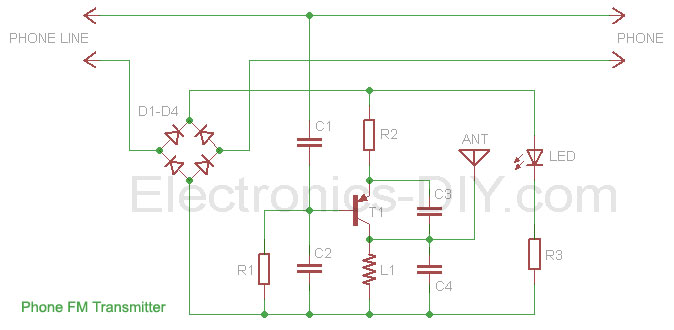
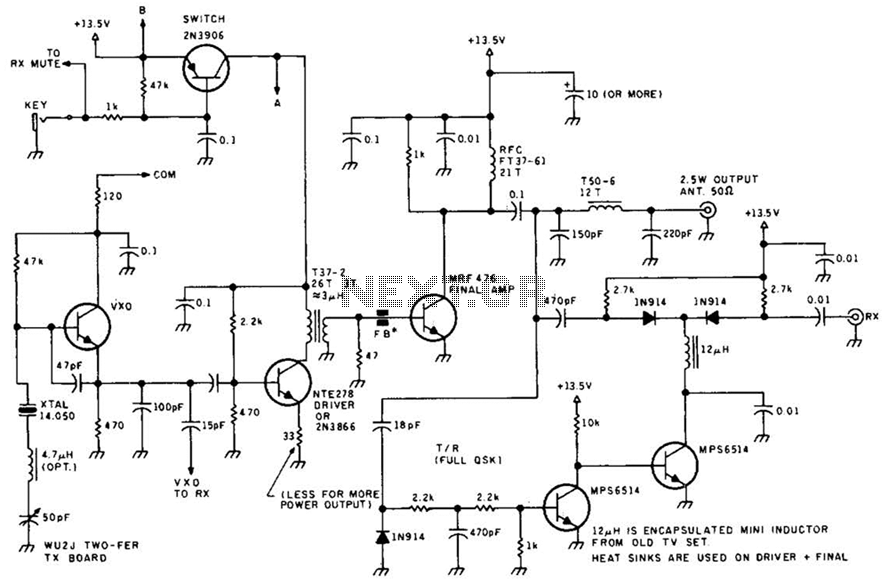
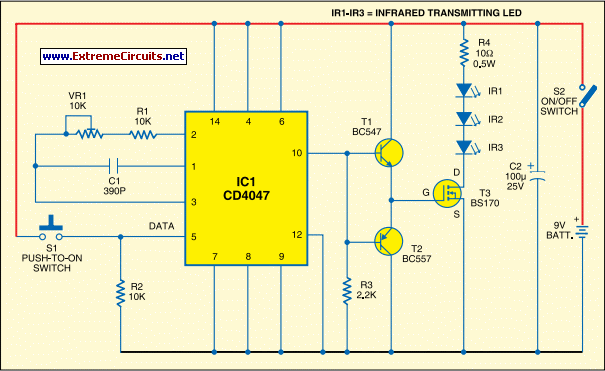
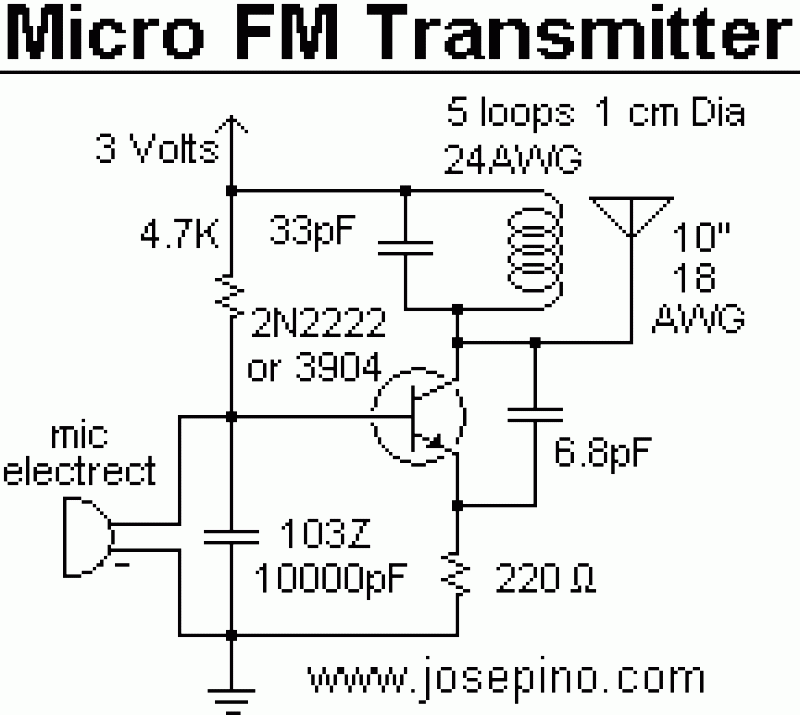
IR S/PDIF Transmitter
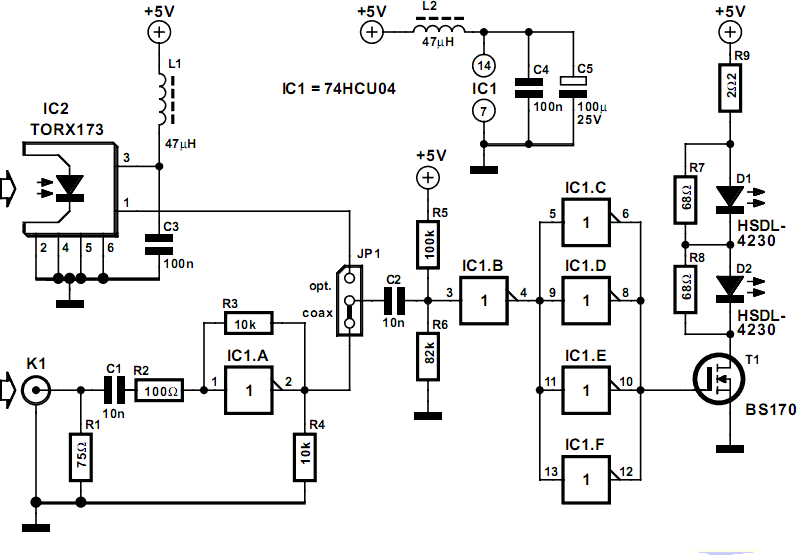
The most recognized methods for transmitting a digital audio signal (S/PDIF) include utilizing a standard 75-ohm coaxial cable or Toslink optical modules with compatible optical connections.
The S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) protocol is widely employed for transmitting high-quality digital audio signals between devices such as CD players, digital audio converters, and home theater systems. The two primary transmission methods utilized in S/PDIF are coaxial and optical, each offering distinct advantages.
Coaxial transmission utilizes a 75-ohm coaxial cable, which consists of a central conductor surrounded by an insulating layer and an outer conductive shield. This configuration minimizes signal loss and electromagnetic interference, making it suitable for high-fidelity audio applications. The coaxial cable typically connects to RCA jacks on the audio equipment, ensuring a secure and reliable connection. The electrical signal transmitted through the coaxial cable is a voltage-based representation of the audio data, which can be easily processed by compatible digital-to-analog converters (DACs).
On the other hand, Toslink optical transmission employs fiber optic cables to transmit audio signals as pulses of light. This method offers the advantage of electrical isolation, which eliminates the risk of ground loop noise and interference from nearby electronic devices. Toslink connectors are typically used for this type of connection, allowing for a straightforward plug-and-play setup. The optical modules convert the digital audio signal into light pulses, which travel through the fiber optic medium and are then converted back into an electrical signal by the receiving device's optical receiver.
Both transmission methods support various audio formats, including stereo PCM and multi-channel audio formats such as Dolby Digital and DTS. The choice between coaxial and Toslink depends on the specific requirements of the audio system, including the distance between devices, the potential for interference, and the available connection ports. Proper selection and implementation of these transmission methods are crucial for achieving optimal audio performance in digital audio systems.The best-known ways to transmit a digital audio signal (S/PDIF) are to use a standard 75? coaxial cable or Toslink optical modules with matching optical c.. 🔗 External reference
The S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) protocol is widely employed for transmitting high-quality digital audio signals between devices such as CD players, digital audio converters, and home theater systems. The two primary transmission methods utilized in S/PDIF are coaxial and optical, each offering distinct advantages.
Coaxial transmission utilizes a 75-ohm coaxial cable, which consists of a central conductor surrounded by an insulating layer and an outer conductive shield. This configuration minimizes signal loss and electromagnetic interference, making it suitable for high-fidelity audio applications. The coaxial cable typically connects to RCA jacks on the audio equipment, ensuring a secure and reliable connection. The electrical signal transmitted through the coaxial cable is a voltage-based representation of the audio data, which can be easily processed by compatible digital-to-analog converters (DACs).
On the other hand, Toslink optical transmission employs fiber optic cables to transmit audio signals as pulses of light. This method offers the advantage of electrical isolation, which eliminates the risk of ground loop noise and interference from nearby electronic devices. Toslink connectors are typically used for this type of connection, allowing for a straightforward plug-and-play setup. The optical modules convert the digital audio signal into light pulses, which travel through the fiber optic medium and are then converted back into an electrical signal by the receiving device's optical receiver.
Both transmission methods support various audio formats, including stereo PCM and multi-channel audio formats such as Dolby Digital and DTS. The choice between coaxial and Toslink depends on the specific requirements of the audio system, including the distance between devices, the potential for interference, and the available connection ports. Proper selection and implementation of these transmission methods are crucial for achieving optimal audio performance in digital audio systems.The best-known ways to transmit a digital audio signal (S/PDIF) are to use a standard 75? coaxial cable or Toslink optical modules with matching optical c.. 🔗 External reference