mini audio analyzer
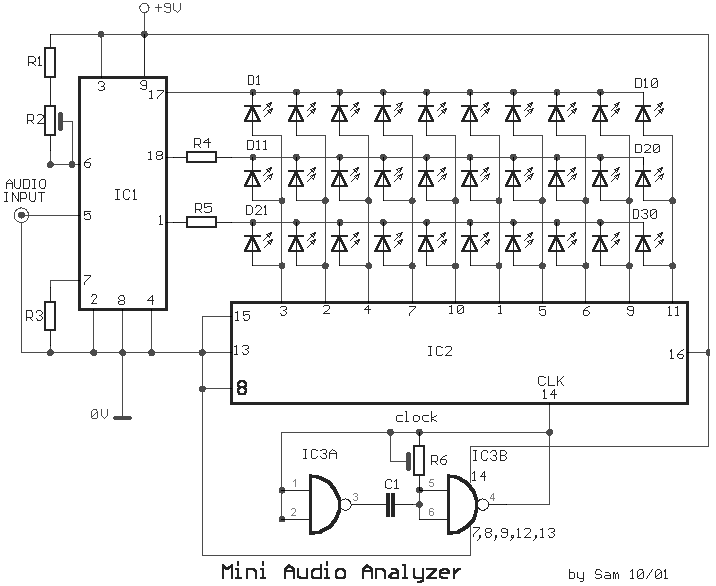
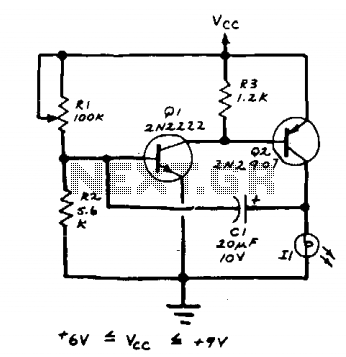
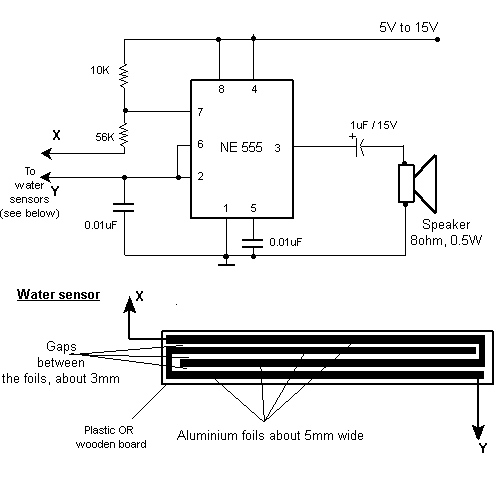
This device is a sensitive instrument that detects frequency changes and the width of an acoustic signal. The brightness of the LED that activates at each moment is proportional to the signal width, while the color corresponds to the frequency.
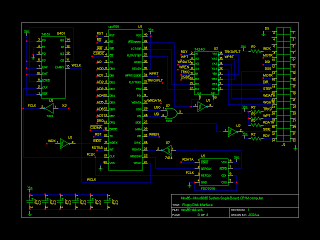
The circuit described operates as an acoustic signal analyzer, utilizing an LED as a visual output to represent the characteristics of the incoming signal. The core components of the circuit include a microphone or piezoelectric sensor to capture the acoustic signals, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital signal processing, and a microcontroller to interpret the signal data.
The microphone converts sound waves into electrical signals, which are then fed into the ADC. The ADC samples the analog signal and converts it into a digital format that can be processed by the microcontroller. The microcontroller analyzes the digital signal to determine both the frequency and the width of the signal.
To represent the signal width, the microcontroller adjusts the brightness of the LED. This is achieved through pulse-width modulation (PWM), where the duty cycle of the PWM signal controls the average power delivered to the LED. A wider signal translates to a higher duty cycle, resulting in increased brightness.
For frequency representation, the microcontroller may use a color LED or a multi-color LED that can change color based on the frequency detected. By mapping specific frequency ranges to corresponding colors, the system provides a visual representation of the frequency content of the acoustic signal.
This circuit can have applications in various fields such as audio engineering, sound analysis, and educational tools for demonstrating acoustic principles. Proper calibration and tuning of the circuit are essential to ensure accurate representation of the signal characteristics, which can be achieved through adjustments in the software algorithms and hardware components.This analyst is, a sensitive instrument, in the frequency changes and width of a acoustic signal. Thus the brightness of LED that turns on each moment of is proportional signal width, while the colour of proportionally frequency.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described operates as an acoustic signal analyzer, utilizing an LED as a visual output to represent the characteristics of the incoming signal. The core components of the circuit include a microphone or piezoelectric sensor to capture the acoustic signals, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital signal processing, and a microcontroller to interpret the signal data.
The microphone converts sound waves into electrical signals, which are then fed into the ADC. The ADC samples the analog signal and converts it into a digital format that can be processed by the microcontroller. The microcontroller analyzes the digital signal to determine both the frequency and the width of the signal.
To represent the signal width, the microcontroller adjusts the brightness of the LED. This is achieved through pulse-width modulation (PWM), where the duty cycle of the PWM signal controls the average power delivered to the LED. A wider signal translates to a higher duty cycle, resulting in increased brightness.
For frequency representation, the microcontroller may use a color LED or a multi-color LED that can change color based on the frequency detected. By mapping specific frequency ranges to corresponding colors, the system provides a visual representation of the frequency content of the acoustic signal.
This circuit can have applications in various fields such as audio engineering, sound analysis, and educational tools for demonstrating acoustic principles. Proper calibration and tuning of the circuit are essential to ensure accurate representation of the signal characteristics, which can be achieved through adjustments in the software algorithms and hardware components.This analyst is, a sensitive instrument, in the frequency changes and width of a acoustic signal. Thus the brightness of LED that turns on each moment of is proportional signal width, while the colour of proportionally frequency.. 🔗 External reference