Lead-Acid Battery Charger Circuit
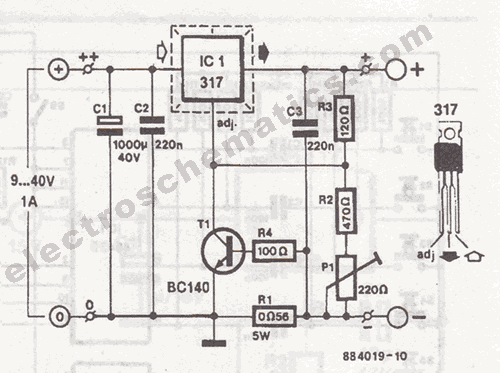
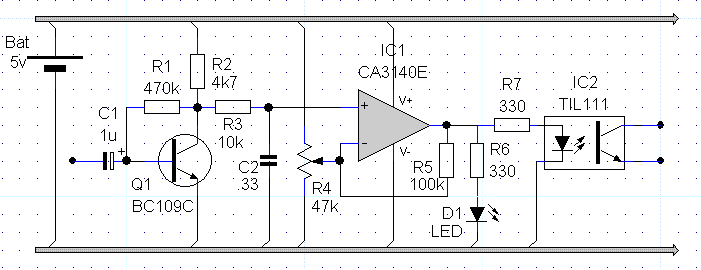
This circuit delivers an initial voltage of 2.5V per cell to rapidly charge a car battery. The charging current decreases as the battery charges.
This circuit is designed to provide an efficient charging solution for car batteries by applying an initial voltage of 2.5V per cell. The charging process is characterized by a rapid voltage application, which facilitates a quick energy transfer to the battery. As the charging progresses, the charging current is dynamically adjusted, decreasing in magnitude as the battery approaches its full charge state. This behavior is essential for preventing overcharging, which can lead to battery damage and reduced lifespan.
The circuit may incorporate a voltage regulator to maintain the output voltage at 2.5V per cell, ensuring that the charging remains within safe limits. Additionally, a current sensing mechanism could be integrated to monitor the charging current in real-time. This feedback loop would allow for automatic adjustments to the charging current, ensuring that it tapers off as the battery's state of charge increases.
Further enhancements could include temperature monitoring to prevent overheating during the charging process. A microcontroller or dedicated charging IC could be employed to manage these functions, providing precise control over voltage and current delivery.
Overall, this circuit design focuses on efficient and safe charging practices, ensuring that the battery is charged quickly while minimizing the risk of damage due to excessive current or voltage.This circuit delivers an initial voltage of 2.5V per cell to rapidly charge a car battery. The charging current decreases as the battery charges and when t.. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to provide an efficient charging solution for car batteries by applying an initial voltage of 2.5V per cell. The charging process is characterized by a rapid voltage application, which facilitates a quick energy transfer to the battery. As the charging progresses, the charging current is dynamically adjusted, decreasing in magnitude as the battery approaches its full charge state. This behavior is essential for preventing overcharging, which can lead to battery damage and reduced lifespan.
The circuit may incorporate a voltage regulator to maintain the output voltage at 2.5V per cell, ensuring that the charging remains within safe limits. Additionally, a current sensing mechanism could be integrated to monitor the charging current in real-time. This feedback loop would allow for automatic adjustments to the charging current, ensuring that it tapers off as the battery's state of charge increases.
Further enhancements could include temperature monitoring to prevent overheating during the charging process. A microcontroller or dedicated charging IC could be employed to manage these functions, providing precise control over voltage and current delivery.
Overall, this circuit design focuses on efficient and safe charging practices, ensuring that the battery is charged quickly while minimizing the risk of damage due to excessive current or voltage.This circuit delivers an initial voltage of 2.5V per cell to rapidly charge a car battery. The charging current decreases as the battery charges and when t.. 🔗 External reference