Co-axial cable tester
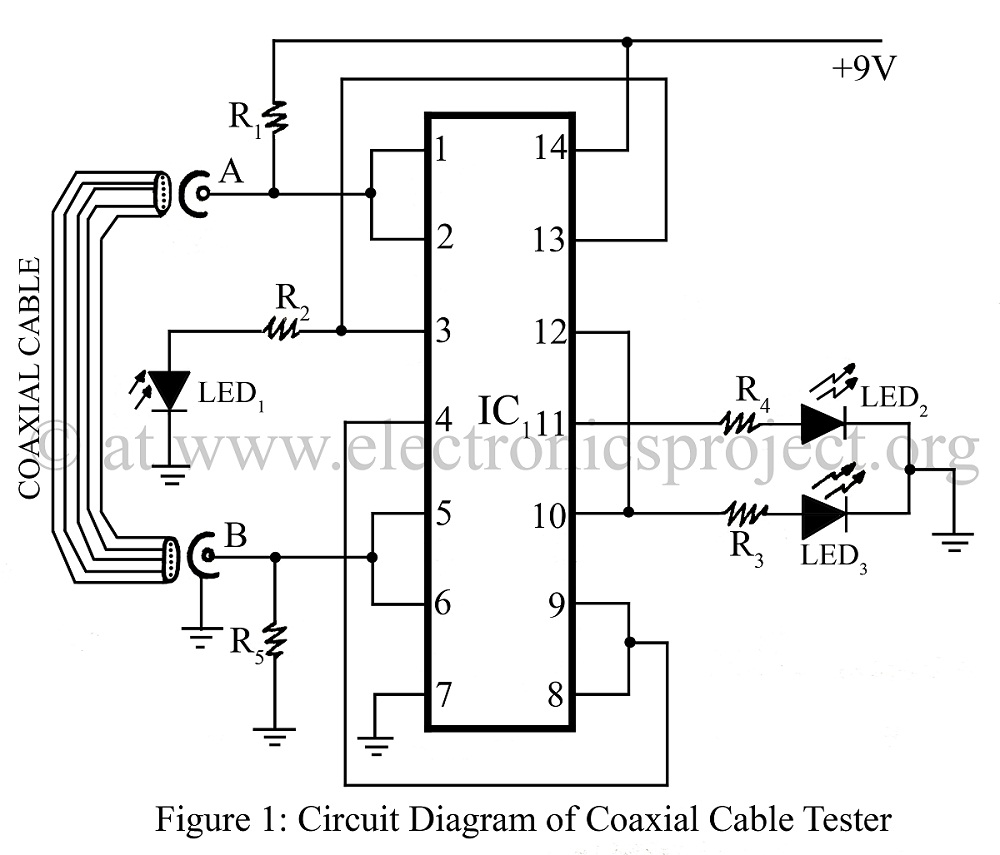
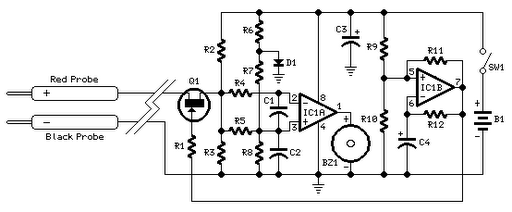
A coaxial cable tester is utilized to determine the condition of a coaxial cable, identifying whether it is open, short-circuited, or functioning correctly. This device employs a digital IC 4001 and includes a circuit description along with a parts list for various projects.
The coaxial cable tester circuit is designed to provide an efficient means of testing the integrity of coaxial cables, which are commonly used in television and internet applications. The core component of this tester is the digital IC 4001, which is a quad two-input NOR gate. This IC is instrumental in processing the signals that indicate the state of the coaxial cable.
The circuit typically consists of the following components:
1. **Digital IC 4001**: This IC is the heart of the tester, used to perform logic operations that help determine the cable's condition.
2. **Resistors**: Various resistors are used to limit current and set the appropriate voltage levels within the circuit.
3. **Capacitors**: Capacitors may be included for filtering and stabilization of the power supply to the IC.
4. **LED Indicators**: Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are employed to visually indicate the status of the cable. For example, a green LED can indicate a good connection, while a red LED may signify an open or short circuit.
5. **Power Supply**: A suitable power supply, often a battery, is required to power the circuit.
6. **Test Probes**: These are connected to the ends of the coaxial cable being tested, allowing for easy connection to the circuit.
The operation of the tester involves connecting the test probes to the ends of the coaxial cable. The IC 4001 processes the feedback from the cable and drives the LEDs based on the results of the tests. If the cable is intact, the circuit completes, and the corresponding LED lights up. Conversely, if there is an open circuit or a short circuit, the respective LED indicators will illuminate, allowing the user to diagnose the issue efficiently.
This circuit is beneficial for technicians and engineers who need to quickly assess the condition of coaxial cables in various applications, ensuring reliable performance in communication systems. The inclusion of a parts list enables users to replicate the design for their testing needs, making it a versatile tool in the field of electronics.Co-axial cable tester is used to test whether the co-axial cable is open or short circuit or good using digital IC 4001 circuit description with parts list and various project. 🔗 External reference
The coaxial cable tester circuit is designed to provide an efficient means of testing the integrity of coaxial cables, which are commonly used in television and internet applications. The core component of this tester is the digital IC 4001, which is a quad two-input NOR gate. This IC is instrumental in processing the signals that indicate the state of the coaxial cable.
The circuit typically consists of the following components:
1. **Digital IC 4001**: This IC is the heart of the tester, used to perform logic operations that help determine the cable's condition.
2. **Resistors**: Various resistors are used to limit current and set the appropriate voltage levels within the circuit.
3. **Capacitors**: Capacitors may be included for filtering and stabilization of the power supply to the IC.
4. **LED Indicators**: Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are employed to visually indicate the status of the cable. For example, a green LED can indicate a good connection, while a red LED may signify an open or short circuit.
5. **Power Supply**: A suitable power supply, often a battery, is required to power the circuit.
6. **Test Probes**: These are connected to the ends of the coaxial cable being tested, allowing for easy connection to the circuit.
The operation of the tester involves connecting the test probes to the ends of the coaxial cable. The IC 4001 processes the feedback from the cable and drives the LEDs based on the results of the tests. If the cable is intact, the circuit completes, and the corresponding LED lights up. Conversely, if there is an open circuit or a short circuit, the respective LED indicators will illuminate, allowing the user to diagnose the issue efficiently.
This circuit is beneficial for technicians and engineers who need to quickly assess the condition of coaxial cables in various applications, ensuring reliable performance in communication systems. The inclusion of a parts list enables users to replicate the design for their testing needs, making it a versatile tool in the field of electronics.Co-axial cable tester is used to test whether the co-axial cable is open or short circuit or good using digital IC 4001 circuit description with parts list and various project. 🔗 External reference