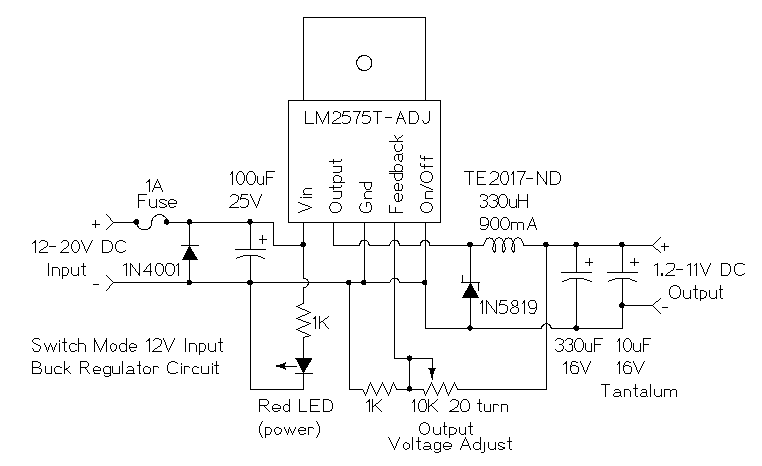
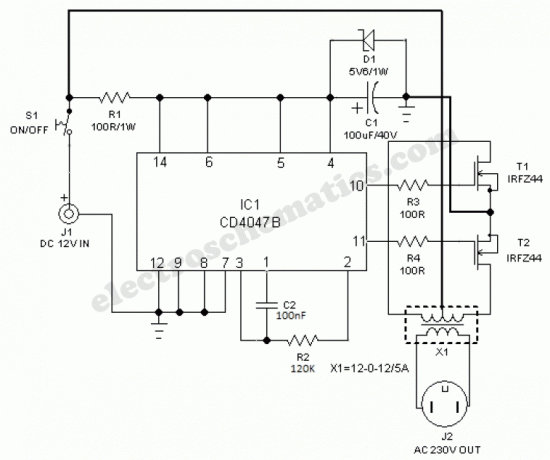
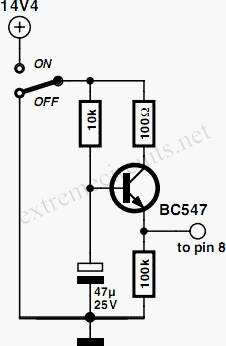
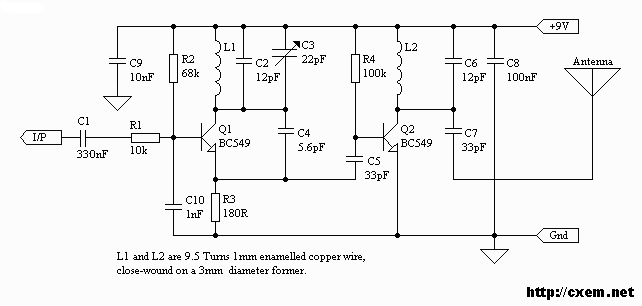
Low power regulator reference
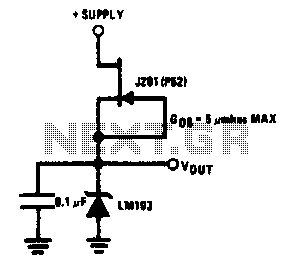
This simple reference circuit provides a stable voltage reference that is nearly free from supply voltage noise. Typical power supply rejection exceeds 100 dB.
The described voltage reference circuit is designed to deliver a consistent output voltage while minimizing the influence of fluctuations in the supply voltage, a characteristic referred to as power supply rejection ratio (PSRR). A PSRR exceeding 100 dB indicates that the circuit is highly effective at filtering out noise and variations from the power supply, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable under varying load conditions.
The circuit typically employs a bandgap reference or a zener diode to establish a stable reference voltage. The use of op-amps can further enhance the performance by buffering the output, providing additional isolation from load variations. Key components may include resistors for setting gain, capacitors for filtering, and possibly a voltage regulator to maintain output stability.
In practical applications, this type of voltage reference circuit is crucial for precision analog circuits, such as analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) and digital-to-analog converters (DACs), where stable reference voltages are necessary for accurate signal processing. The high PSRR allows the circuit to function effectively in environments with significant electrical noise, making it suitable for use in industrial and consumer electronics where power supply variations are common.
Design considerations include the selection of components that can withstand the expected range of operating conditions, as well as thermal stability to ensure that the reference voltage does not drift with temperature changes. Overall, this voltage reference circuit is an essential building block in the design of reliable electronic systems.This simple reference circuit provides a stable voltage reference almost totally free of supply voltage hash Typical power supply rejection exceeds 100 dB.
The described voltage reference circuit is designed to deliver a consistent output voltage while minimizing the influence of fluctuations in the supply voltage, a characteristic referred to as power supply rejection ratio (PSRR). A PSRR exceeding 100 dB indicates that the circuit is highly effective at filtering out noise and variations from the power supply, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable under varying load conditions.
The circuit typically employs a bandgap reference or a zener diode to establish a stable reference voltage. The use of op-amps can further enhance the performance by buffering the output, providing additional isolation from load variations. Key components may include resistors for setting gain, capacitors for filtering, and possibly a voltage regulator to maintain output stability.
In practical applications, this type of voltage reference circuit is crucial for precision analog circuits, such as analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) and digital-to-analog converters (DACs), where stable reference voltages are necessary for accurate signal processing. The high PSRR allows the circuit to function effectively in environments with significant electrical noise, making it suitable for use in industrial and consumer electronics where power supply variations are common.
Design considerations include the selection of components that can withstand the expected range of operating conditions, as well as thermal stability to ensure that the reference voltage does not drift with temperature changes. Overall, this voltage reference circuit is an essential building block in the design of reliable electronic systems.This simple reference circuit provides a stable voltage reference almost totally free of supply voltage hash Typical power supply rejection exceeds 100 dB.