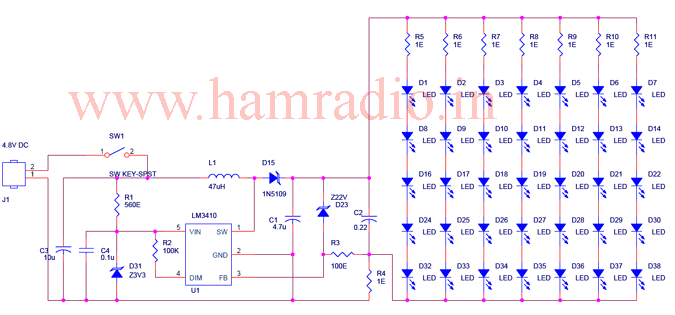
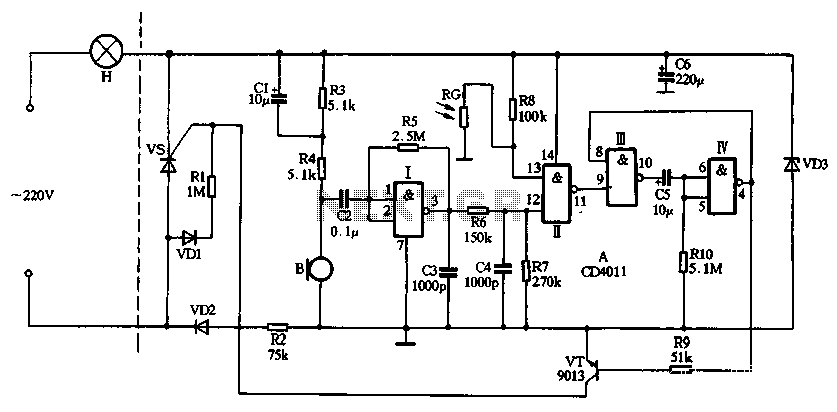
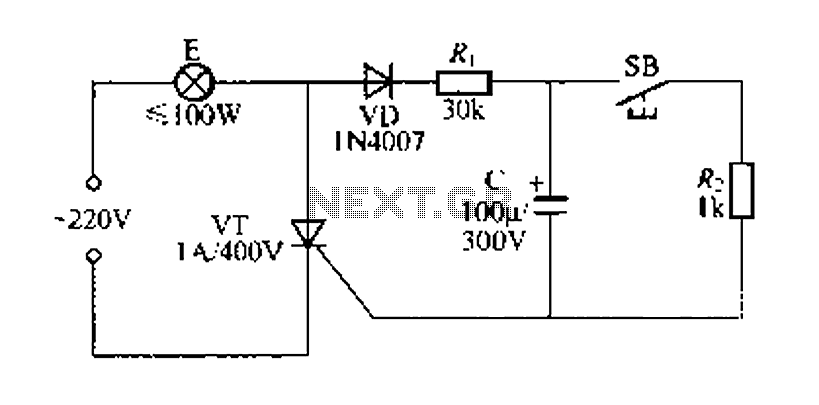
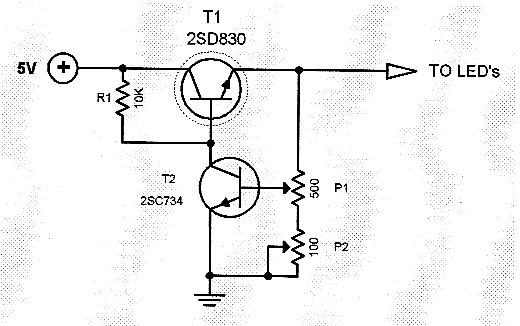
Lamp Dimmer
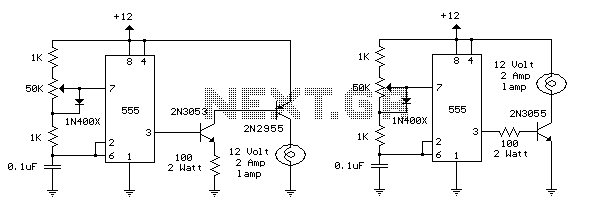
This project presents an effective solution for reducing electricity bills when using high-wattage bulbs. By utilizing miniature components and exercising meticulous care, it is possible to create a low-power lamp dimmer directly within the socket. Instead of employing a relatively expensive trigger diode, a standard neon lamp, such as the NE-83 or NE-2 variety, can be utilized. The NE-83 is designed for dark operation, providing more consistent performance. The neon lamp does not activate the gate until it begins to conduct, allowing the lamp to illuminate at a medium brightness level. Subsequently, the brightness can be adjusted down to a soft glow. However, since the neon lamp ceases to conduct when the applied voltage drops below its holding voltage of approximately 40V, the dimming range is not as extensive as that achievable with a diode trigger.
This project involves the design of a lamp dimmer circuit that integrates a neon lamp as the primary triggering component. The circuit operates by controlling the power delivered to high-wattage bulbs, enabling users to adjust brightness levels and thereby conserve energy. The core of the design includes a neon lamp, which serves as a voltage-dependent switch. When the voltage across the lamp reaches a certain threshold, the neon lamp conducts and triggers the dimming action.
The circuit can be constructed using a few essential components: a neon lamp (NE-83 or NE-2), a variable resistor (potentiometer) for adjusting brightness, and a capacitor to filter the signal. The neon lamp is connected in parallel with the load (the high-wattage bulb), and the variable resistor is placed in series, allowing for fine-tuning of the brightness level.
When the circuit is powered, the neon lamp remains off until the voltage reaches its breakdown voltage, at which point it conducts and allows current to flow through the bulb. The variable resistor adjusts the amount of current flowing to the load, thereby controlling the brightness. As the resistance is increased, the current decreases, resulting in dimmer light output.
It is important to note that the operational characteristics of the neon lamp limit the dimming range. The lamp will not allow the voltage to drop below its holding voltage of approximately 40V, which restricts the lowest brightness setting achievable with this design. Users may find this limitation acceptable for general lighting applications, but for more precise control, alternative methods such as using a triac-based dimmer may be considered.
In summary, this lamp dimmer project offers a cost-effective solution for managing high-wattage bulbs, leveraging a neon lamp for triggering. The simplicity of the design makes it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike, while providing a practical means of reducing energy consumption in residential or commercial lighting applications.This project is a wonderful idea of saving electric bill when you are using a heavy wattage bulbs. With miniature components and extreme care you can build a low power lamp dimmer right into the socket. Instead of a relativity expensive trigger diode, an ordinary neon lamp of the NE-83 or NE-2 variety can be used.
(An NE-83 is treaded for dark ope ration and will provide more consistent operation. ) Because the neon does not trip the gate until it conducts, the lamp turns on at medium brilliance. The lamp can then be backed off to a soft glow. Because the neon drops out when the applied voltage falls below the neon holding voltage of approximately 40V the lamp cannot be adjusted as low as it can with a diode trigger. 🔗 External reference
This project involves the design of a lamp dimmer circuit that integrates a neon lamp as the primary triggering component. The circuit operates by controlling the power delivered to high-wattage bulbs, enabling users to adjust brightness levels and thereby conserve energy. The core of the design includes a neon lamp, which serves as a voltage-dependent switch. When the voltage across the lamp reaches a certain threshold, the neon lamp conducts and triggers the dimming action.
The circuit can be constructed using a few essential components: a neon lamp (NE-83 or NE-2), a variable resistor (potentiometer) for adjusting brightness, and a capacitor to filter the signal. The neon lamp is connected in parallel with the load (the high-wattage bulb), and the variable resistor is placed in series, allowing for fine-tuning of the brightness level.
When the circuit is powered, the neon lamp remains off until the voltage reaches its breakdown voltage, at which point it conducts and allows current to flow through the bulb. The variable resistor adjusts the amount of current flowing to the load, thereby controlling the brightness. As the resistance is increased, the current decreases, resulting in dimmer light output.
It is important to note that the operational characteristics of the neon lamp limit the dimming range. The lamp will not allow the voltage to drop below its holding voltage of approximately 40V, which restricts the lowest brightness setting achievable with this design. Users may find this limitation acceptable for general lighting applications, but for more precise control, alternative methods such as using a triac-based dimmer may be considered.
In summary, this lamp dimmer project offers a cost-effective solution for managing high-wattage bulbs, leveraging a neon lamp for triggering. The simplicity of the design makes it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike, while providing a practical means of reducing energy consumption in residential or commercial lighting applications.This project is a wonderful idea of saving electric bill when you are using a heavy wattage bulbs. With miniature components and extreme care you can build a low power lamp dimmer right into the socket. Instead of a relativity expensive trigger diode, an ordinary neon lamp of the NE-83 or NE-2 variety can be used.
(An NE-83 is treaded for dark ope ration and will provide more consistent operation. ) Because the neon does not trip the gate until it conducts, the lamp turns on at medium brilliance. The lamp can then be backed off to a soft glow. Because the neon drops out when the applied voltage falls below the neon holding voltage of approximately 40V the lamp cannot be adjusted as low as it can with a diode trigger. 🔗 External reference