. The inclusion of a phototransistor and a high-gain amplifier ensures that the system can effectively process infrared signals and deliver high-quality audio output.The circuit consists of Ql—a phototransistor that responds to an intensity of amplitude-modulated IR light source—and a three-stage, high-gain audio amplifier. Transformer Tl is used to match the output impedance of the receiver to today's popular low-impedance (low-Z) headphones;
but if a set of 1000-2000 ohm, magnetic (not crystal), high-impedance (high-Z) phones are to be used, remove Tl and connect the high-Z phones in place of Tl's primary winding—the 1000-ohm winding.
The circuit design integrates a phototransistor (Q1) that is sensitive to amplitude-modulated infrared light, allowing it to effectively detect signals transmitted via infrared communication. The phototransistor acts as a light-to-voltage converter, where the intensity of the incoming infrared light modulates the collector current, producing an electrical signal that can be further amplified.
The three-stage high-gain audio amplifier is essential for boosting the low-level signals generated by the phototransistor. This amplifier configuration typically includes multiple transistor stages, each providing additional gain while maintaining signal integrity. The use of a high-gain amplifier is crucial for ensuring that the output signal is strong enough to drive headphones or other audio output devices.
Transformer T1 plays a pivotal role in impedance matching, which is necessary for optimal power transfer between the amplifier and the load (headphones). Low-impedance headphones, which are commonly used today, require a specific output impedance from the amplifier to function effectively. The transformer is designed to step down the impedance from the amplifier to match the low-Z headphones, enhancing audio quality and preventing distortion.
In scenarios where high-impedance (high-Z) headphones are employed, the circuit can be modified by removing the transformer T1. High-Z headphones typically have a higher resistance (1000-2000 ohms) and can be directly connected to the circuit. This adjustment allows for a direct interface with the amplifier output, ensuring that the audio signal is delivered effectively without the need for impedance matching.
Overall, this circuit design provides flexibility in headphone compatibility, allowing users to choose between low-impedance and high-impedance options based on their preferences and equipment. The inclusion of a phototransistor and a high-gain amplifier ensures that the system can effectively process infrared signals and deliver high-quality audio output.The circuit consists of Ql—a phototransistor that responds to an intensity of amplitude-modulated IR light source—and a three-stage, high-gain audio amplifier. Transformer Tl is used to match the output impedance of the receiver to today's popular low-impedance (low-Z) headphones;
but if a set of 1000-2000 ohm, magnetic (not crystal), high-impedance (high-Z) phones are to be used, remove Tl and connect the high-Z phones in place of Tl's primary winding—the 1000-ohm winding.