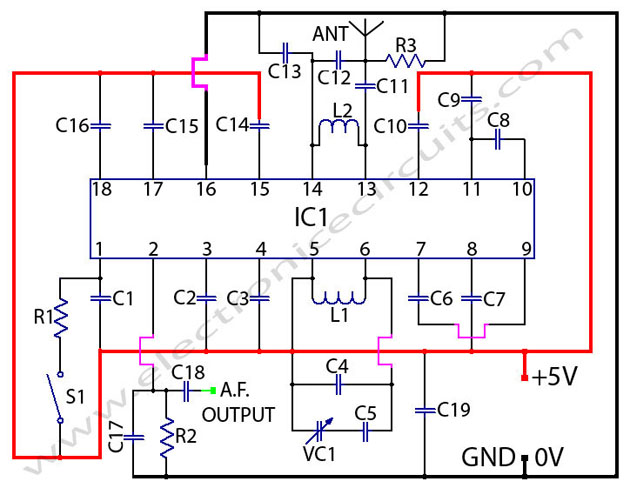
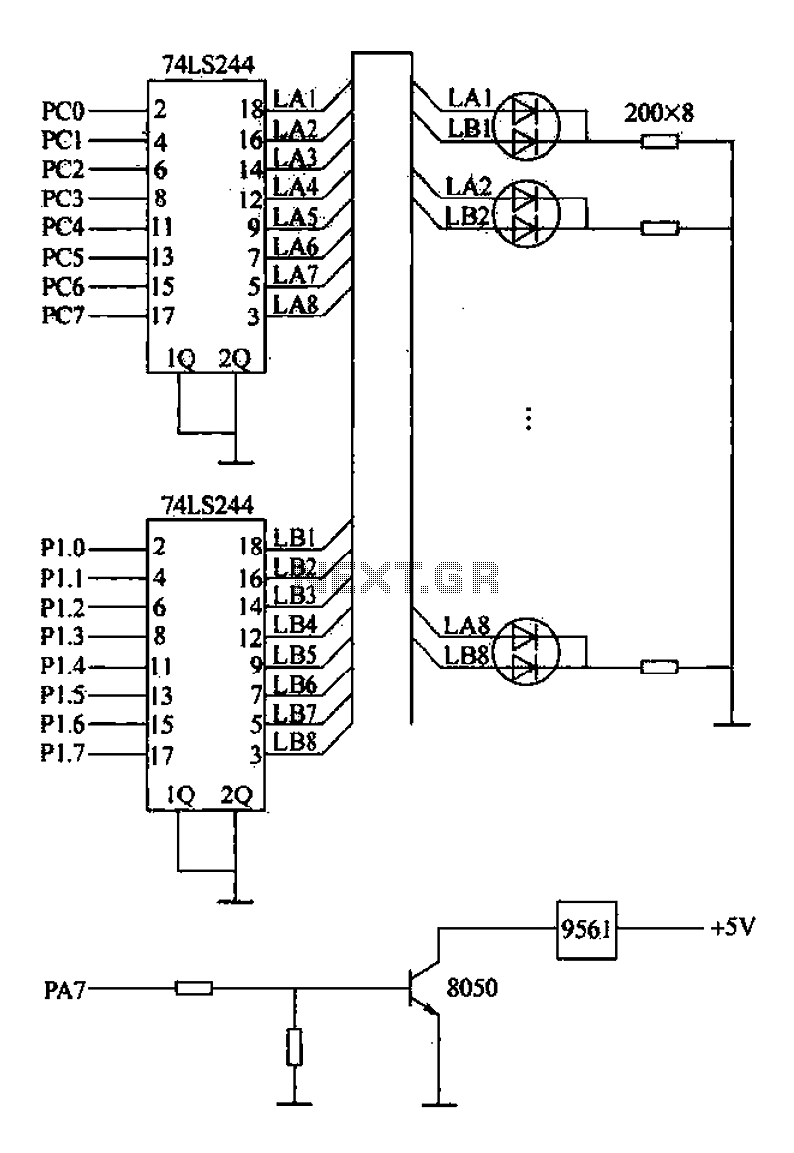
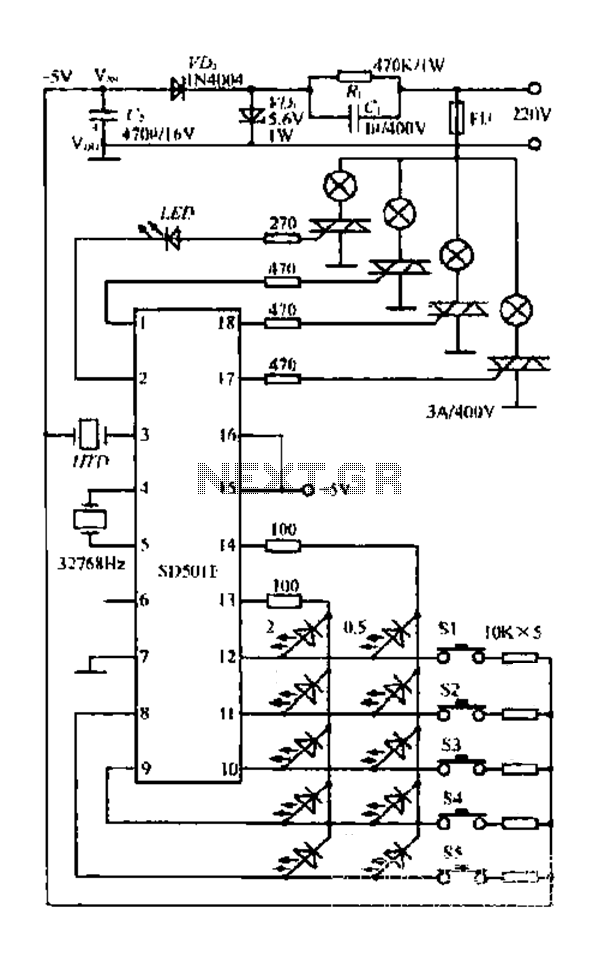
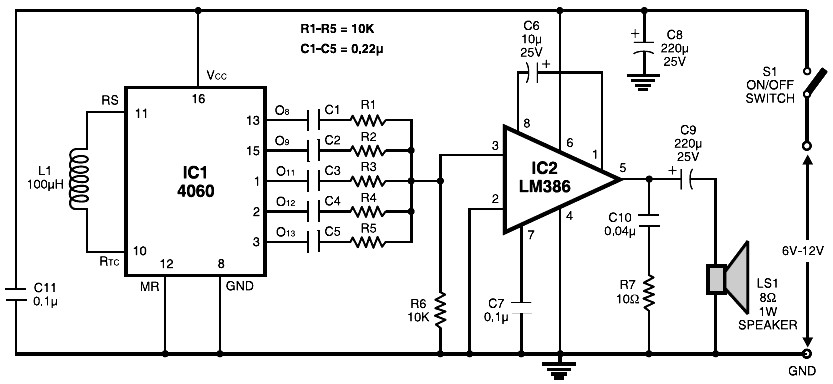
Long distance infrared transmitter circuit diagram
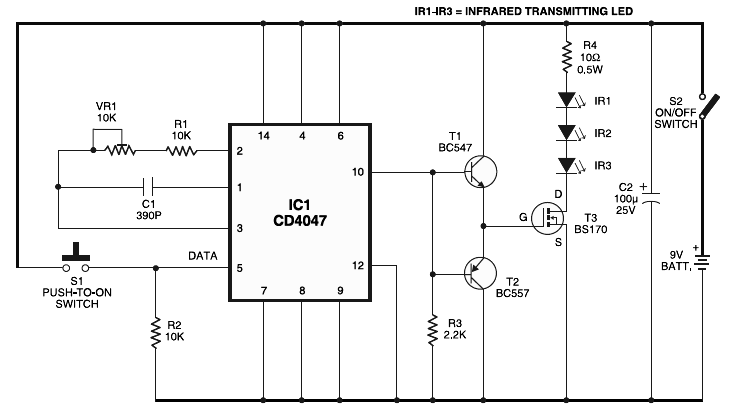
Long-distance infrared transmitter circuit diagram. This simple circuit offers a considerable range by utilizing three infrared transmitting LEDs (IR1 through IR3) in series to enhance the radiated power. To further improve directivity and power density, the IR LEDs can be assembled within the reflector of a torch. The long-range infrared transmitter circuit provides additional power for infrared transmission. Most infrared remotes operate reliably within a range of 5 meters. However, the circuit complexity increases when designing an IR transmitter for effective operation beyond this range, such as extending it to 10 meters. Additionally, a remote control tester circuit is available, which is a straightforward and cost-effective solution for verifying the basic operations of an infrared remote control unit. This tester is based on the infrared receiver module TSOP1738, and it indicates the operation of the remote control through an audible tone. The circuit consists of an infrared transmitter-receiver pair that uses IR beam transmission to switch a toy car on or off. This circuit can be modified to control the direction of the toy car. To operate the toy car, the remote control must be held within range. Another circuit provides an output indicator for the temperature surrounding the circuit. This indicator consists of two LEDs (D1 and D2) that indicate temperatures above and below 80 degrees Celsius. The well-known IC LM35 is used as the temperature sensor in this circuit. Furthermore, a simple battery level indicator circuit is presented. Typically, mobile phones display battery levels in dot or bar styles for easy recognition. The circuit provided helps to indicate the battery level of an instrument.
The long-distance infrared transmitter circuit is designed to achieve an extended operational range by employing three infrared LEDs in series. This configuration not only amplifies the output power but also enhances the overall efficiency of the infrared transmission. The incorporation of a reflector, such as that found in a flashlight, allows for a more focused beam of infrared light, which is essential for long-distance applications, as it minimizes dispersion and maximizes the intensity of the emitted infrared signal.
In practical applications, the circuit can be utilized for remote controlling devices over significant distances, making it suitable for various remote control systems. The increase in complexity for achieving ranges greater than 5 meters is primarily due to the need for more robust components and careful circuit design to handle the increased power demands and maintain signal integrity.
The remote control tester circuit, based on the TSOP1738 infrared receiver module, serves as an essential tool for hobbyists and engineers alike. It provides a simple means to verify the functionality of infrared remote controls without requiring complex setups. The audible tone emitted by the tester upon receiving an IR signal acts as a clear indicator of successful communication, making it an invaluable resource for troubleshooting and testing.
The toy car control circuit exemplifies the practical application of infrared technology in consumer electronics. By utilizing the infrared transmitter-receiver pair, users can easily control the movement of the toy car, showcasing the versatility of infrared communication. The ability to modify the circuit for directional control adds an additional layer of functionality, allowing for a more interactive experience.
Temperature monitoring is another significant application of infrared technology, as demonstrated by the circuit featuring the LM35 temperature sensor. The dual LED indicator provides a straightforward visual representation of temperature thresholds, allowing users to monitor conditions effectively. This simple yet effective design illustrates the potential of infrared technology in creating practical solutions for everyday challenges.
Lastly, the battery level indicator circuit offers a visual method for users to assess battery status, which is particularly useful in portable devices. By employing a straightforward design, this circuit enables users to quickly gauge the remaining charge, promoting efficient usage and timely recharging of devices. Overall, these circuits showcase the diverse applications of infrared technology in electronics, highlighting its importance in modern electronic design.Long distance infrared transmitter circuit diagram. Here is a simple circuit that will give you a pretty long range. It uses three infrared transmitting LEDs (IR1 through IR3) in series to increase the radiated power. Further, to increase the directivity and so also the power density, you may assemble the IR LEDs inside the reflector of a torch. H ere the long range/distance Infrared transmitter circuit, give you extra power for your Infrared transmitter. The majority of the IR remotes do the job reliably within a range of 5 metres. The circuit complexity increases in case you design the IR transmitter for good operation more than a extended distance, for example, 10 metres.
To. Here is the remote control tester circuit. This circuit is really a simple and easy tester for verifying the basic operations of an infrared remote control unit. It is low-cost and very easy to construct. The tester is designed around infrared receiver module TSOP1738. Operation of the remote control is identified by a tone from. The circuit, consisting of an infrared transmitter-receiver pair, utilizes IR beam transmission to switch the toy car on` or off`, yeah.
it will be only switching on and switching off, you may modify this circuit to make the toy car to turn left or right. To operate the toy car, you have to hold the. This circuit is a circuit which will provide output indicator of the temperature around the circuit. The indicator is just 2 pieces LEDs (D1 and D2) which indicates the heat of above 80 degrees Celsius and below 80 degrees Celsius.
A well-known IC LM35 is chosen to be the temperature sensor in this circuit. Output. Here the circuit diagram of simple and easy made battery level indicator. In general, in mobile phones, the battery levels is displayed in dot or bar style. This helps you to effortlessly acknowledge the battery level. On this page we provide a circuit that helps you to recognize the battery level of a instrument from. 🔗 External reference
The long-distance infrared transmitter circuit is designed to achieve an extended operational range by employing three infrared LEDs in series. This configuration not only amplifies the output power but also enhances the overall efficiency of the infrared transmission. The incorporation of a reflector, such as that found in a flashlight, allows for a more focused beam of infrared light, which is essential for long-distance applications, as it minimizes dispersion and maximizes the intensity of the emitted infrared signal.
In practical applications, the circuit can be utilized for remote controlling devices over significant distances, making it suitable for various remote control systems. The increase in complexity for achieving ranges greater than 5 meters is primarily due to the need for more robust components and careful circuit design to handle the increased power demands and maintain signal integrity.
The remote control tester circuit, based on the TSOP1738 infrared receiver module, serves as an essential tool for hobbyists and engineers alike. It provides a simple means to verify the functionality of infrared remote controls without requiring complex setups. The audible tone emitted by the tester upon receiving an IR signal acts as a clear indicator of successful communication, making it an invaluable resource for troubleshooting and testing.
The toy car control circuit exemplifies the practical application of infrared technology in consumer electronics. By utilizing the infrared transmitter-receiver pair, users can easily control the movement of the toy car, showcasing the versatility of infrared communication. The ability to modify the circuit for directional control adds an additional layer of functionality, allowing for a more interactive experience.
Temperature monitoring is another significant application of infrared technology, as demonstrated by the circuit featuring the LM35 temperature sensor. The dual LED indicator provides a straightforward visual representation of temperature thresholds, allowing users to monitor conditions effectively. This simple yet effective design illustrates the potential of infrared technology in creating practical solutions for everyday challenges.
Lastly, the battery level indicator circuit offers a visual method for users to assess battery status, which is particularly useful in portable devices. By employing a straightforward design, this circuit enables users to quickly gauge the remaining charge, promoting efficient usage and timely recharging of devices. Overall, these circuits showcase the diverse applications of infrared technology in electronics, highlighting its importance in modern electronic design.Long distance infrared transmitter circuit diagram. Here is a simple circuit that will give you a pretty long range. It uses three infrared transmitting LEDs (IR1 through IR3) in series to increase the radiated power. Further, to increase the directivity and so also the power density, you may assemble the IR LEDs inside the reflector of a torch. H ere the long range/distance Infrared transmitter circuit, give you extra power for your Infrared transmitter. The majority of the IR remotes do the job reliably within a range of 5 metres. The circuit complexity increases in case you design the IR transmitter for good operation more than a extended distance, for example, 10 metres.
To. Here is the remote control tester circuit. This circuit is really a simple and easy tester for verifying the basic operations of an infrared remote control unit. It is low-cost and very easy to construct. The tester is designed around infrared receiver module TSOP1738. Operation of the remote control is identified by a tone from. The circuit, consisting of an infrared transmitter-receiver pair, utilizes IR beam transmission to switch the toy car on` or off`, yeah.
it will be only switching on and switching off, you may modify this circuit to make the toy car to turn left or right. To operate the toy car, you have to hold the. This circuit is a circuit which will provide output indicator of the temperature around the circuit. The indicator is just 2 pieces LEDs (D1 and D2) which indicates the heat of above 80 degrees Celsius and below 80 degrees Celsius.
A well-known IC LM35 is chosen to be the temperature sensor in this circuit. Output. Here the circuit diagram of simple and easy made battery level indicator. In general, in mobile phones, the battery levels is displayed in dot or bar style. This helps you to effortlessly acknowledge the battery level. On this page we provide a circuit that helps you to recognize the battery level of a instrument from. 🔗 External reference