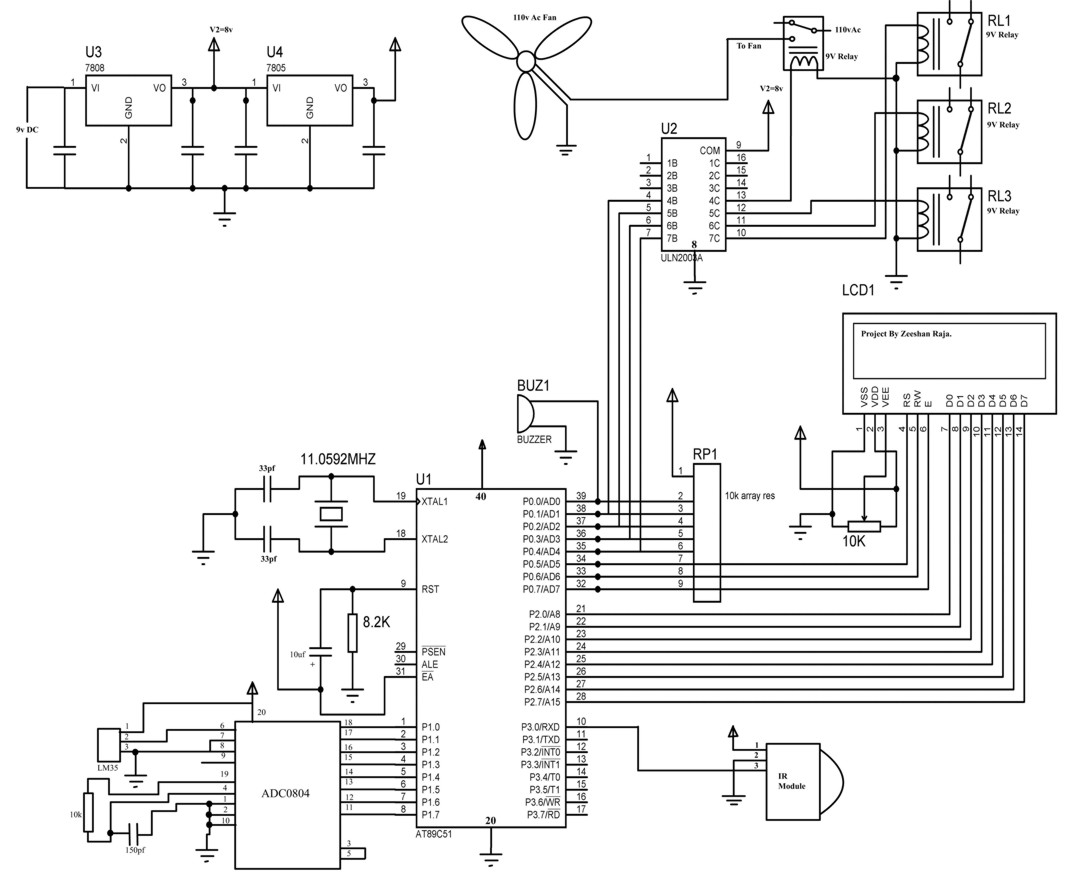
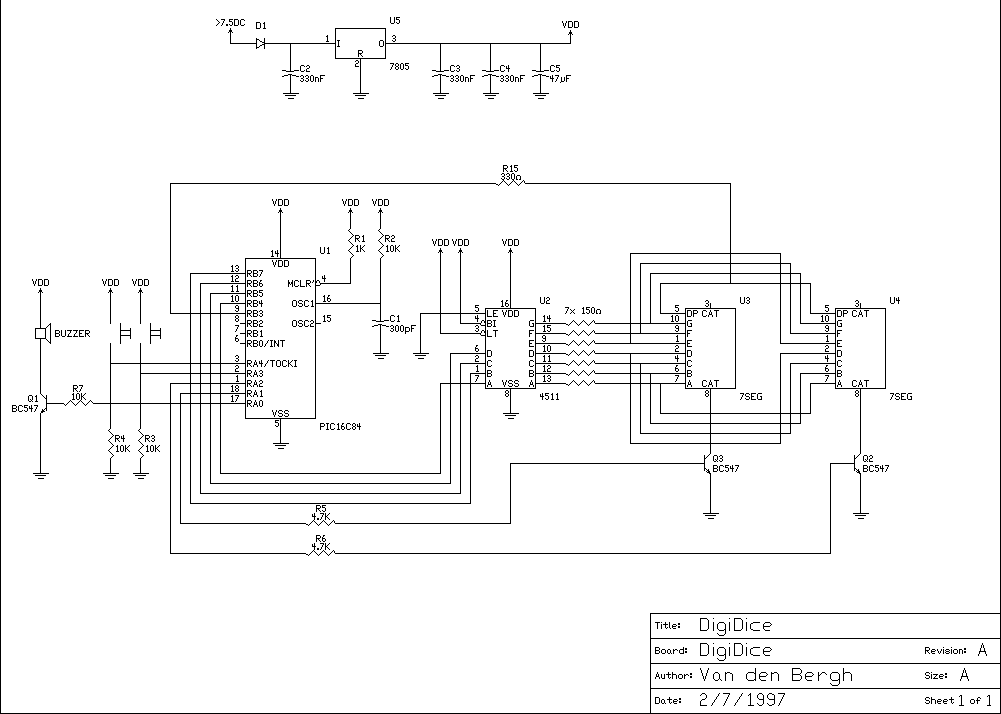
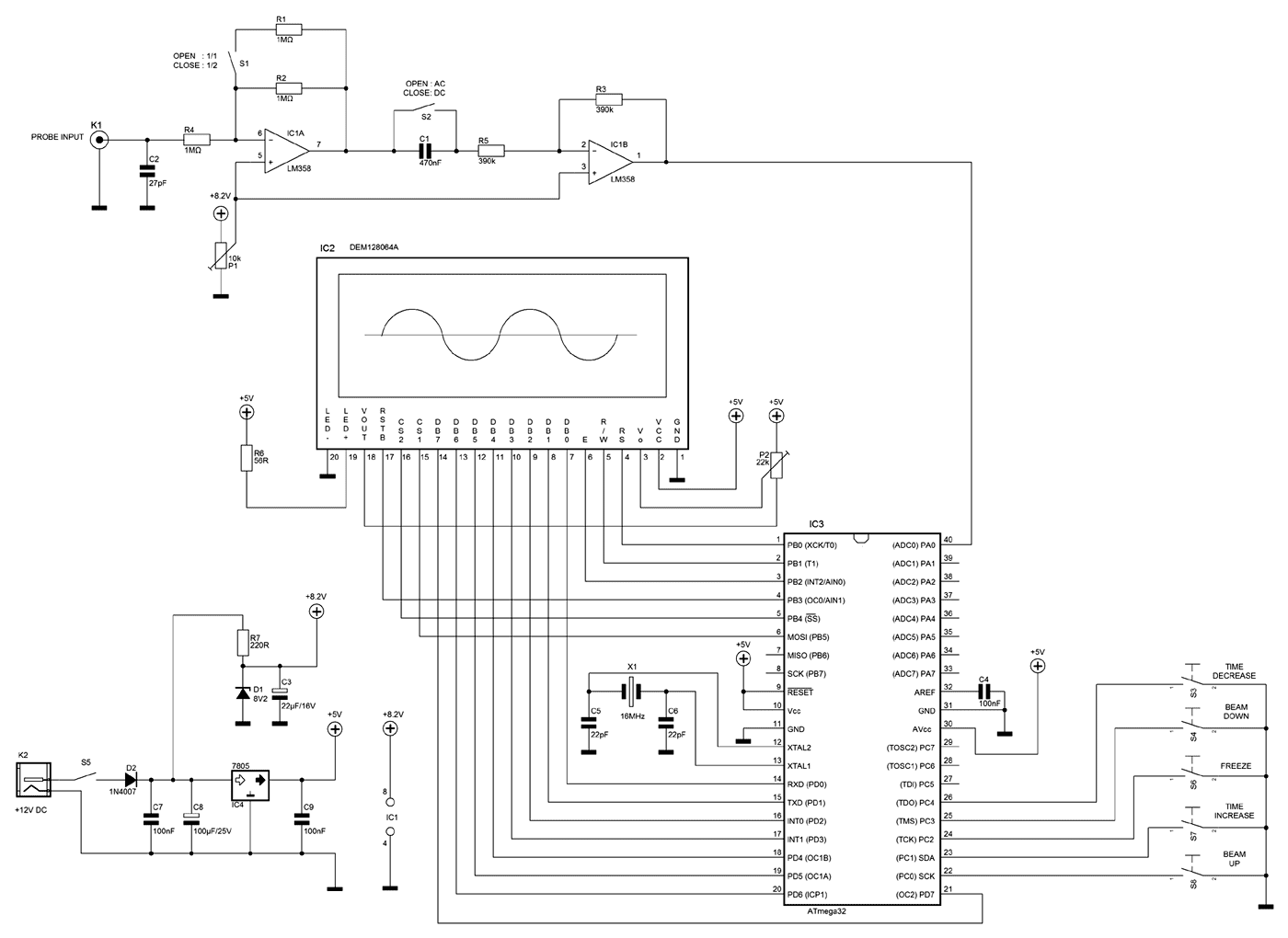
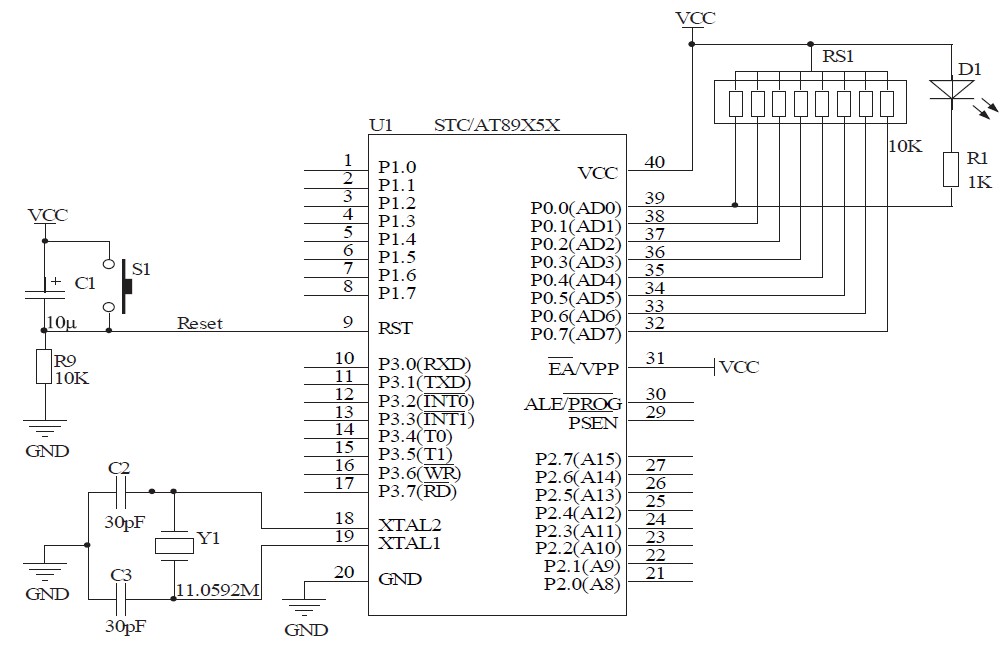
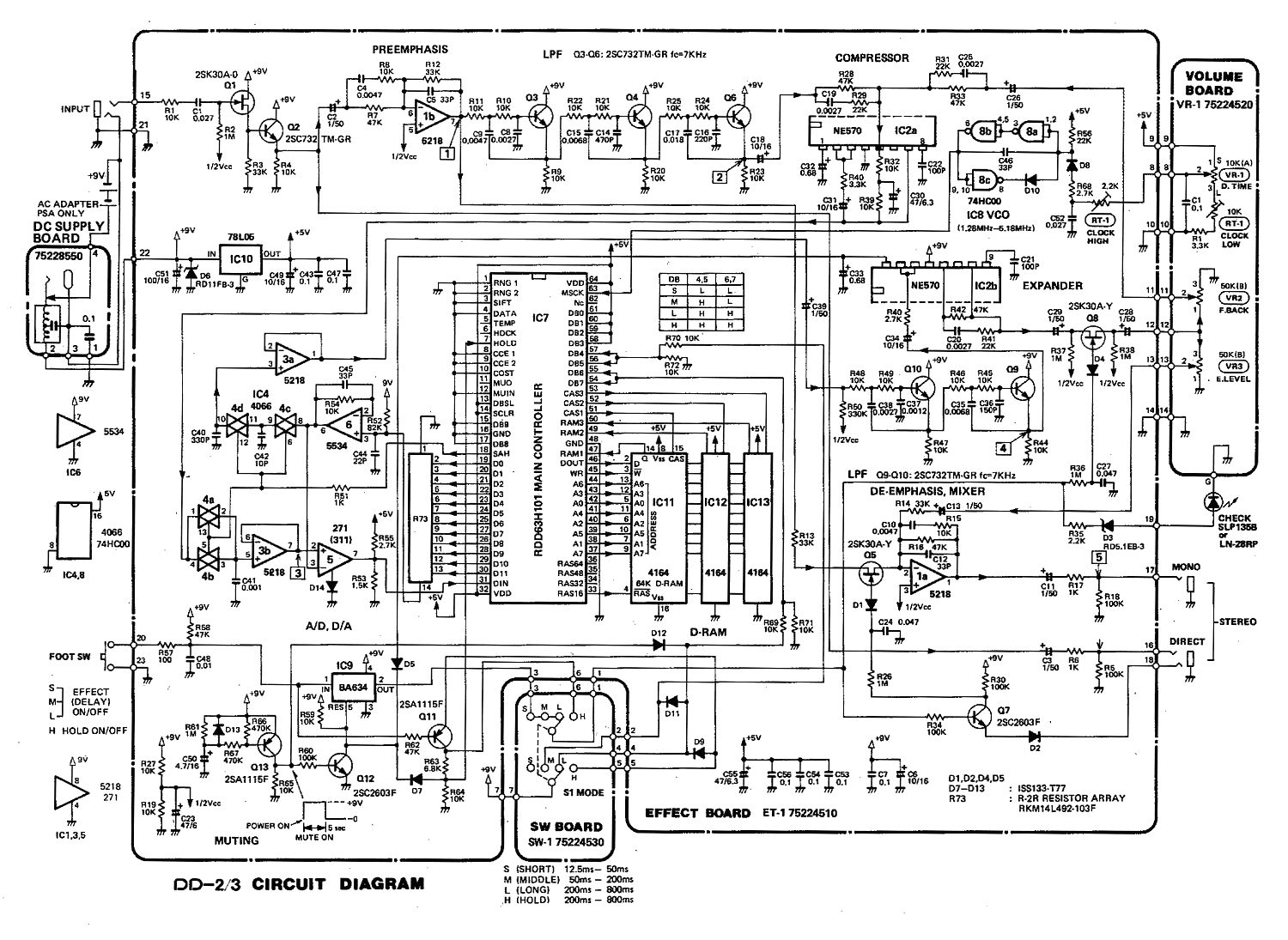
LCD 7 digit HF counter
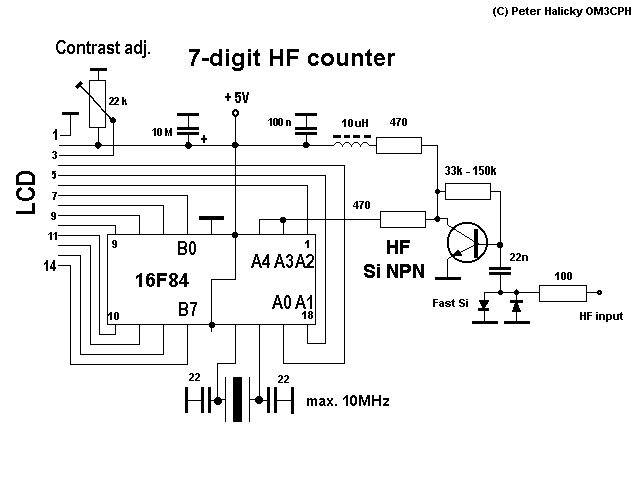
The resistor between basis and collector (around 47k) is to be individually set according to transistor characteristics. Without PIC in socket at the collector should be 2.5 V.
The circuit described involves a transistor configuration where a resistor, typically valued at around 47k ohms, is placed between the base and collector terminals of a transistor. This resistor serves a critical role in determining the operating point of the transistor, allowing for adjustments based on the specific characteristics of the transistor used in the application.
In this configuration, the transistor operates in a common-emitter mode, where the base-emitter junction is forward-biased, and the collector-emitter junction is reverse-biased. The choice of resistor value is essential, as it influences the base current and, consequently, the collector current. A higher resistance value may result in reduced base current, which can lead to lower collector current, while a lower resistance value increases the base current, allowing for greater amplification.
The mention of a PIC (Peripheral Interface Controller) indicates that this circuit may be part of a larger system where the PIC controls the transistor's operation. In the absence of the PIC, it is specified that the voltage at the collector should be maintained at 2.5 V. This suggests that the circuit is designed to operate at a specific voltage level, which could be critical for interfacing with other components or for ensuring proper operation within the intended application.
The design allows for flexibility in tuning the circuit by changing the resistor value to match the characteristics of different transistors, which may have varying current gain (beta) values and threshold voltages. This adaptability is crucial in applications requiring precise control over signal amplification or switching functions. Overall, the configuration aims to achieve reliable performance while accommodating variations in transistor specifications.The resistor between basis and collector (around 47k) is to be individually set according transistor characteristics. Without PIC in socket at the collector should be 2.5 V. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described involves a transistor configuration where a resistor, typically valued at around 47k ohms, is placed between the base and collector terminals of a transistor. This resistor serves a critical role in determining the operating point of the transistor, allowing for adjustments based on the specific characteristics of the transistor used in the application.
In this configuration, the transistor operates in a common-emitter mode, where the base-emitter junction is forward-biased, and the collector-emitter junction is reverse-biased. The choice of resistor value is essential, as it influences the base current and, consequently, the collector current. A higher resistance value may result in reduced base current, which can lead to lower collector current, while a lower resistance value increases the base current, allowing for greater amplification.
The mention of a PIC (Peripheral Interface Controller) indicates that this circuit may be part of a larger system where the PIC controls the transistor's operation. In the absence of the PIC, it is specified that the voltage at the collector should be maintained at 2.5 V. This suggests that the circuit is designed to operate at a specific voltage level, which could be critical for interfacing with other components or for ensuring proper operation within the intended application.
The design allows for flexibility in tuning the circuit by changing the resistor value to match the characteristics of different transistors, which may have varying current gain (beta) values and threshold voltages. This adaptability is crucial in applications requiring precise control over signal amplification or switching functions. Overall, the configuration aims to achieve reliable performance while accommodating variations in transistor specifications.The resistor between basis and collector (around 47k) is to be individually set according transistor characteristics. Without PIC in socket at the collector should be 2.5 V. 🔗 External reference