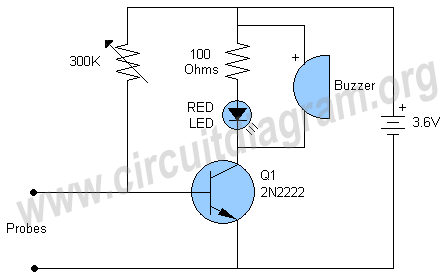
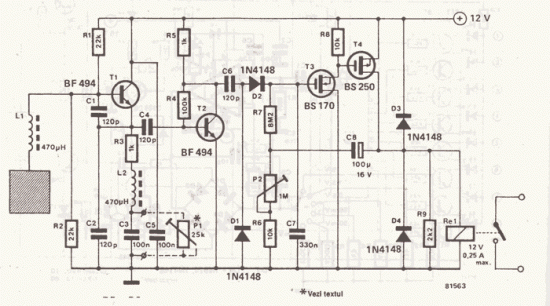
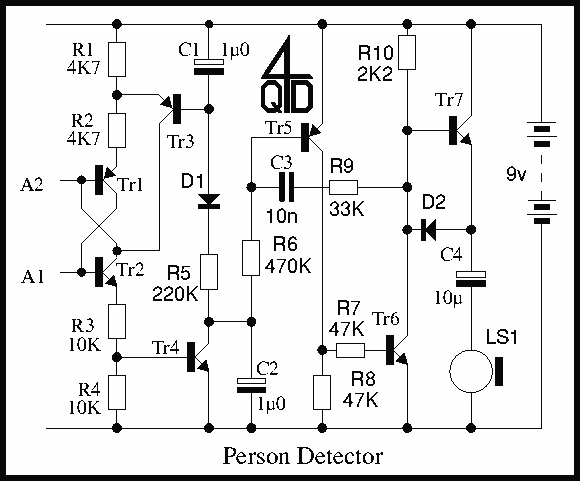
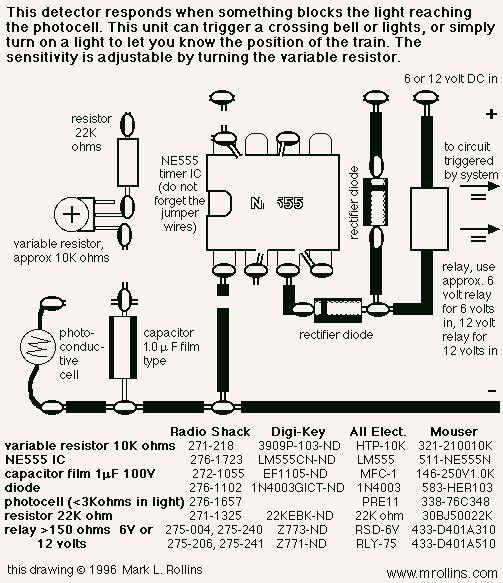
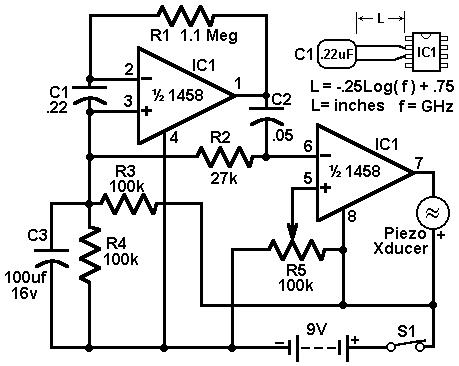
Metal Detector
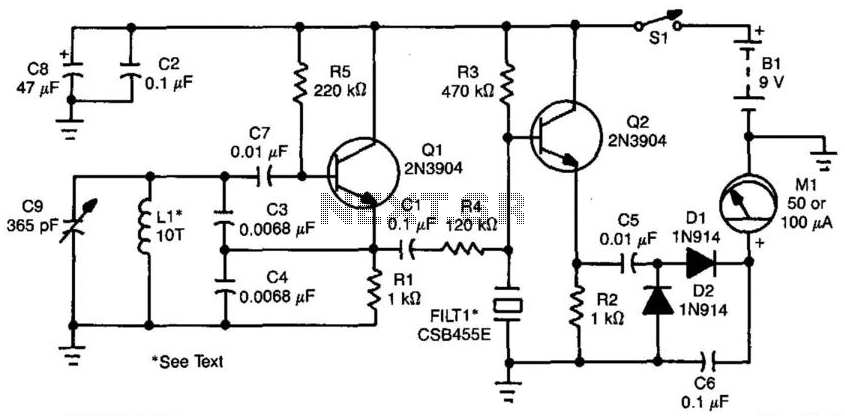
An oscillator operating at 455 kHz is utilized in the metal detector circuit to provide an indication on meter Ml. When the oscillator frequency varies due to the presence of metal within the field of inductor Ll, this variation manifests as a change in frequency, leading to a corresponding increase or decrease in the meter reading. The ceramic filter FILT1 offers a selective bandpass that facilitates this response. Inductor Ll can be constructed as a 4-inch diameter coil wound on an appropriate plastic form, requiring approximately 10 turns of #26 wire. A frequency counter should be employed to fine-tune inductor Ll and confirm that oscillator Ql is functioning at or near 455 kHz.
The metal detector circuit primarily consists of an oscillator, a frequency-sensitive inductor, and a ceramic filter, all of which work in conjunction to detect metallic objects. The oscillator generates a stable frequency signal, which is critical for the operation of the circuit. The frequency of this oscillator is set to 455 kHz, a common frequency used in metal detection applications due to its effective balance between sensitivity and noise rejection.
Inductor Ll is a crucial component of the circuit, as it creates a magnetic field that responds to nearby metallic objects. The design of this inductor, specifically its dimensions and the number of turns, greatly influences the circuit's performance. A 4-inch diameter coil with approximately 10 turns of #26 wire is recommended to achieve optimal inductance and sensitivity. The choice of wire gauge is important, as it affects the resistance and quality factor of the coil, ultimately impacting the circuit's efficiency.
The ceramic filter FILT1 serves to isolate the desired frequency range, allowing the circuit to focus on the frequency changes induced by the presence of metal. This selective bandpass filter enhances the circuit's ability to discern between the signal generated by the oscillator and any extraneous noise, ensuring that only relevant frequency variations are registered on the meter Ml.
To ensure proper operation, a frequency counter is employed to measure the oscillation frequency and to facilitate adjustments to inductor Ll. This verification process is essential, as it confirms that the oscillator is functioning within the intended frequency range, thus ensuring reliable detection of metallic objects. Proper calibration of the circuit is vital for achieving maximum sensitivity and accuracy in detecting metals, making the frequency counter an indispensable tool in the setup and maintenance of the metal detector circuit. Using an oscillator running at 455 kHz, the metal-detector circuit produces an indication on the meter Ml. When the oscillat or frequency changes because of metal in the field of Ll, the change will show as an increase or decrease in frequency, which produces a charge in the meter reading. The ceramic filter FILT1 produces a selective bandpass that yields this effect. Ll can be a 4" diameter coil wound on a suitable plastic form. About 10 turns of #26 wire are required. Use a frequency counter to adjust Ll and verify that Ql is operating on or near 455 kHz.
The metal detector circuit primarily consists of an oscillator, a frequency-sensitive inductor, and a ceramic filter, all of which work in conjunction to detect metallic objects. The oscillator generates a stable frequency signal, which is critical for the operation of the circuit. The frequency of this oscillator is set to 455 kHz, a common frequency used in metal detection applications due to its effective balance between sensitivity and noise rejection.
Inductor Ll is a crucial component of the circuit, as it creates a magnetic field that responds to nearby metallic objects. The design of this inductor, specifically its dimensions and the number of turns, greatly influences the circuit's performance. A 4-inch diameter coil with approximately 10 turns of #26 wire is recommended to achieve optimal inductance and sensitivity. The choice of wire gauge is important, as it affects the resistance and quality factor of the coil, ultimately impacting the circuit's efficiency.
The ceramic filter FILT1 serves to isolate the desired frequency range, allowing the circuit to focus on the frequency changes induced by the presence of metal. This selective bandpass filter enhances the circuit's ability to discern between the signal generated by the oscillator and any extraneous noise, ensuring that only relevant frequency variations are registered on the meter Ml.
To ensure proper operation, a frequency counter is employed to measure the oscillation frequency and to facilitate adjustments to inductor Ll. This verification process is essential, as it confirms that the oscillator is functioning within the intended frequency range, thus ensuring reliable detection of metallic objects. Proper calibration of the circuit is vital for achieving maximum sensitivity and accuracy in detecting metals, making the frequency counter an indispensable tool in the setup and maintenance of the metal detector circuit. Using an oscillator running at 455 kHz, the metal-detector circuit produces an indication on the meter Ml. When the oscillat or frequency changes because of metal in the field of Ll, the change will show as an increase or decrease in frequency, which produces a charge in the meter reading. The ceramic filter FILT1 produces a selective bandpass that yields this effect. Ll can be a 4" diameter coil wound on a suitable plastic form. About 10 turns of #26 wire are required. Use a frequency counter to adjust Ll and verify that Ql is operating on or near 455 kHz.