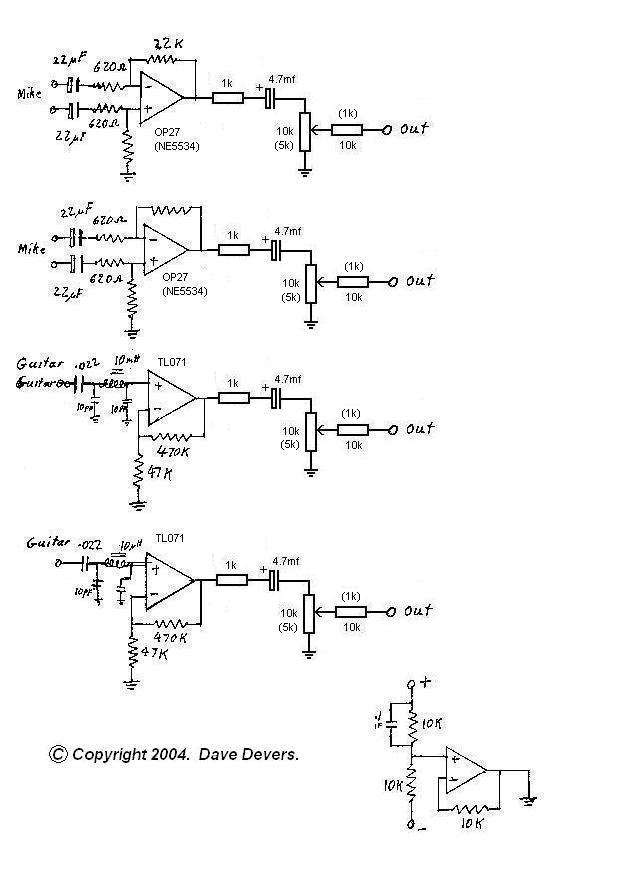
Microphone Preamp Buffer Help

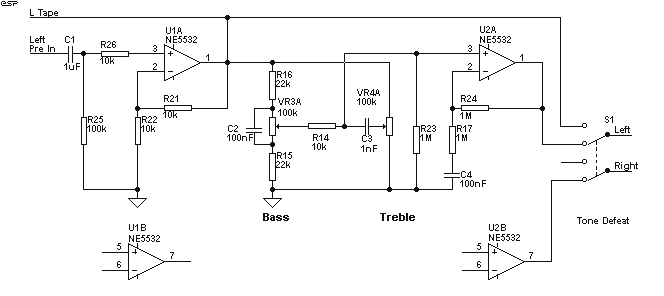
A decision has been made to construct a microphone preamplifier and tone control circuit that was featured on another website. The equalization section is identical to the one used in the...
This microphone preamplifier and tone control circuit is designed to enhance audio signals from microphones, providing both amplification and tonal adjustment capabilities. The circuit typically consists of several key components, including operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, capacitors, and potentiometers.
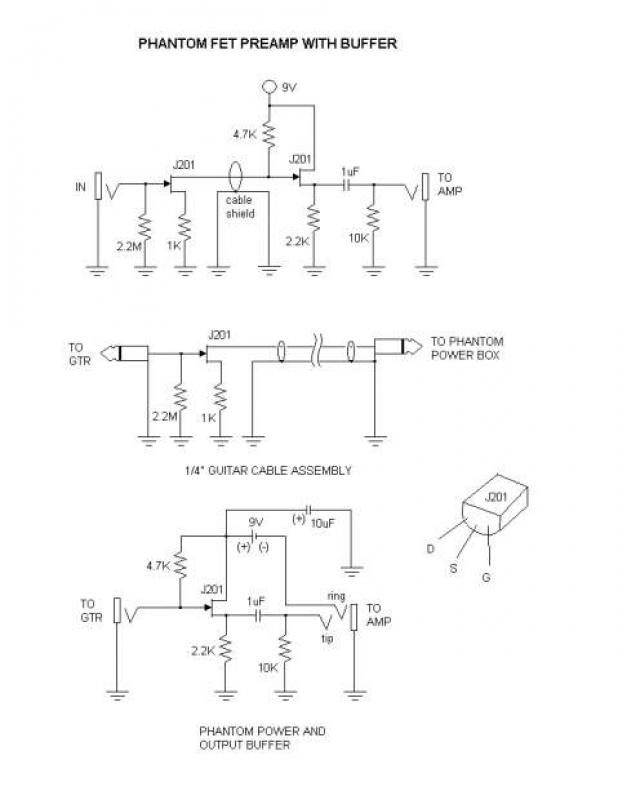
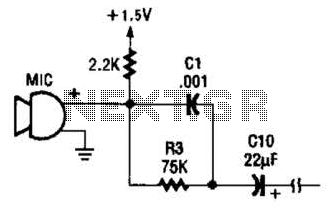
The microphone preamp section serves to boost the low-level audio signals generated by microphones to a more manageable level, suitable for further processing or amplification. This is achieved using a differential amplifier configuration, which helps to minimize noise and enhance signal integrity. The choice of op-amps is crucial, as they must provide low noise and high bandwidth to ensure fidelity in audio reproduction.
The tone control section incorporates active filters that allow for frequency-based adjustments of the audio signal. This section generally includes a combination of high-pass, low-pass, and band-pass filters, which can be adjusted using potentiometers. By varying the resistance in these components, users can modify the bass, midrange, and treble frequencies to tailor the audio output to their preferences.
Power supply considerations are also critical in the design of this circuit. A stable DC power source is required to ensure that the op-amps function correctly without introducing hum or noise into the audio signal. Bypass capacitors may be included to filter out any high-frequency noise from the power supply.
Overall, the successful implementation of this microphone preamp and tone control circuit will result in a versatile audio processing tool that enhances the clarity and quality of sound in various applications, from recording studios to live sound reinforcement. Proper layout and grounding techniques should be employed in the PCB design to further reduce interference and maintain signal integrity.Hi I have decided to build this mic preamp and tone control circuit which was posted on a another site. The Eq section is the same one used in the.. 🔗 External reference
This microphone preamplifier and tone control circuit is designed to enhance audio signals from microphones, providing both amplification and tonal adjustment capabilities. The circuit typically consists of several key components, including operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, capacitors, and potentiometers.
The microphone preamp section serves to boost the low-level audio signals generated by microphones to a more manageable level, suitable for further processing or amplification. This is achieved using a differential amplifier configuration, which helps to minimize noise and enhance signal integrity. The choice of op-amps is crucial, as they must provide low noise and high bandwidth to ensure fidelity in audio reproduction.
The tone control section incorporates active filters that allow for frequency-based adjustments of the audio signal. This section generally includes a combination of high-pass, low-pass, and band-pass filters, which can be adjusted using potentiometers. By varying the resistance in these components, users can modify the bass, midrange, and treble frequencies to tailor the audio output to their preferences.
Power supply considerations are also critical in the design of this circuit. A stable DC power source is required to ensure that the op-amps function correctly without introducing hum or noise into the audio signal. Bypass capacitors may be included to filter out any high-frequency noise from the power supply.
Overall, the successful implementation of this microphone preamp and tone control circuit will result in a versatile audio processing tool that enhances the clarity and quality of sound in various applications, from recording studios to live sound reinforcement. Proper layout and grounding techniques should be employed in the PCB design to further reduce interference and maintain signal integrity.Hi I have decided to build this mic preamp and tone control circuit which was posted on a another site. The Eq section is the same one used in the.. 🔗 External reference