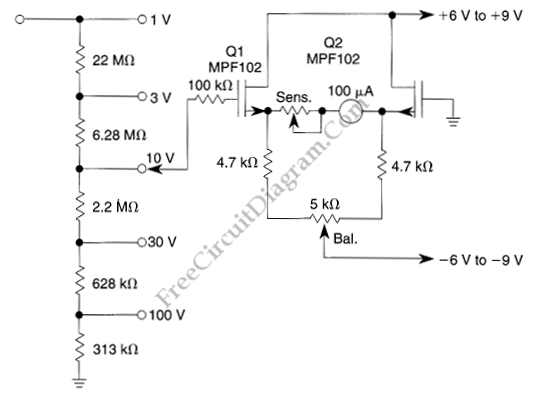
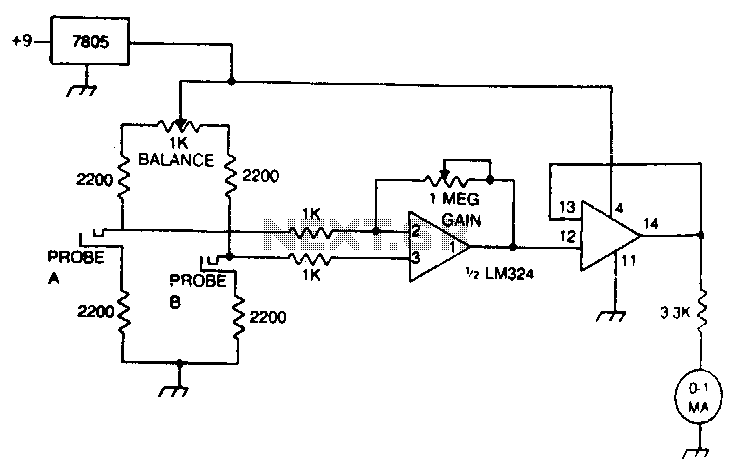
Linear Resistance Meter

Most analog multimeters are capable of measuring resistance over a wide range of values, but they can be inconvenient to use due to the reverse reading scale, which is also non-linear.
Analog multimeters, often referred to as VOMs (Volt-Ohm-Milliammeter), are versatile instruments used for measuring voltage, current, and resistance. The resistance measurement function is particularly useful for testing components in circuits, verifying connections, and troubleshooting electrical systems. However, the design of the analog multimeter presents some challenges, particularly in the context of resistance measurement.
The reverse reading scale is one of the primary inconveniences associated with analog multimeters. In this configuration, higher resistance values are indicated by lower positions on the scale, which can lead to confusion for users accustomed to direct reading instruments. Additionally, the non-linear nature of the scale means that the spacing between values is not uniform, making it more difficult to estimate precise resistance readings. This non-linearity arises from the way the needle deflection correlates with resistance through the use of a galvanometer, which is inherently more sensitive at lower resistance values.
To enhance the usability of analog multimeters, some designs incorporate features such as a linear scale or a digital readout that can provide a more intuitive understanding of resistance measurements. Additionally, the integration of a switchable range can allow users to select the most appropriate scale for the resistance being measured, thus improving accuracy and reducing the potential for reading errors.
In conclusion, while analog multimeters are effective tools for measuring resistance across a broad spectrum, their usability can be hindered by the reverse reading scale and non-linear characteristics. Understanding these limitations is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of these instruments in practical applications.Most analogue multimeters are capable of measuring resistance over quite a wide range of values, but are rather inconvenient in use due to the reverse reading scale which is also non-linear 🔗 External reference
Analog multimeters, often referred to as VOMs (Volt-Ohm-Milliammeter), are versatile instruments used for measuring voltage, current, and resistance. The resistance measurement function is particularly useful for testing components in circuits, verifying connections, and troubleshooting electrical systems. However, the design of the analog multimeter presents some challenges, particularly in the context of resistance measurement.
The reverse reading scale is one of the primary inconveniences associated with analog multimeters. In this configuration, higher resistance values are indicated by lower positions on the scale, which can lead to confusion for users accustomed to direct reading instruments. Additionally, the non-linear nature of the scale means that the spacing between values is not uniform, making it more difficult to estimate precise resistance readings. This non-linearity arises from the way the needle deflection correlates with resistance through the use of a galvanometer, which is inherently more sensitive at lower resistance values.
To enhance the usability of analog multimeters, some designs incorporate features such as a linear scale or a digital readout that can provide a more intuitive understanding of resistance measurements. Additionally, the integration of a switchable range can allow users to select the most appropriate scale for the resistance being measured, thus improving accuracy and reducing the potential for reading errors.
In conclusion, while analog multimeters are effective tools for measuring resistance across a broad spectrum, their usability can be hindered by the reverse reading scale and non-linear characteristics. Understanding these limitations is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of these instruments in practical applications.Most analogue multimeters are capable of measuring resistance over quite a wide range of values, but are rather inconvenient in use due to the reverse reading scale which is also non-linear 🔗 External reference