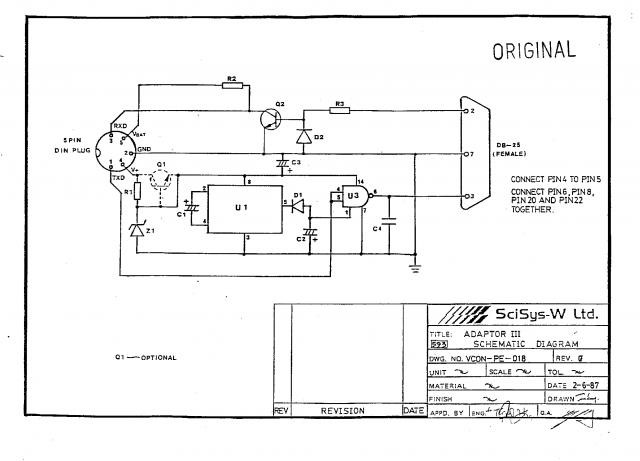
jtag cable
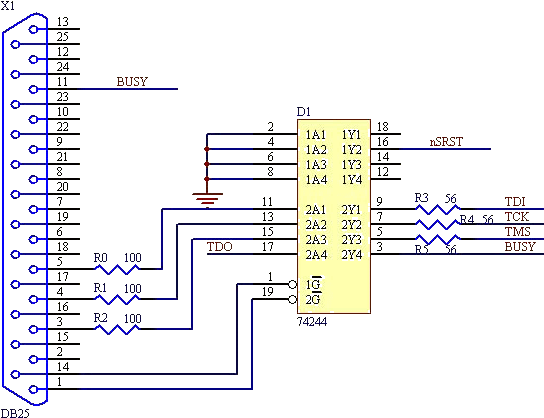
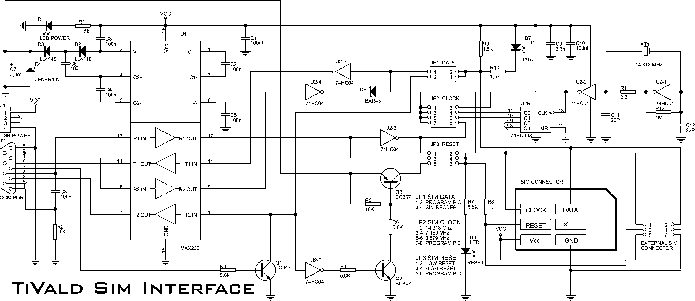
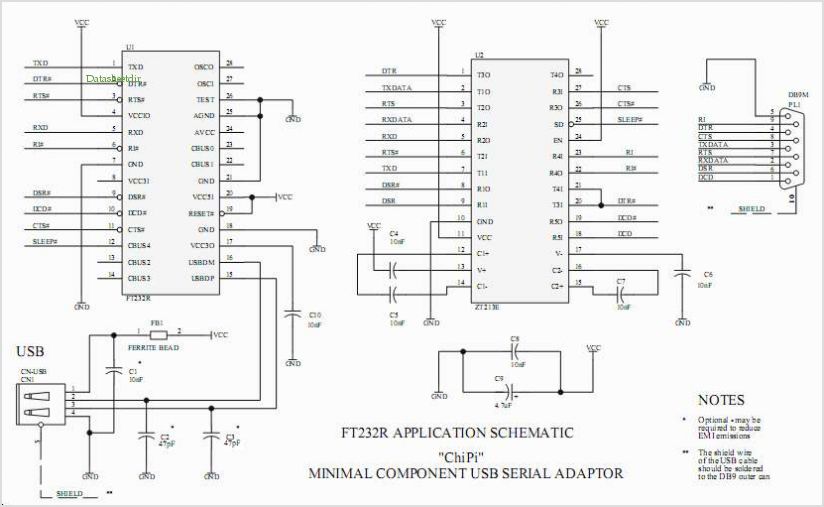
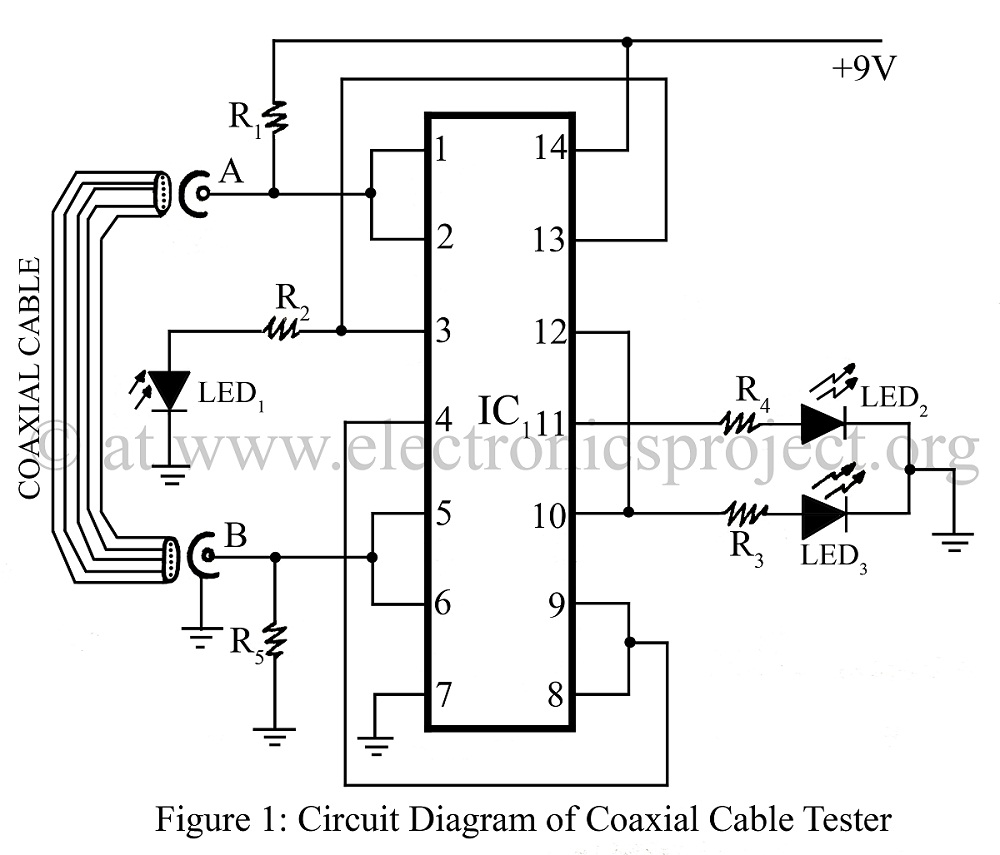
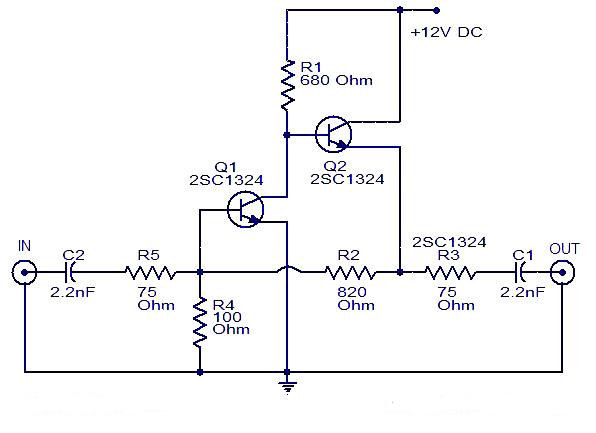
One end of the JTAG cable features a DB25 header designed for connection to the parallel port of a computer, while the opposite end is equipped with a 20-pin (or 14-pin) IDC header intended for interfacing with the user's circuit board. Figures 1 and 2 illustrate the complete circuit diagram for the JTAG cable, with a focus on the 20-pin IDC wiring configuration.
The JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) cable serves as a vital interface for programming and debugging embedded systems. The DB25 header connects to the parallel port of a computer, allowing for communication between the computer and the target device. This connection utilizes a standard protocol for debugging and testing, enabling the transfer of data and commands.
The 20-pin (or 14-pin) IDC header on the opposite end is designed to connect to the user's circuit board. This connection facilitates the integration of the JTAG interface into the target system. The wiring configuration of the 20-pin IDC header is critical for ensuring that the correct signals are transmitted to and from the target device. Each pin in the IDC header corresponds to specific functions, such as TCK (Test Clock), TMS (Test Mode Select), TDI (Test Data In), and TDO (Test Data Out), which are essential for JTAG operations.
The circuit diagram referenced in Figures 1 and 2 provides a visual representation of the connections and pin assignments for the JTAG cable. It is important to follow the specified wiring method to avoid miscommunication and ensure proper functionality during debugging and programming sessions. The design may also include additional components, such as resistors or capacitors, to stabilize the signal and improve reliability.
In summary, the JTAG cable is a critical tool for developers working with embedded systems, providing a straightforward means of connecting a computer to a target circuit board for programming and debugging purposes. The precise wiring and connection methods outlined in the accompanying circuit diagrams are essential for successful implementation.One end of JTAG Cable is a DB25 header used for connecting the parallel port of computer and the other end is a 20 pin (or 14 pin) IDC header used for connecting the user`s circuit board. Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 form a complete JTAG Cable circuit diagram. The diagram only shows 20 pin IDC wiring method. 🔗 External reference
The JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) cable serves as a vital interface for programming and debugging embedded systems. The DB25 header connects to the parallel port of a computer, allowing for communication between the computer and the target device. This connection utilizes a standard protocol for debugging and testing, enabling the transfer of data and commands.
The 20-pin (or 14-pin) IDC header on the opposite end is designed to connect to the user's circuit board. This connection facilitates the integration of the JTAG interface into the target system. The wiring configuration of the 20-pin IDC header is critical for ensuring that the correct signals are transmitted to and from the target device. Each pin in the IDC header corresponds to specific functions, such as TCK (Test Clock), TMS (Test Mode Select), TDI (Test Data In), and TDO (Test Data Out), which are essential for JTAG operations.
The circuit diagram referenced in Figures 1 and 2 provides a visual representation of the connections and pin assignments for the JTAG cable. It is important to follow the specified wiring method to avoid miscommunication and ensure proper functionality during debugging and programming sessions. The design may also include additional components, such as resistors or capacitors, to stabilize the signal and improve reliability.
In summary, the JTAG cable is a critical tool for developers working with embedded systems, providing a straightforward means of connecting a computer to a target circuit board for programming and debugging purposes. The precise wiring and connection methods outlined in the accompanying circuit diagrams are essential for successful implementation.One end of JTAG Cable is a DB25 header used for connecting the parallel port of computer and the other end is a 20 pin (or 14 pin) IDC header used for connecting the user`s circuit board. Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 form a complete JTAG Cable circuit diagram. The diagram only shows 20 pin IDC wiring method. 🔗 External reference