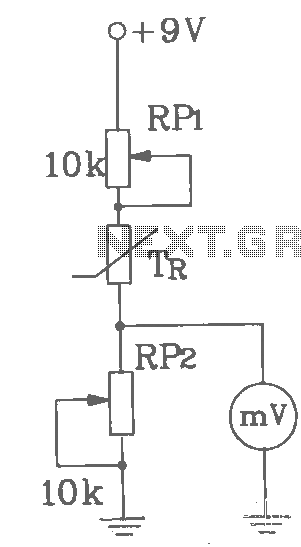
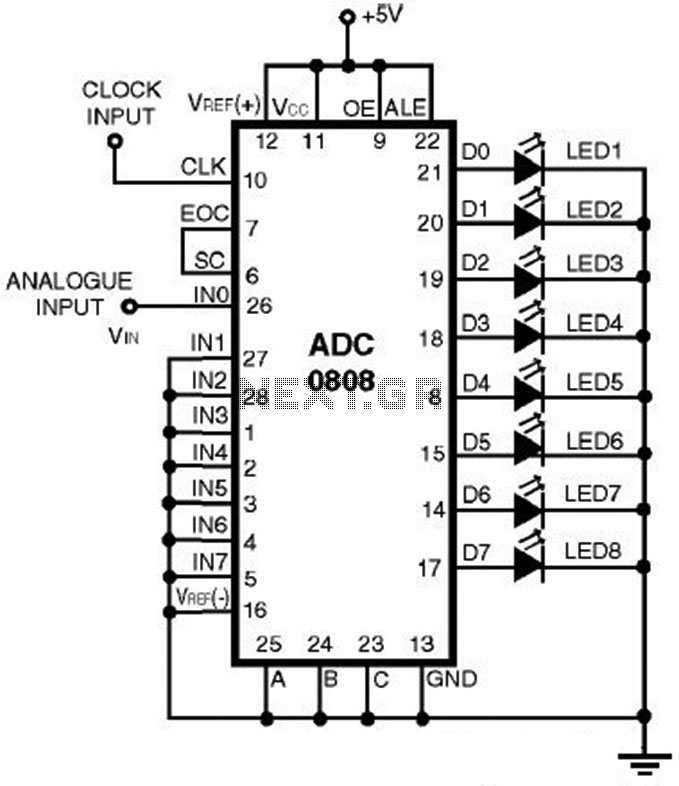
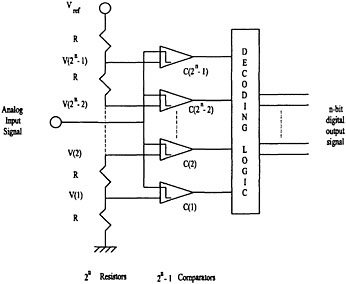
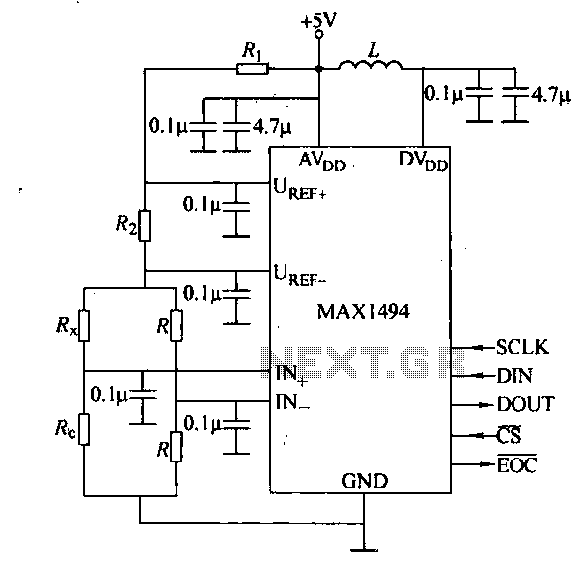
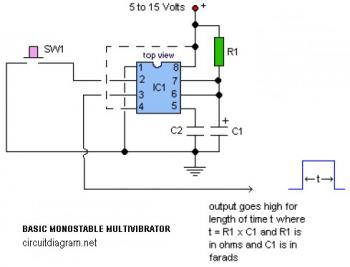
Basic digital thermometer
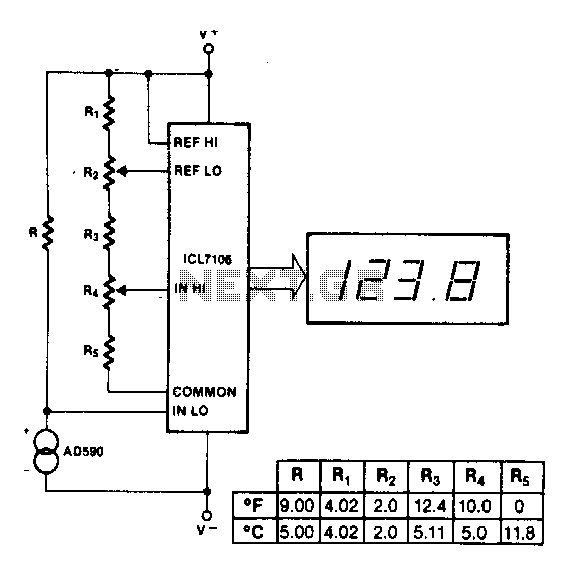
The maximum reading on the Celsius range is 199.9 °C, which is limited by the short-term maximum allowable sensor temperature. The maximum reading on the Fahrenheit range is 199 °F (93 °C), constrained by the number of display digits. The reference voltage (Vref) for both scales is 500 mV.
The electronic circuit described involves a temperature measurement system capable of displaying values in both Celsius and Fahrenheit. The sensor used in this system is designed to operate within specific thermal limits, ensuring accurate readings up to a maximum of 199.9 °C. This limitation is crucial to prevent damage to the sensor and maintain the integrity of the readings.
For the Fahrenheit scale, the system is limited to a maximum reading of 199 °F, which corresponds to approximately 93 °C. This limitation is primarily due to the constraints of the display digits, which may not accommodate higher values effectively without compromising readability.
The reference voltage (Vref) of 500 mV serves as a critical parameter for the analog-to-digital conversion process within the circuit. It establishes a baseline for the sensor's output signal, allowing for precise scaling and conversion of the temperature readings into a digital format that can be displayed. The choice of Vref is essential for ensuring that the entire measurement range is utilized effectively and that the readings are accurate across both temperature scales.
In summary, this temperature measurement circuit is designed with specific operational limits and a defined reference voltage, ensuring reliable and accurate temperature readings in both Celsius and Fahrenheit. The design considerations take into account both the physical limitations of the sensor and the functional constraints of the display system.Maximum reading on the Celsius range is 199,9 °C, limited by the (short-term) maximum allowable sensor temperature. Maximum reading on the Fahrenheit range is 199 °F (93 °C), limited by the number of display digits Vref for both scales is 500 mV.
The electronic circuit described involves a temperature measurement system capable of displaying values in both Celsius and Fahrenheit. The sensor used in this system is designed to operate within specific thermal limits, ensuring accurate readings up to a maximum of 199.9 °C. This limitation is crucial to prevent damage to the sensor and maintain the integrity of the readings.
For the Fahrenheit scale, the system is limited to a maximum reading of 199 °F, which corresponds to approximately 93 °C. This limitation is primarily due to the constraints of the display digits, which may not accommodate higher values effectively without compromising readability.
The reference voltage (Vref) of 500 mV serves as a critical parameter for the analog-to-digital conversion process within the circuit. It establishes a baseline for the sensor's output signal, allowing for precise scaling and conversion of the temperature readings into a digital format that can be displayed. The choice of Vref is essential for ensuring that the entire measurement range is utilized effectively and that the readings are accurate across both temperature scales.
In summary, this temperature measurement circuit is designed with specific operational limits and a defined reference voltage, ensuring reliable and accurate temperature readings in both Celsius and Fahrenheit. The design considerations take into account both the physical limitations of the sensor and the functional constraints of the display system.Maximum reading on the Celsius range is 199,9 °C, limited by the (short-term) maximum allowable sensor temperature. Maximum reading on the Fahrenheit range is 199 °F (93 °C), limited by the number of display digits Vref for both scales is 500 mV.