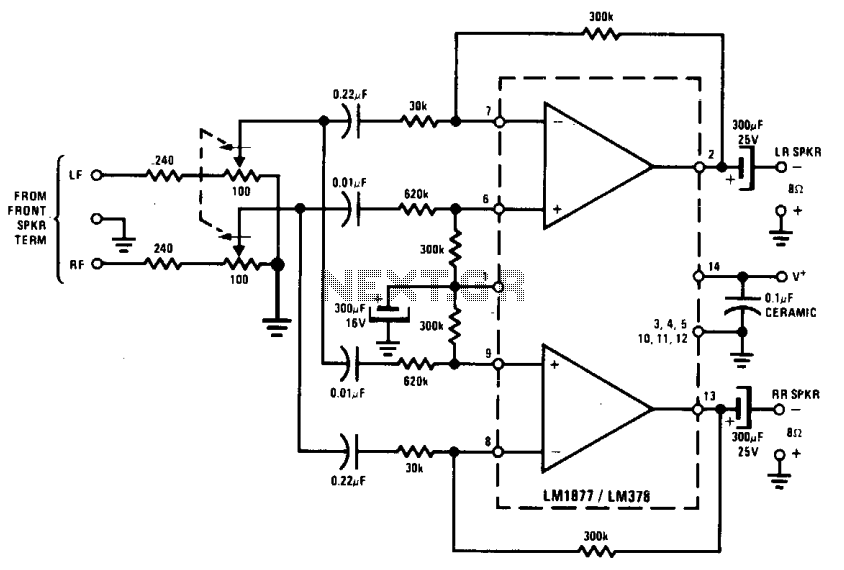
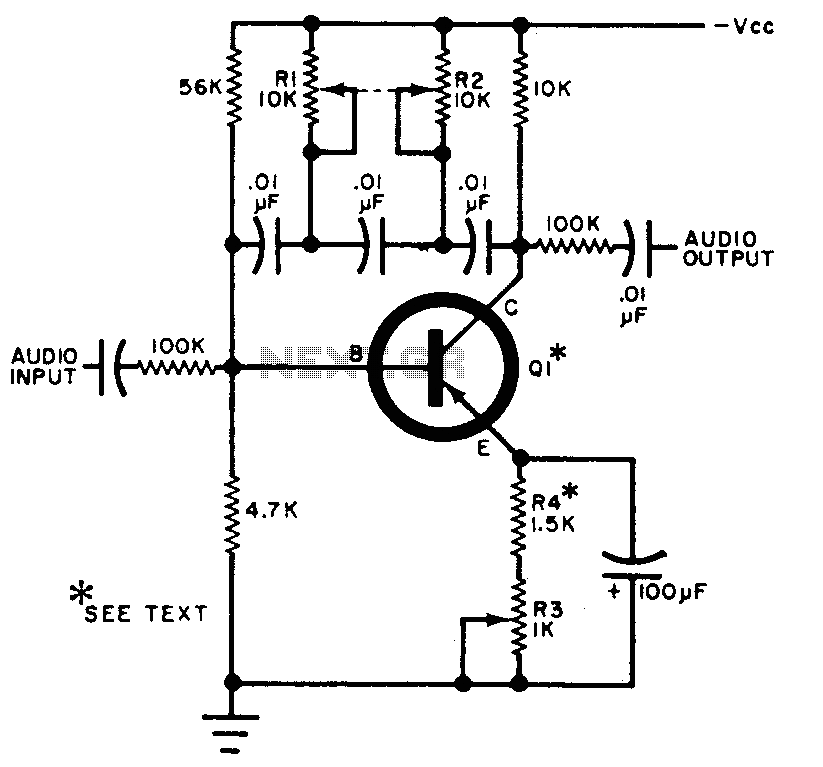
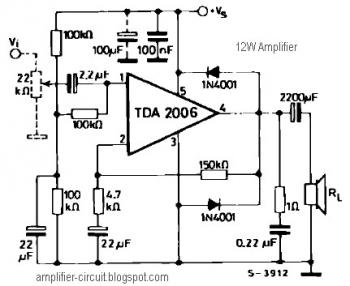
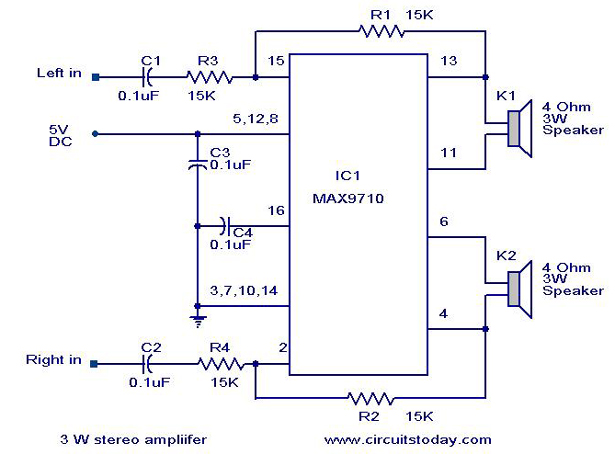
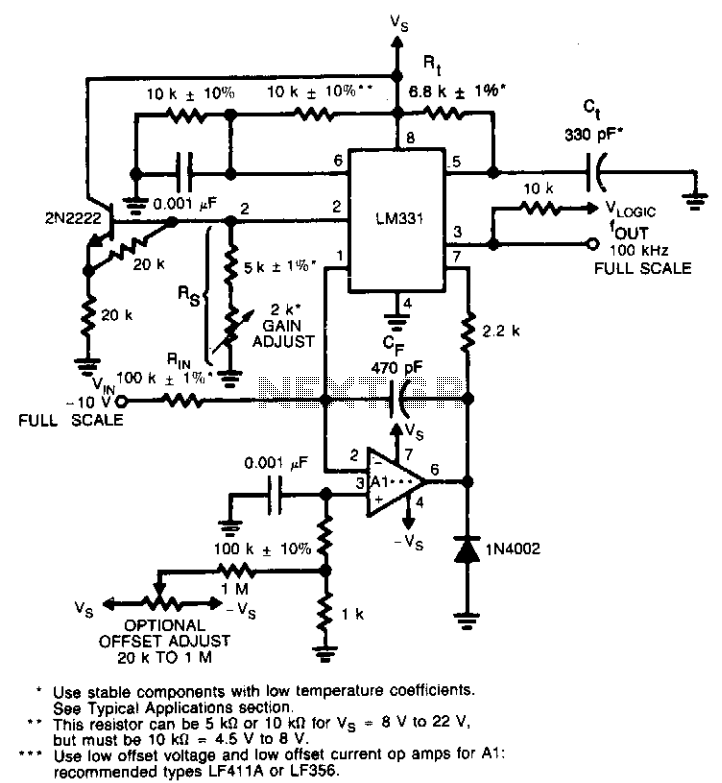
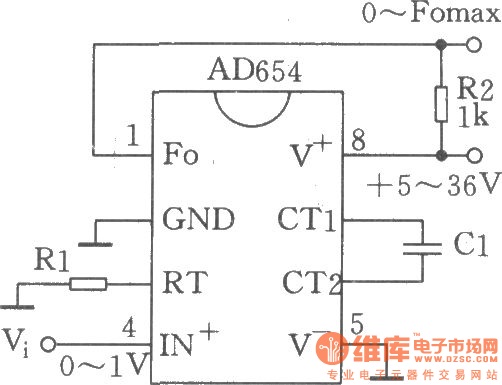
low frequency amplifier

Gain increases by decades as the binary input decreases from 1,1 to 0,0. Minimum gain is 1 and maximum gain is 1000. More: Since the switch is static in this type of amplifier, the power dissipation of the switch will be less than a tenth of a milliwatt.
This circuit operates on a binary input system where the gain of the amplifier varies logarithmically. As the binary input transitions from the maximum state (1,1) to the minimum state (0,0), the gain experiences a significant increase, spanning several decades. The gain is calibrated to range from a minimum value of 1 to a maximum value of 1000, allowing for substantial amplification of the input signal.
The design incorporates a static switch mechanism, which is crucial for minimizing power dissipation within the circuit. The static nature of the switch ensures that the power loss remains extremely low, quantified at less than 0.1 milliwatt. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in applications where energy efficiency is paramount, as it allows for prolonged operation without substantial heat generation or power drain.
The amplifier's architecture may include operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in a feedback loop to achieve the desired gain characteristics. The binary inputs can be processed through a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) if necessary, to facilitate smooth transitions between gain states. Additionally, careful selection of resistors and capacitors in the feedback network can help stabilize the gain and reduce noise.
In summary, this amplifier circuit is designed for efficient gain control based on binary input, with a focus on low power dissipation and high performance across a wide range of gain values.Gain increases by decades as the binary input decreases from 1,1 to 0,0. Minimum gain is 1 and maximum gain is 1000. Since the switch is static in this type of amplifier the power dissipation of the switch will be less than a tenth of a milliwatt.
This circuit operates on a binary input system where the gain of the amplifier varies logarithmically. As the binary input transitions from the maximum state (1,1) to the minimum state (0,0), the gain experiences a significant increase, spanning several decades. The gain is calibrated to range from a minimum value of 1 to a maximum value of 1000, allowing for substantial amplification of the input signal.
The design incorporates a static switch mechanism, which is crucial for minimizing power dissipation within the circuit. The static nature of the switch ensures that the power loss remains extremely low, quantified at less than 0.1 milliwatt. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in applications where energy efficiency is paramount, as it allows for prolonged operation without substantial heat generation or power drain.
The amplifier's architecture may include operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in a feedback loop to achieve the desired gain characteristics. The binary inputs can be processed through a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) if necessary, to facilitate smooth transitions between gain states. Additionally, careful selection of resistors and capacitors in the feedback network can help stabilize the gain and reduce noise.
In summary, this amplifier circuit is designed for efficient gain control based on binary input, with a focus on low power dissipation and high performance across a wide range of gain values.Gain increases by decades as the binary input decreases from 1,1 to 0,0. Minimum gain is 1 and maximum gain is 1000. Since the switch is static in this type of amplifier the power dissipation of the switch will be less than a tenth of a milliwatt.