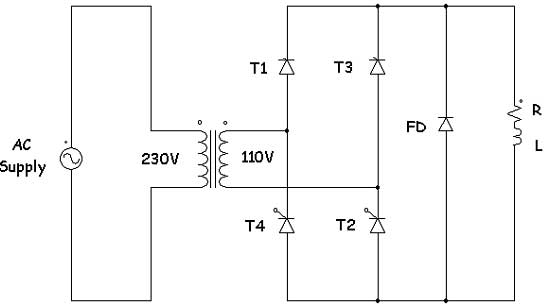
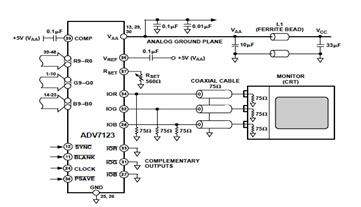
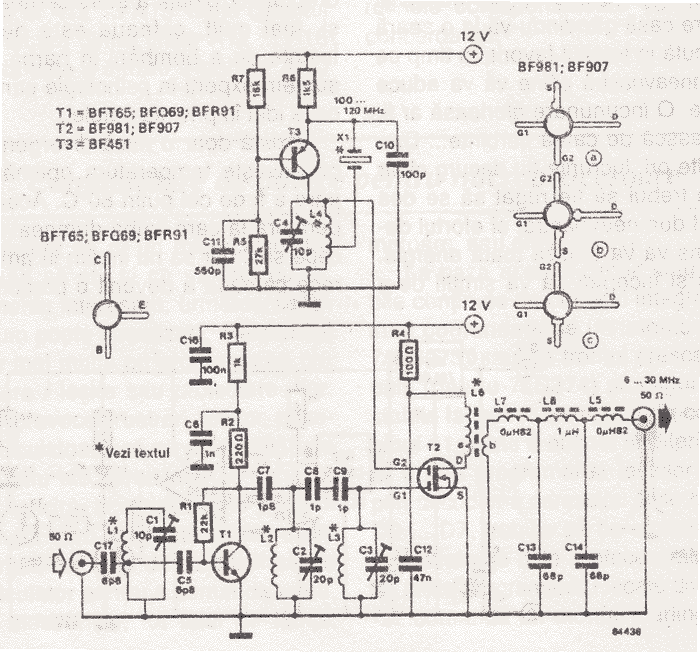
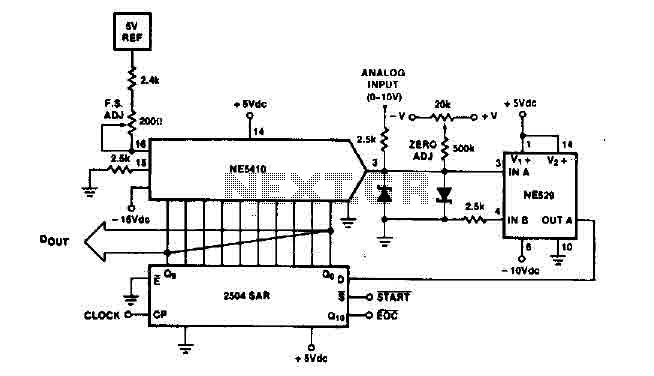
LTC1045 TTL RS-232 Converter
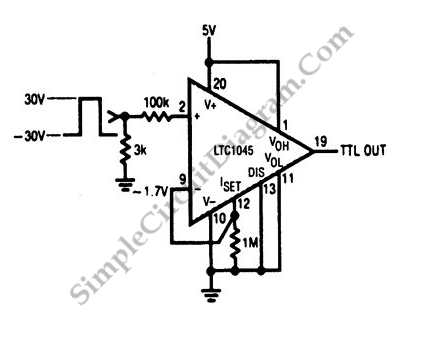
A simple method to construct a battery-powered RS-232 receiver circuit is illustrated in the schematic diagram below. This circuit converts RS-232 levels to TTL levels.
The RS-232 standard is widely used for serial communication, and it operates at voltage levels that are not directly compatible with TTL logic levels used in most digital circuits. The proposed circuit effectively bridges this gap by converting the higher voltage RS-232 signals (typically ranging from -15V to +15V) to TTL levels (0V to +5V).
The circuit typically includes a level shifter, which can be implemented using a combination of transistors or dedicated ICs designed for this purpose, such as the MAX232. The MAX232 is a popular choice as it contains built-in charge pumps that generate the required voltage levels for RS-232 communication while providing the necessary signal inversion.
The circuit layout would include an RS-232 connector, which connects to the serial data source, and a TTL output that interfaces with microcontrollers or other digital logic devices. Proper decoupling capacitors should be included close to the power supply pins of the level shifter to ensure stable operation. Additionally, the circuit may feature protection diodes to safeguard against voltage spikes or incorrect connections.
Powering the circuit from batteries allows for portable applications, making it ideal for remote data acquisition systems or mobile devices that require serial communication without being tethered to a power outlet. The design should also consider power efficiency to prolong battery life, which can involve using low-power components and optimizing the circuit layout.
In summary, this simple battery-powered RS-232 receiver circuit is an essential tool for interfacing RS-232 communication with TTL logic, enabling a wide range of applications in electronics and embedded systems.A simple way to build a battery-powered RS-232 receiver circuit is shown on the following schematic diagram. This circuit convert RS232 level to TTL level.. 🔗 External reference
The RS-232 standard is widely used for serial communication, and it operates at voltage levels that are not directly compatible with TTL logic levels used in most digital circuits. The proposed circuit effectively bridges this gap by converting the higher voltage RS-232 signals (typically ranging from -15V to +15V) to TTL levels (0V to +5V).
The circuit typically includes a level shifter, which can be implemented using a combination of transistors or dedicated ICs designed for this purpose, such as the MAX232. The MAX232 is a popular choice as it contains built-in charge pumps that generate the required voltage levels for RS-232 communication while providing the necessary signal inversion.
The circuit layout would include an RS-232 connector, which connects to the serial data source, and a TTL output that interfaces with microcontrollers or other digital logic devices. Proper decoupling capacitors should be included close to the power supply pins of the level shifter to ensure stable operation. Additionally, the circuit may feature protection diodes to safeguard against voltage spikes or incorrect connections.
Powering the circuit from batteries allows for portable applications, making it ideal for remote data acquisition systems or mobile devices that require serial communication without being tethered to a power outlet. The design should also consider power efficiency to prolong battery life, which can involve using low-power components and optimizing the circuit layout.
In summary, this simple battery-powered RS-232 receiver circuit is an essential tool for interfacing RS-232 communication with TTL logic, enabling a wide range of applications in electronics and embedded systems.A simple way to build a battery-powered RS-232 receiver circuit is shown on the following schematic diagram. This circuit convert RS232 level to TTL level.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713