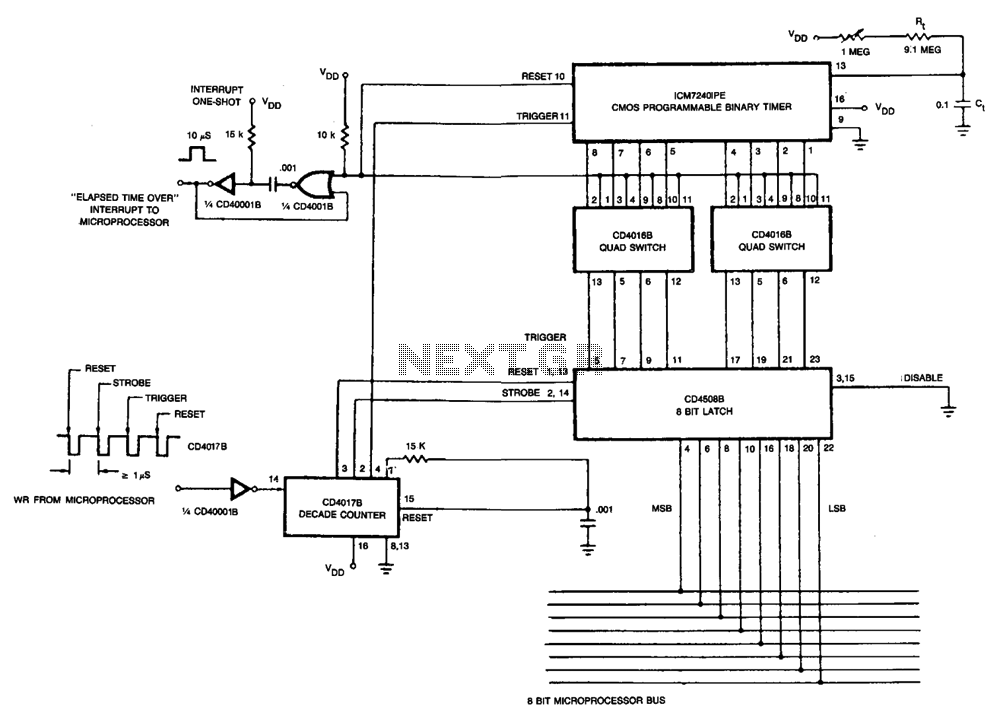
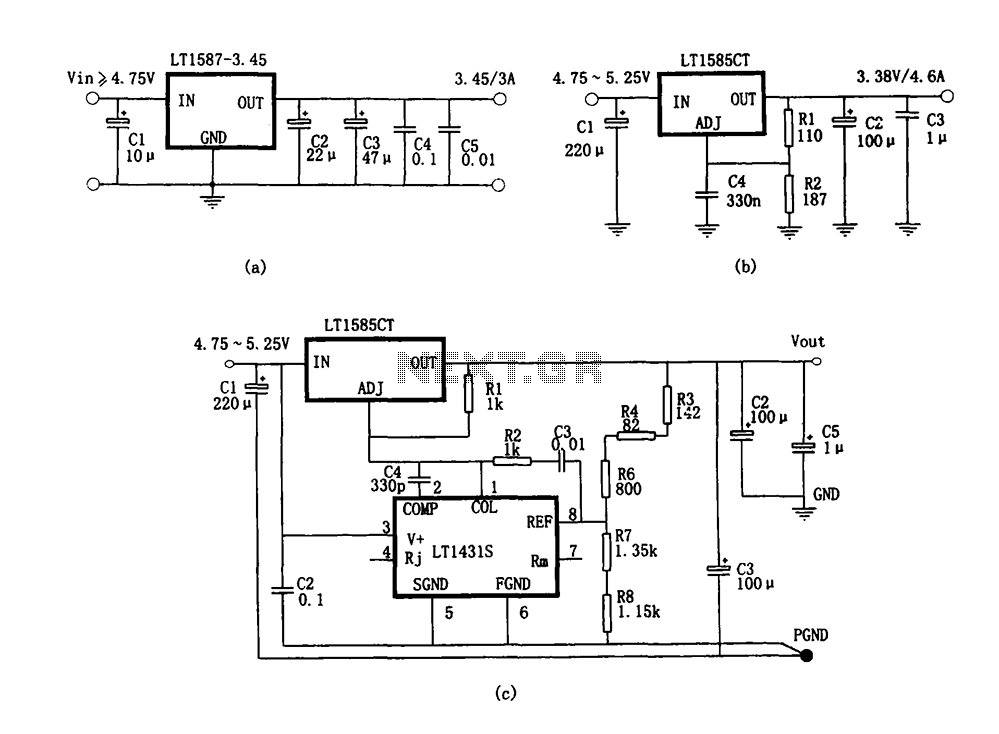
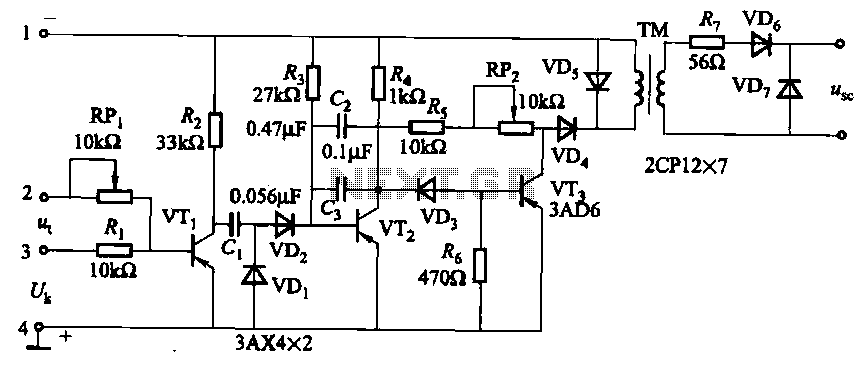
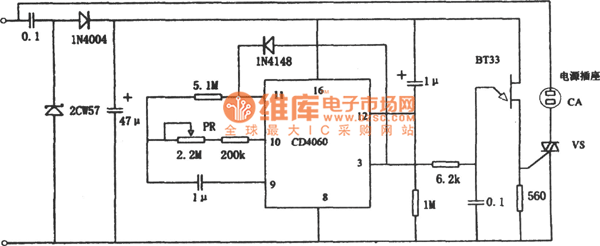
Microprocessor RS-232 Reset
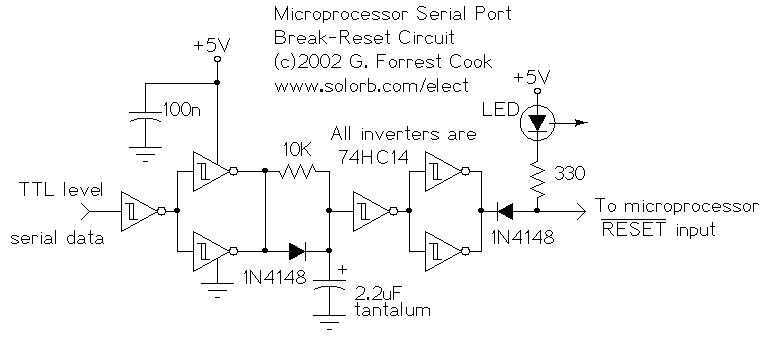
This circuit allows a remote microprocessor to be reset by a controlling host over a remote RS-232 or similar protocol serial line. With the use of a program loader on the remote host, a program may be downloaded and run. This allows a target processor to run different code in RAM, thus getting rid of the need to burn multiple EPROMs. The circuit is usually used for developing code on a target processor, but it can also be used for permanent applications where the target program lives on a host system's disk.
The described circuit facilitates communication between a controlling host and a remote microprocessor via an RS-232 serial interface. The primary function of this circuit is to enable the resetting of the microprocessor remotely, which is crucial for development and debugging processes. By utilizing a program loader on the host machine, software can be transmitted to the target microprocessor, allowing it to execute different programs stored in RAM. This capability eliminates the necessity of using multiple EPROMs for program storage, thereby streamlining the development process.
The circuit typically includes components such as a voltage level shifter to ensure compatibility between the RS-232 signal levels and the logic levels of the microprocessor. Additionally, a reset circuit may be incorporated, which can be triggered by a specific command sent from the host. This reset mechanism is essential for initializing the microprocessor after a new program has been uploaded.
Furthermore, the design may feature a microcontroller or a dedicated UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) to handle the serial communication. This allows for efficient data transfer rates and error-checking capabilities, ensuring that the program loader can reliably send data to the target processor. The circuit may also include a buffer to temporarily hold incoming data before it is processed by the microprocessor, thus accommodating variations in data transmission speeds.
In applications beyond development, this circuit can serve in permanent installations where the target program is stored on a host system's disk. This setup provides flexibility in updating the program without physical access to the microprocessor, enhancing the adaptability of the system for various operational requirements. Overall, the circuit represents a significant advancement in remote programming and debugging techniques for embedded systems.This circuit allows a remote microprocessor to be reset by a controlling host over a remote RS-232 or similar protocol serial line. With the use of a program loader on the remote host, a program may be downloaded and run. This allows a target processor to run different code in RAM, thus getting rid of the need to burn multiple EPROMs.
The circuit is usually used for developing code on a target processor, but it can also be used for permanent applications where the target program lives on a host system`s disk. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit facilitates communication between a controlling host and a remote microprocessor via an RS-232 serial interface. The primary function of this circuit is to enable the resetting of the microprocessor remotely, which is crucial for development and debugging processes. By utilizing a program loader on the host machine, software can be transmitted to the target microprocessor, allowing it to execute different programs stored in RAM. This capability eliminates the necessity of using multiple EPROMs for program storage, thereby streamlining the development process.
The circuit typically includes components such as a voltage level shifter to ensure compatibility between the RS-232 signal levels and the logic levels of the microprocessor. Additionally, a reset circuit may be incorporated, which can be triggered by a specific command sent from the host. This reset mechanism is essential for initializing the microprocessor after a new program has been uploaded.
Furthermore, the design may feature a microcontroller or a dedicated UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) to handle the serial communication. This allows for efficient data transfer rates and error-checking capabilities, ensuring that the program loader can reliably send data to the target processor. The circuit may also include a buffer to temporarily hold incoming data before it is processed by the microprocessor, thus accommodating variations in data transmission speeds.
In applications beyond development, this circuit can serve in permanent installations where the target program is stored on a host system's disk. This setup provides flexibility in updating the program without physical access to the microprocessor, enhancing the adaptability of the system for various operational requirements. Overall, the circuit represents a significant advancement in remote programming and debugging techniques for embedded systems.This circuit allows a remote microprocessor to be reset by a controlling host over a remote RS-232 or similar protocol serial line. With the use of a program loader on the remote host, a program may be downloaded and run. This allows a target processor to run different code in RAM, thus getting rid of the need to burn multiple EPROMs.
The circuit is usually used for developing code on a target processor, but it can also be used for permanent applications where the target program lives on a host system`s disk. 🔗 External reference