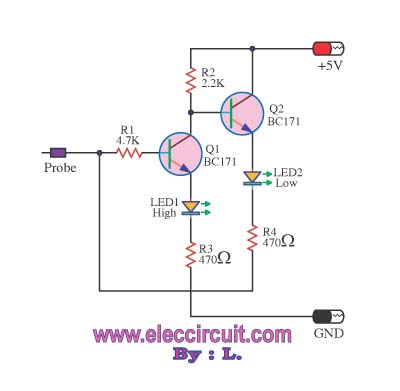
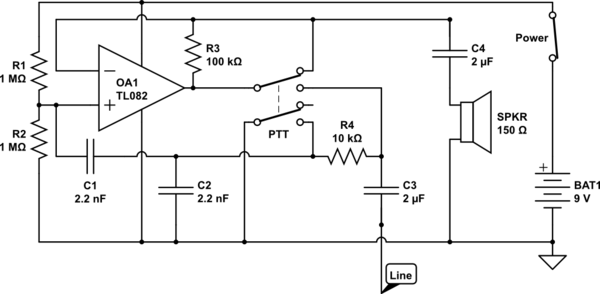
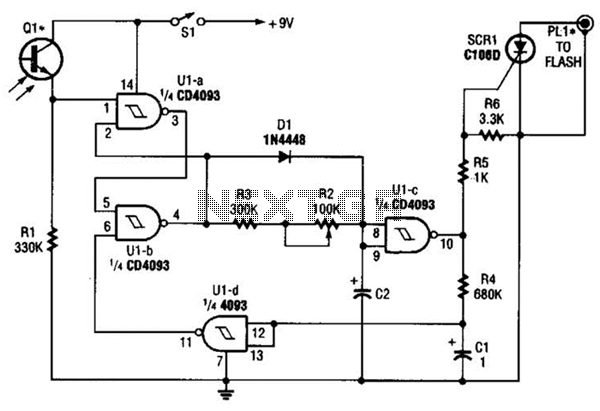
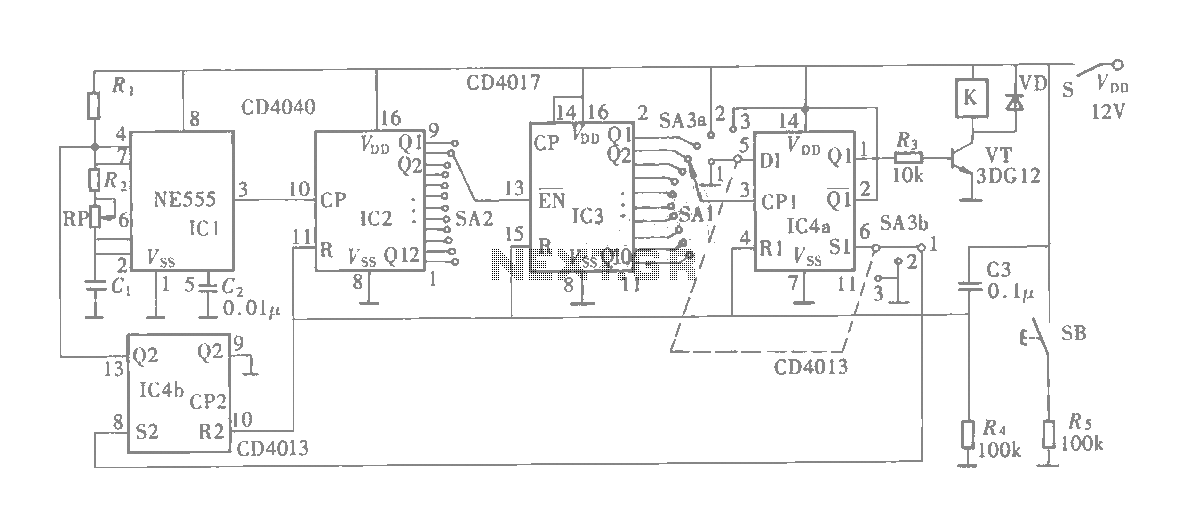
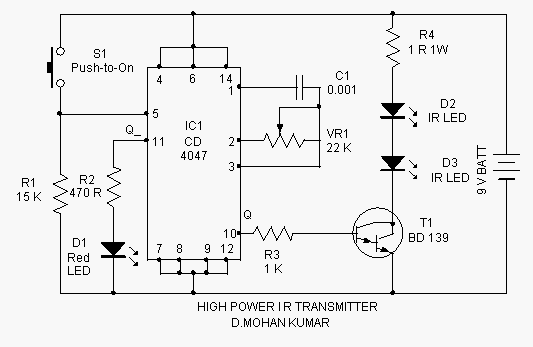
Integrated High Voltage Switching Charger circuit
MSP430 microcontroller and I2C-compatible slave peripheral device. Temperature measurement tasks can be accomplished in a variety of ways.
The MSP430 microcontroller is a low-power, 16-bit device widely used in embedded systems, particularly for applications requiring efficient power management and precise control. This microcontroller is equipped with various integrated peripherals, including timers, ADCs (Analog-to-Digital Converters), and communication interfaces such as I2C, which allows for seamless communication with other devices in a network.
The I2C-compatible slave peripheral device serves as a secondary unit in the I2C communication protocol, enabling the MSP430 to communicate with multiple devices using only two wires: the serial data line (SDA) and the serial clock line (SCL). This configuration simplifies the wiring and reduces the number of pins required on the microcontroller.
Temperature measurement tasks can be implemented using several methods, including the integration of temperature sensors such as thermistors, RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors), or digital temperature sensors like the DS18B20. The choice of sensor depends on the required accuracy, response time, and environmental conditions.
In a typical application, the MSP430 microcontroller would read temperature data from the I2C-compatible sensor, process the information, and potentially control other components based on the measured temperature. The microcontroller's ADC can be utilized to convert the analog signal from a thermistor or RTD into a digital value for further analysis.
Overall, the combination of the MSP430 microcontroller with an I2C-compatible slave device creates a flexible and efficient system for temperature measurement and control, suitable for various applications such as environmental monitoring, HVAC systems, and industrial automation.MSP430 micro-controller and I2C-compatible slave peripheral device. As stated earlier, temperature measurement tasks CAN be accomplished in a number of different 🔗 External reference
The MSP430 microcontroller is a low-power, 16-bit device widely used in embedded systems, particularly for applications requiring efficient power management and precise control. This microcontroller is equipped with various integrated peripherals, including timers, ADCs (Analog-to-Digital Converters), and communication interfaces such as I2C, which allows for seamless communication with other devices in a network.
The I2C-compatible slave peripheral device serves as a secondary unit in the I2C communication protocol, enabling the MSP430 to communicate with multiple devices using only two wires: the serial data line (SDA) and the serial clock line (SCL). This configuration simplifies the wiring and reduces the number of pins required on the microcontroller.
Temperature measurement tasks can be implemented using several methods, including the integration of temperature sensors such as thermistors, RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detectors), or digital temperature sensors like the DS18B20. The choice of sensor depends on the required accuracy, response time, and environmental conditions.
In a typical application, the MSP430 microcontroller would read temperature data from the I2C-compatible sensor, process the information, and potentially control other components based on the measured temperature. The microcontroller's ADC can be utilized to convert the analog signal from a thermistor or RTD into a digital value for further analysis.
Overall, the combination of the MSP430 microcontroller with an I2C-compatible slave device creates a flexible and efficient system for temperature measurement and control, suitable for various applications such as environmental monitoring, HVAC systems, and industrial automation.MSP430 micro-controller and I2C-compatible slave peripheral device. As stated earlier, temperature measurement tasks CAN be accomplished in a number of different 🔗 External reference