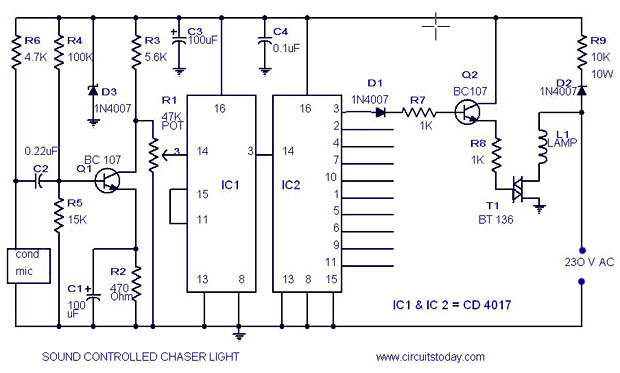
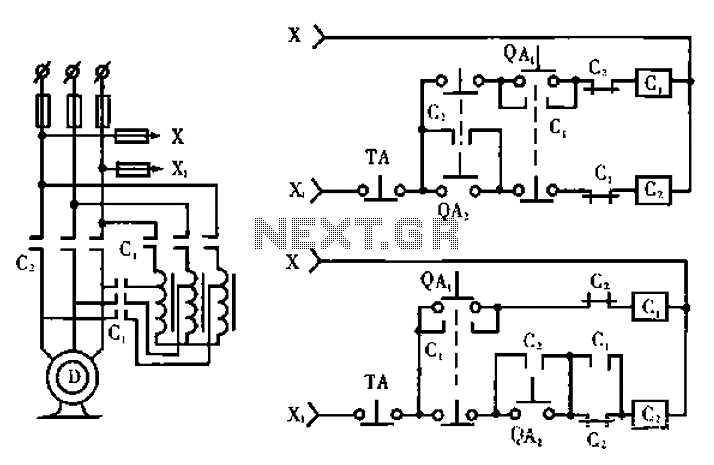
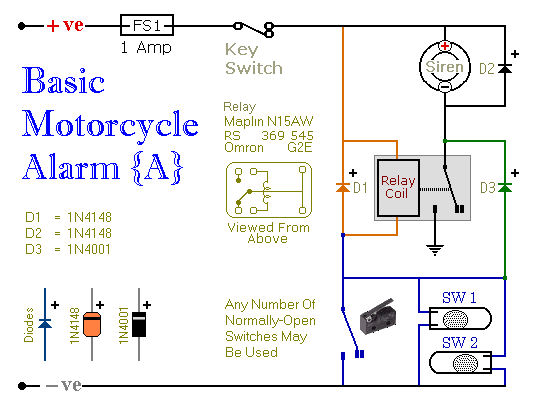
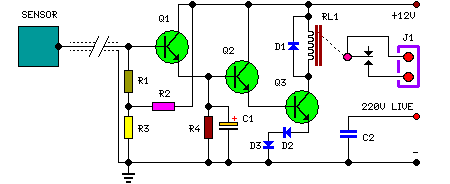
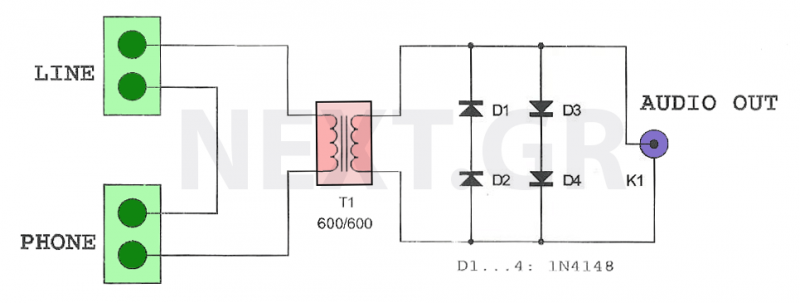
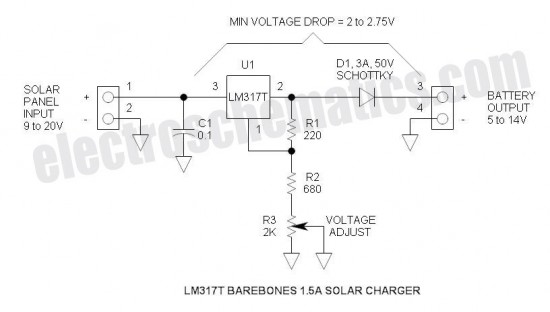
Metal halide electronic ballast constant power control circuit diagram
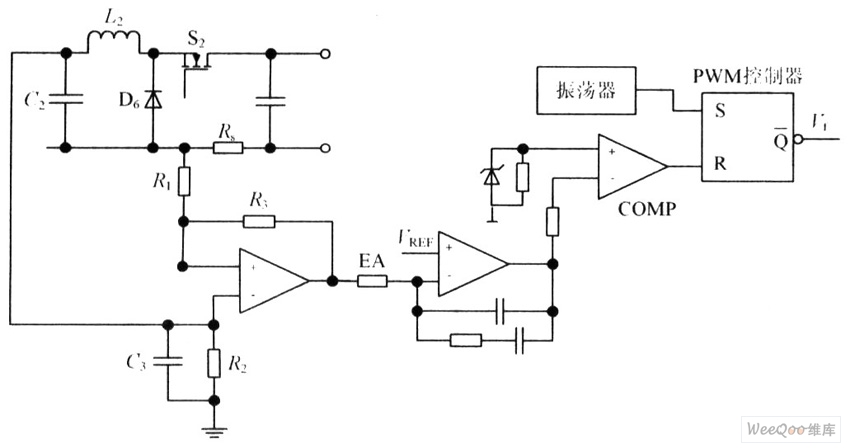
The circuit is capable of enhancing the system power factor to a value exceeding 0.99. It effectively reduces the waveform distortion of the input supply current, ensuring compliance with GB15144 standards, with a distortion index lower than level L. Additionally, it guarantees that the crest factor of the HID lamp current remains below 1.7.
This circuit is designed to optimize the power factor in electrical systems, which is crucial for improving energy efficiency and reducing losses in power distribution. By achieving a power factor greater than 0.99, the circuit minimizes reactive power, thereby enhancing the overall performance of the electrical system.
The circuit incorporates advanced filtering techniques to suppress harmonic distortion in the input supply current. This is achieved through the use of inductors and capacitors configured as passive filters, which effectively attenuate unwanted frequency components. The compliance with GB15144 standards indicates that the circuit meets stringent regulatory requirements for harmonic distortion, promoting better integration with the power grid and reducing potential penalties from utility providers.
Moreover, the circuit is tailored for use with High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lamps, which are known for their high efficiency and brightness. The design ensures that the crest factor of the lamp current, which is the ratio of the peak lamp current to the root mean square (RMS) current, is maintained below 1.7. This is important for the longevity and reliability of the HID lamps, as excessive crest factors can lead to increased thermal stress and reduced operational life.
In summary, this circuit not only enhances the power factor and reduces harmonic distortion but also ensures optimal performance and reliability of HID lighting systems through careful design and compliance with industry standards.The circuit can increase the system power factor ? to the number higher than 0.99, and it can effectively suppress the waveform distortion of the input supply current iin to meet requirements of GB15144 with the distortion index being lower than L level, and it can ensure that the HID lamp current crest factor to be less than 1.7.. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to optimize the power factor in electrical systems, which is crucial for improving energy efficiency and reducing losses in power distribution. By achieving a power factor greater than 0.99, the circuit minimizes reactive power, thereby enhancing the overall performance of the electrical system.
The circuit incorporates advanced filtering techniques to suppress harmonic distortion in the input supply current. This is achieved through the use of inductors and capacitors configured as passive filters, which effectively attenuate unwanted frequency components. The compliance with GB15144 standards indicates that the circuit meets stringent regulatory requirements for harmonic distortion, promoting better integration with the power grid and reducing potential penalties from utility providers.
Moreover, the circuit is tailored for use with High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lamps, which are known for their high efficiency and brightness. The design ensures that the crest factor of the lamp current, which is the ratio of the peak lamp current to the root mean square (RMS) current, is maintained below 1.7. This is important for the longevity and reliability of the HID lamps, as excessive crest factors can lead to increased thermal stress and reduced operational life.
In summary, this circuit not only enhances the power factor and reduces harmonic distortion but also ensures optimal performance and reliability of HID lighting systems through careful design and compliance with industry standards.The circuit can increase the system power factor ? to the number higher than 0.99, and it can effectively suppress the waveform distortion of the input supply current iin to meet requirements of GB15144 with the distortion index being lower than L level, and it can ensure that the HID lamp current crest factor to be less than 1.7.. 🔗 External reference