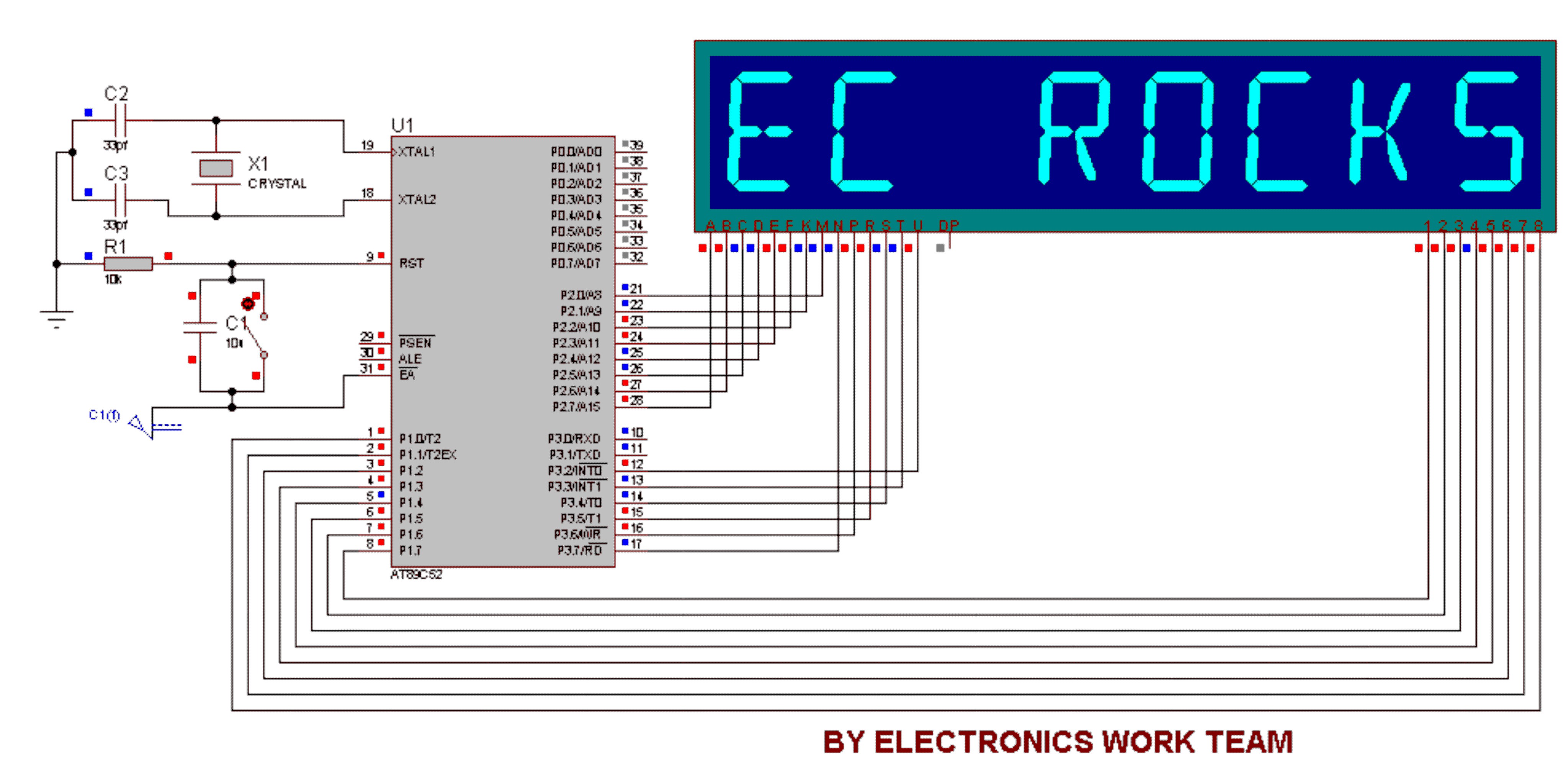
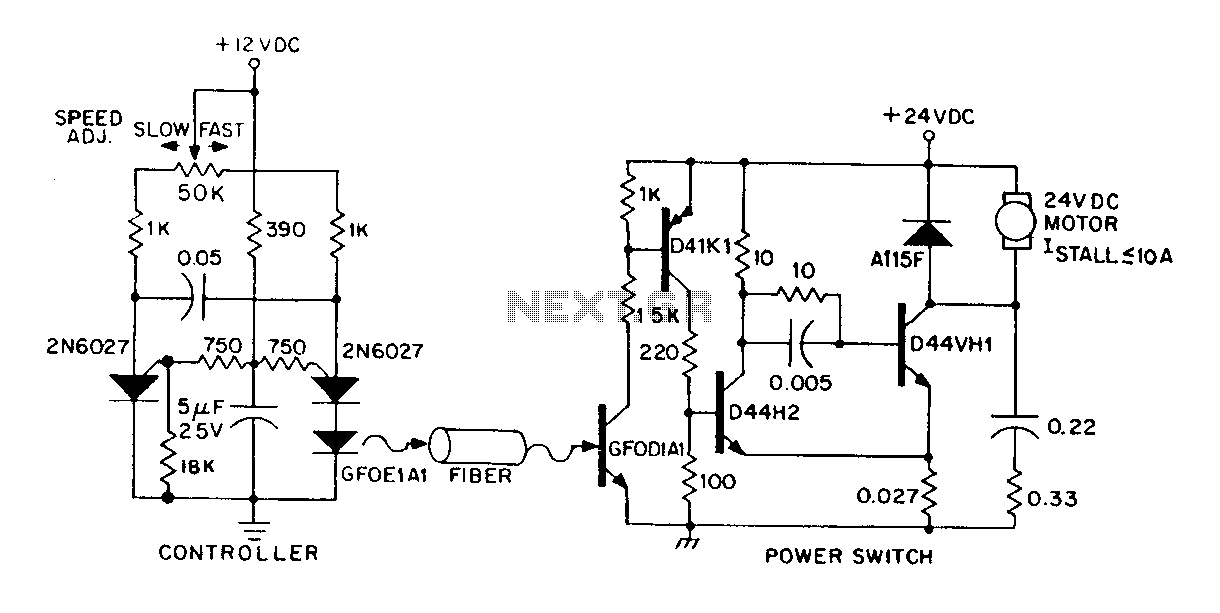
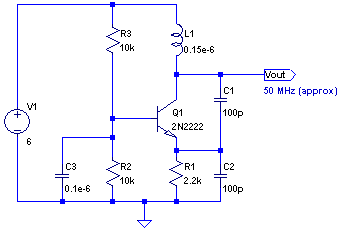
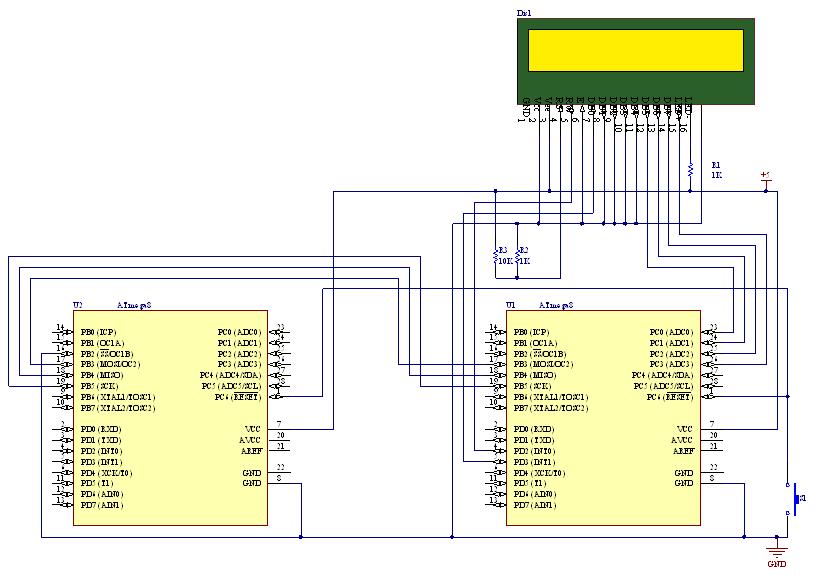
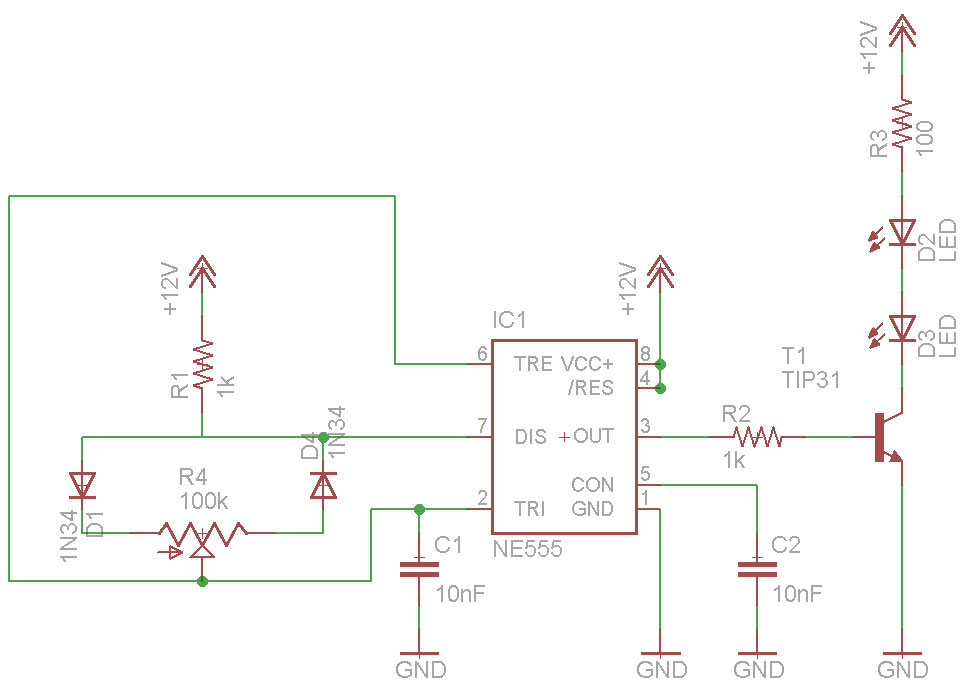
LM324N PWM Motor Speed Controller
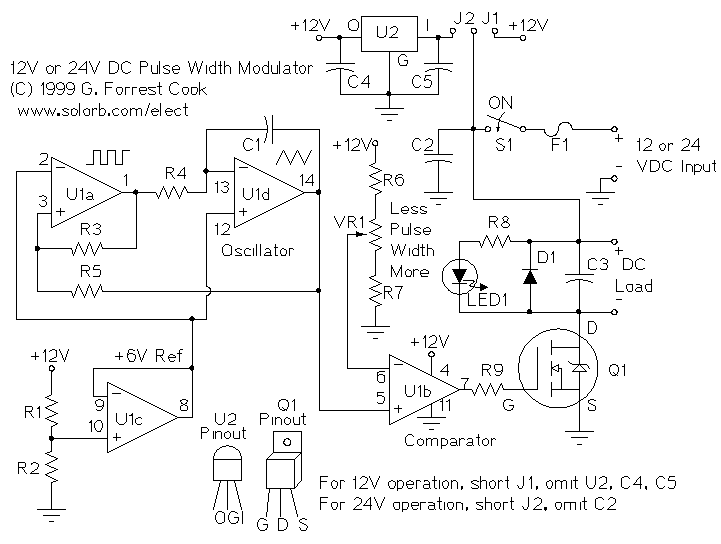
PWM is a device that can be utilized as an efficient light dimmer or DC motor speed controller. Function: for a general-purpose device that can...
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is a versatile technique widely employed in various electronic applications, particularly for controlling the brightness of lights and regulating the speed of DC motors. The fundamental principle of PWM involves varying the width of the pulses in a signal while maintaining a constant frequency. This modulation allows for precise control over the average power delivered to a load, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient energy management.
In light dimming applications, PWM adjusts the perceived brightness by altering the duty cycle of the signal sent to the light source. A higher duty cycle corresponds to increased brightness, while a lower duty cycle results in dimmer light. This method is not only energy-efficient but also minimizes heat generation compared to traditional resistive dimming methods.
For DC motor speed control, PWM provides a means to adjust the motor speed effectively. By changing the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the average voltage and current supplied to the motor can be varied, thus controlling its speed. This approach allows for smooth acceleration and deceleration, enhancing the performance and longevity of the motor.
A typical PWM circuit consists of a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM generator, which produces the PWM signal, and a power stage, often including a transistor or MOSFET, that switches the load on and off in accordance with the PWM signal. Additional components such as diodes may be included to protect against back EMF in motor applications, while filtering capacitors can be employed to smooth the output signal for lighting applications.
Overall, PWM is an essential technique for efficient power control in various electronic systems, enabling enhanced functionality and energy savings.PWM is a device that may be used as an efficient light dimmer or DC motor speed controller. Function: for a general purpose device that can .. 🔗 External reference
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is a versatile technique widely employed in various electronic applications, particularly for controlling the brightness of lights and regulating the speed of DC motors. The fundamental principle of PWM involves varying the width of the pulses in a signal while maintaining a constant frequency. This modulation allows for precise control over the average power delivered to a load, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient energy management.
In light dimming applications, PWM adjusts the perceived brightness by altering the duty cycle of the signal sent to the light source. A higher duty cycle corresponds to increased brightness, while a lower duty cycle results in dimmer light. This method is not only energy-efficient but also minimizes heat generation compared to traditional resistive dimming methods.
For DC motor speed control, PWM provides a means to adjust the motor speed effectively. By changing the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the average voltage and current supplied to the motor can be varied, thus controlling its speed. This approach allows for smooth acceleration and deceleration, enhancing the performance and longevity of the motor.
A typical PWM circuit consists of a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM generator, which produces the PWM signal, and a power stage, often including a transistor or MOSFET, that switches the load on and off in accordance with the PWM signal. Additional components such as diodes may be included to protect against back EMF in motor applications, while filtering capacitors can be employed to smooth the output signal for lighting applications.
Overall, PWM is an essential technique for efficient power control in various electronic systems, enabling enhanced functionality and energy savings.PWM is a device that may be used as an efficient light dimmer or DC motor speed controller. Function: for a general purpose device that can .. 🔗 External reference