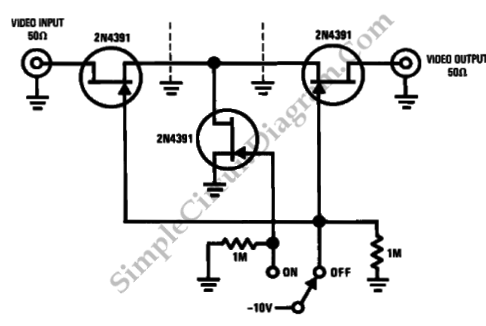
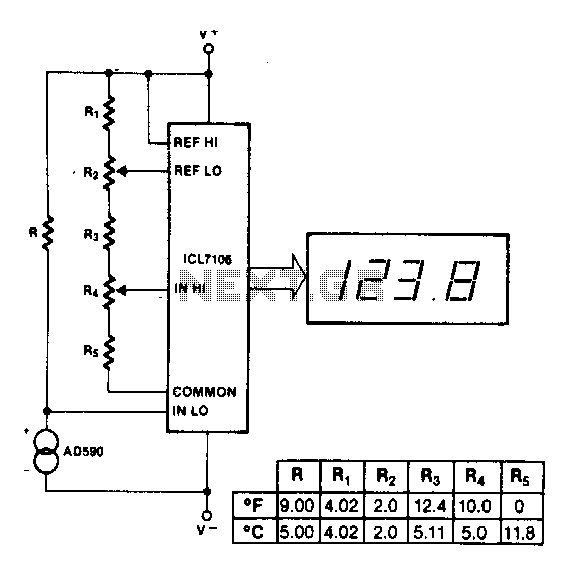
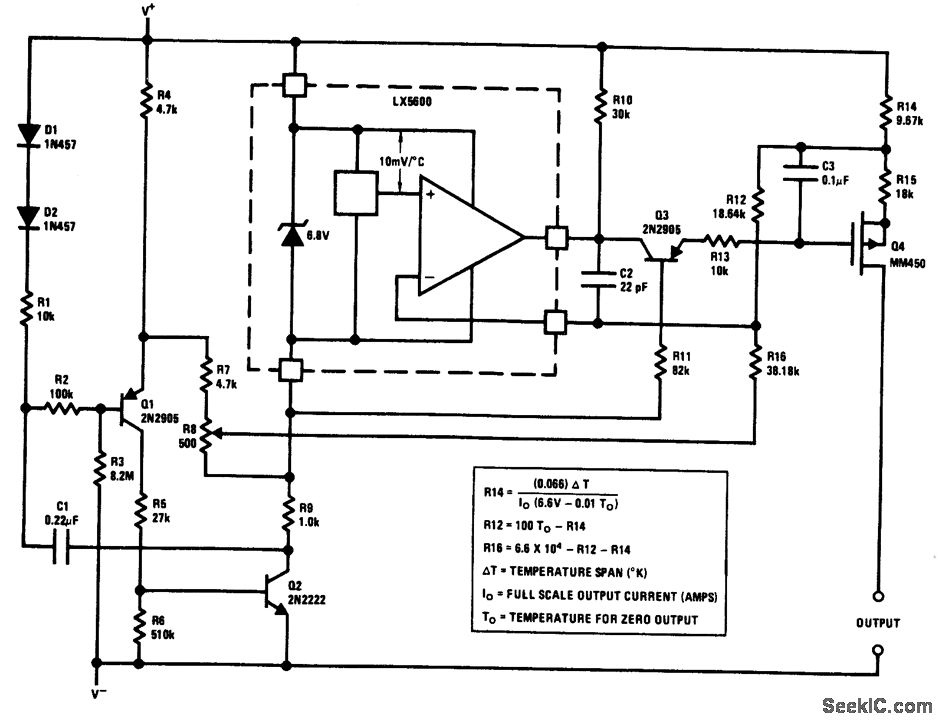
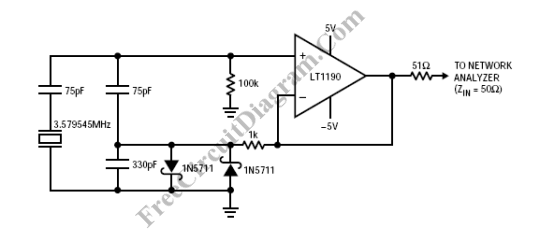
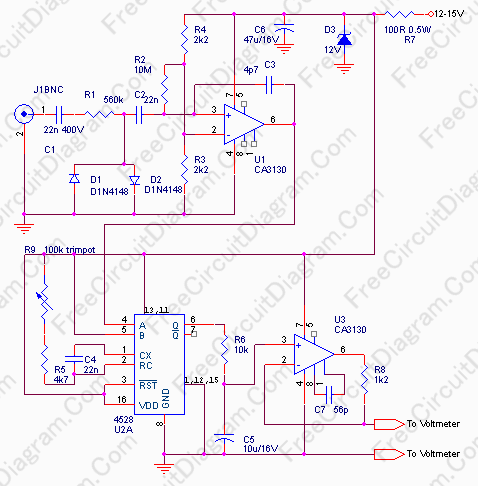
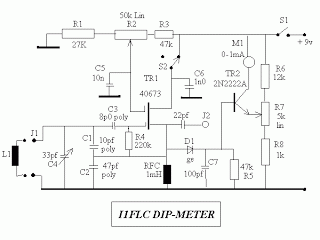
Linear frequency meter

The 555 timer is utilized in a monostable multivibrator circuit that generates a pulse of fixed time width, which is activated by an unknown input frequency.
The 555 timer in a monostable configuration operates by producing a single output pulse in response to a triggering input. When the input signal transitions from a low to a high state, the timer is triggered, causing the output to switch from low to high for a predetermined duration, defined by external resistors and capacitors connected to the timer.
In this configuration, the time width of the output pulse (T) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ T = 1.1 \times R \times C \]
where \( R \) is the resistance in ohms, and \( C \) is the capacitance in farads. The output pulse width remains constant regardless of the duration of the trigger input, making it suitable for applications that require a consistent output signal.
The circuit typically includes a resistor connected between the discharge pin (pin 7) and the supply voltage (Vcc), and a capacitor connected between the threshold pin (pin 6) and ground. The trigger input is connected to the trigger pin (pin 2). Upon receiving a trigger pulse, the capacitor begins to charge through the resistor until it reaches approximately 2/3 of the supply voltage, at which point the output returns to its low state, and the capacitor discharges.
This monostable multivibrator configuration is widely used in timer applications, pulse generation, and as a switch for various electronic devices. Its ability to produce a precise output pulse in response to varying input frequencies makes it a versatile component in electronic design.The 555 is used in a monostable multivibrator circuit that puts out a fixed timewidth pulse which is triggered by the unknown input frequency.
The 555 timer in a monostable configuration operates by producing a single output pulse in response to a triggering input. When the input signal transitions from a low to a high state, the timer is triggered, causing the output to switch from low to high for a predetermined duration, defined by external resistors and capacitors connected to the timer.
In this configuration, the time width of the output pulse (T) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ T = 1.1 \times R \times C \]
where \( R \) is the resistance in ohms, and \( C \) is the capacitance in farads. The output pulse width remains constant regardless of the duration of the trigger input, making it suitable for applications that require a consistent output signal.
The circuit typically includes a resistor connected between the discharge pin (pin 7) and the supply voltage (Vcc), and a capacitor connected between the threshold pin (pin 6) and ground. The trigger input is connected to the trigger pin (pin 2). Upon receiving a trigger pulse, the capacitor begins to charge through the resistor until it reaches approximately 2/3 of the supply voltage, at which point the output returns to its low state, and the capacitor discharges.
This monostable multivibrator configuration is widely used in timer applications, pulse generation, and as a switch for various electronic devices. Its ability to produce a precise output pulse in response to varying input frequencies makes it a versatile component in electronic design.The 555 is used in a monostable multivibrator circuit that puts out a fixed timewidth pulse which is triggered by the unknown input frequency.