Loudspeaker Protector Circuit
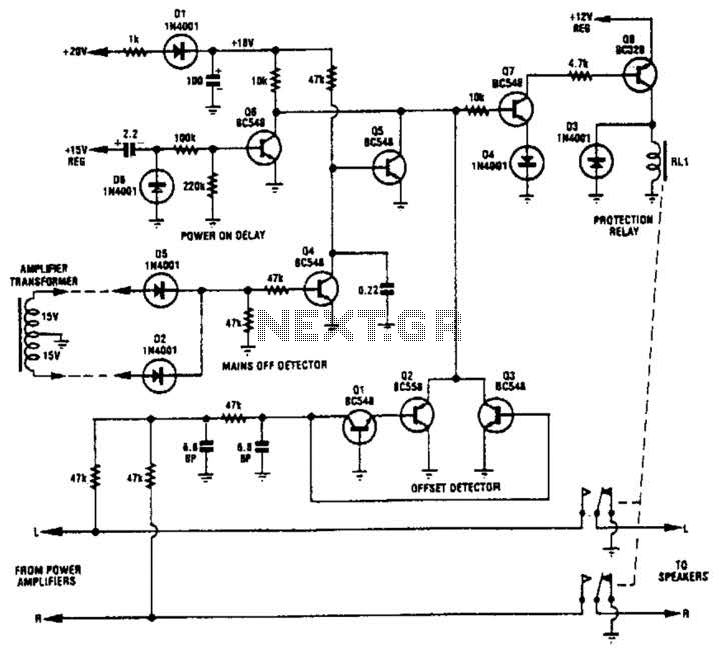
Transistors Q1, Q2, and Q3 monitor the two outputs of the stereo amplifier. If the offsets exceed 2 V, Q7 is turned off, which in turn deactivates Q8 and the normally on relay. Diodes D2 and D5, along with Q4, serve as a mains voltage monitor. When the AC input voltage drops, such as when the amplifier is powered off, Q4 deactivates and Q5 activates. This sequence turns off Q7, Q8, and the relay. Consequently, the loudspeakers are disconnected immediately after the amplifier is turned off.
The circuit employs transistors Q1, Q2, and Q3 for monitoring the output offsets of the stereo amplifier, ensuring that any deviation beyond 2 V triggers a protective response. When the output offsets exceed the specified threshold, Q7 is deactivated. This action leads to the deactivation of Q8, which is connected to a relay that is normally energized. The relay's function is to disconnect the loudspeakers from the amplifier to prevent potential damage from excessive voltage offsets.
Diodes D2 and D5, in conjunction with Q4, act as a mains voltage monitoring system. Their role is critical in detecting the presence of AC voltage. When the amplifier is powered down, the AC input voltage drops, causing Q4 to turn off. This transition activates Q5, which is designed to maintain the protective state by turning off Q7 and Q8, thereby ensuring the relay is also deactivated.
The design emphasizes safety and protection for the loudspeakers, ensuring they are disconnected promptly in the event of power loss or significant output offset. This circuit configuration is vital in maintaining the integrity of audio equipment and preventing damage during operation and shutdown scenarios. Transistors Ql, Q2, and Q3 monitor the two outputs of the stereo amplifier. If the offsets exceed 2 V, Q7 is turned off, which turns off Q8 and the normally on relay. Diodes D2 and D5, together with Q4, provide a mains voltage monitor. As soon as the ac input voltage disappears, as when the amplifier is turned off, Q4 turns off arid Q5 turns on. This turns off Q7, Q8, and the relay. Hence, the loudspeakers axe disconnected immediately after the amplifier is turned off.
The circuit employs transistors Q1, Q2, and Q3 for monitoring the output offsets of the stereo amplifier, ensuring that any deviation beyond 2 V triggers a protective response. When the output offsets exceed the specified threshold, Q7 is deactivated. This action leads to the deactivation of Q8, which is connected to a relay that is normally energized. The relay's function is to disconnect the loudspeakers from the amplifier to prevent potential damage from excessive voltage offsets.
Diodes D2 and D5, in conjunction with Q4, act as a mains voltage monitoring system. Their role is critical in detecting the presence of AC voltage. When the amplifier is powered down, the AC input voltage drops, causing Q4 to turn off. This transition activates Q5, which is designed to maintain the protective state by turning off Q7 and Q8, thereby ensuring the relay is also deactivated.
The design emphasizes safety and protection for the loudspeakers, ensuring they are disconnected promptly in the event of power loss or significant output offset. This circuit configuration is vital in maintaining the integrity of audio equipment and preventing damage during operation and shutdown scenarios. Transistors Ql, Q2, and Q3 monitor the two outputs of the stereo amplifier. If the offsets exceed 2 V, Q7 is turned off, which turns off Q8 and the normally on relay. Diodes D2 and D5, together with Q4, provide a mains voltage monitor. As soon as the ac input voltage disappears, as when the amplifier is turned off, Q4 turns off arid Q5 turns on. This turns off Q7, Q8, and the relay. Hence, the loudspeakers axe disconnected immediately after the amplifier is turned off.