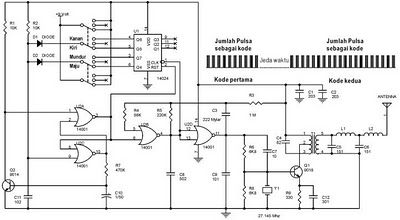
ir detector circuit
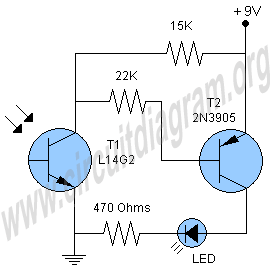
The human eye is highly sensitive to visible light but cannot detect infrared (IR) radiation. This limitation can make it challenging to test or verify equipment that emits infrared radiation. An IR detector circuit has been developed to address this issue; it detects IR radiation from any emitting device and activates an LED to indicate the presence of an IR beam. The core component of this circuit is Phototransistor T1, which senses the infrared light. Transistor T2 functions as an amplifier, boosting the output from T1 to illuminate the LED, confirming that the equipment is operational and emitting an infrared beam.
The IR detector circuit operates on the principle of phototransistor detection, where Phototransistor T1 is sensitive to infrared wavelengths. When an IR source is directed towards T1, it generates a small current in response to the incoming infrared light. This current is not sufficient to drive an LED directly; hence, the signal is fed into transistor T2, which is configured in a common-emitter amplifier configuration.
Transistor T2 amplifies the small current from T1, resulting in a larger output current capable of driving the LED. The LED is connected in series with a current-limiting resistor to prevent excessive current from damaging the LED. The circuit may also include a power supply, typically a battery, and additional passive components such as capacitors for stability and filtering, as well as potentiometers for adjusting sensitivity.
In practical applications, this IR detector circuit can be used in remote control systems, motion detectors, and other devices that rely on infrared communication. The simplicity of the design allows for easy integration into various projects, providing a visual indicator of infrared activity, which is essential for troubleshooting and verification of IR-emitting devices.Our eyes are very sensitive to light but they cannot see the IR (Infrared) radiations so it is some time difficult to test or check the equipments which emits infrared to confirm that either they are working or not. So here is the IR detector circuit which will detect IR from any equipment which emits IR and lights up an LED which will show the in
dication of IR beam. The heart of the circuit is Phototransistor T1 which will detect the infrared beam. The transistor T2 is working as an amplifier which amplifies the output of T1 and lights the LED which indicates that your equipment is working and emitting infrared beam. 🔗 External reference
The IR detector circuit operates on the principle of phototransistor detection, where Phototransistor T1 is sensitive to infrared wavelengths. When an IR source is directed towards T1, it generates a small current in response to the incoming infrared light. This current is not sufficient to drive an LED directly; hence, the signal is fed into transistor T2, which is configured in a common-emitter amplifier configuration.
Transistor T2 amplifies the small current from T1, resulting in a larger output current capable of driving the LED. The LED is connected in series with a current-limiting resistor to prevent excessive current from damaging the LED. The circuit may also include a power supply, typically a battery, and additional passive components such as capacitors for stability and filtering, as well as potentiometers for adjusting sensitivity.
In practical applications, this IR detector circuit can be used in remote control systems, motion detectors, and other devices that rely on infrared communication. The simplicity of the design allows for easy integration into various projects, providing a visual indicator of infrared activity, which is essential for troubleshooting and verification of IR-emitting devices.Our eyes are very sensitive to light but they cannot see the IR (Infrared) radiations so it is some time difficult to test or check the equipments which emits infrared to confirm that either they are working or not. So here is the IR detector circuit which will detect IR from any equipment which emits IR and lights up an LED which will show the in
dication of IR beam. The heart of the circuit is Phototransistor T1 which will detect the infrared beam. The transistor T2 is working as an amplifier which amplifies the output of T1 and lights the LED which indicates that your equipment is working and emitting infrared beam. 🔗 External reference