LINEAR VCO
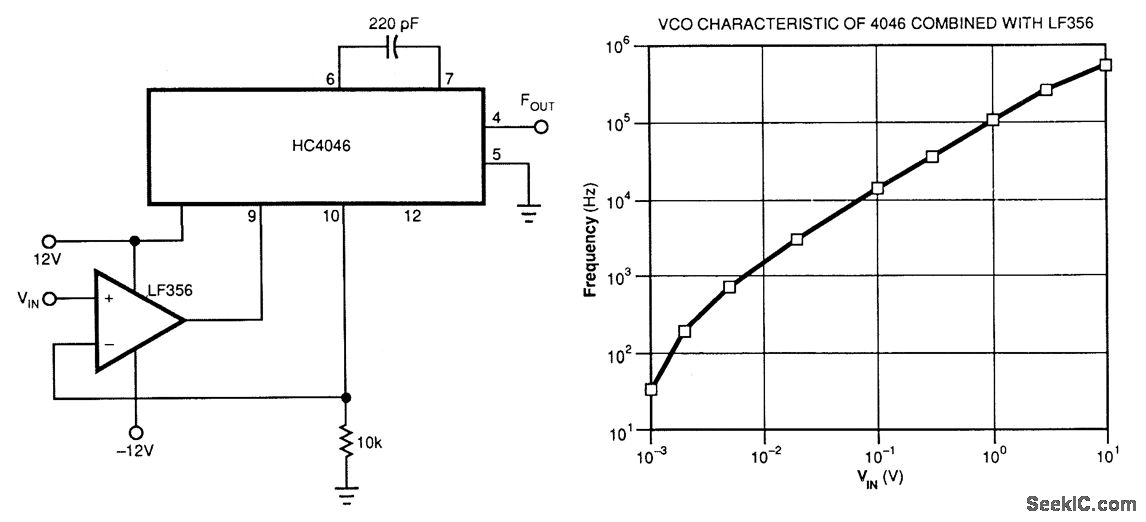
This voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) utilizes an LF356 operational amplifier to generate a linear frequency versus voltage characteristic in conjunction with the CMOS HC4046. The frequency range can be adjusted by modifying the capacitor linked between pins 6 and 7 of the HC4046. The linearization depicted in Figure 98-5(b) is accomplished by employing the HC4046's internal transistor rather than an external component.
The VCO circuit operates by leveraging the characteristics of the LF356 op-amp, which is known for its low noise and high-speed performance. The LF356 is configured in a feedback loop that processes the input voltage, effectively controlling the output frequency of the oscillator. The HC4046 phase-locked loop (PLL) integrates various functions, including frequency division and phase detection, allowing for precise control over the frequency output.
To adjust the frequency range, a capacitor is connected between pins 6 and 7 of the HC4046. Changing this capacitor alters the timing characteristics of the internal oscillator, thereby shifting the frequency output. This feature provides flexibility in designing applications that require different frequency ranges, such as in communication systems or signal processing.
The internal transistor of the HC4046 plays a critical role in achieving linearization. By utilizing this internal component, the circuit minimizes external parts, leading to a more compact design and potentially reducing overall system costs. The linearization process ensures that the frequency output varies linearly with the input voltage, which is essential for applications requiring accurate frequency modulation.
Overall, this VCO design presents a robust solution for generating a linear frequency response, making it suitable for various electronic applications where precise frequency control is essential.This VCO uses an LF356 op amp to produce a linear frequency vs. voltage characteristic using the CMOS HC4046. The frequency range can be changed by changing the capacitor connected between pins 6 and 7 of the HC4046. Using the HC4046`s internal transistor instead of an external component achieves the linearization in Fig.
98-5(b). 🔗 External reference
The VCO circuit operates by leveraging the characteristics of the LF356 op-amp, which is known for its low noise and high-speed performance. The LF356 is configured in a feedback loop that processes the input voltage, effectively controlling the output frequency of the oscillator. The HC4046 phase-locked loop (PLL) integrates various functions, including frequency division and phase detection, allowing for precise control over the frequency output.
To adjust the frequency range, a capacitor is connected between pins 6 and 7 of the HC4046. Changing this capacitor alters the timing characteristics of the internal oscillator, thereby shifting the frequency output. This feature provides flexibility in designing applications that require different frequency ranges, such as in communication systems or signal processing.
The internal transistor of the HC4046 plays a critical role in achieving linearization. By utilizing this internal component, the circuit minimizes external parts, leading to a more compact design and potentially reducing overall system costs. The linearization process ensures that the frequency output varies linearly with the input voltage, which is essential for applications requiring accurate frequency modulation.
Overall, this VCO design presents a robust solution for generating a linear frequency response, making it suitable for various electronic applications where precise frequency control is essential.This VCO uses an LF356 op amp to produce a linear frequency vs. voltage characteristic using the CMOS HC4046. The frequency range can be changed by changing the capacitor connected between pins 6 and 7 of the HC4046. Using the HC4046`s internal transistor instead of an external component achieves the linearization in Fig.
98-5(b). 🔗 External reference