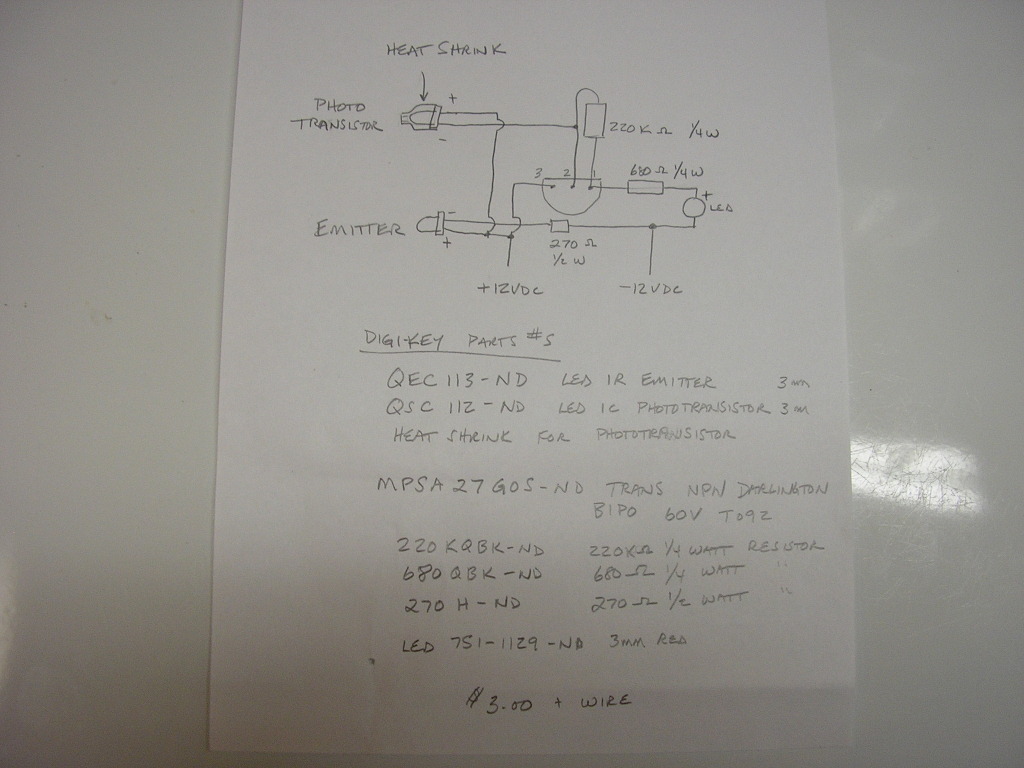
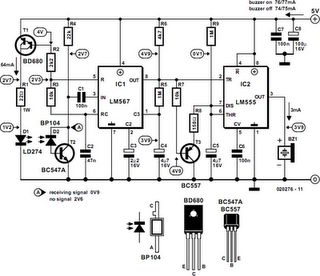
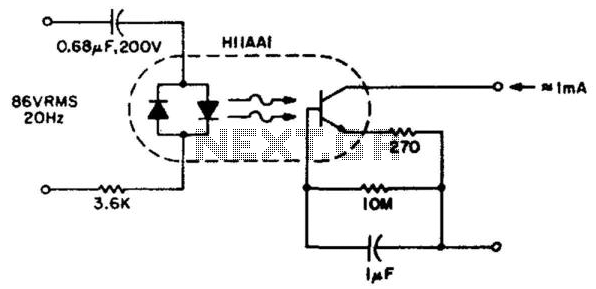
Moisture detector
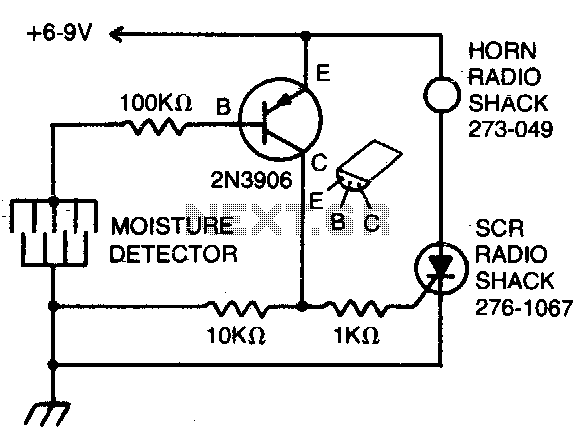
The detector consists of fine wires spaced approximately one to two inches apart. When the area between a pair of wires becomes moist, an alarm will sound. To deactivate the alarm, the DC power must be disconnected.
The described moisture detector employs a simple yet effective design utilizing fine wires arranged in parallel with a specified spacing. This configuration allows for the detection of moisture between the wires, which serves as the primary sensing mechanism. When moisture bridges the gap between any two wires, it completes an electrical circuit, triggering an alarm system, typically in the form of a horn or buzzer.
The circuit can be powered by a DC power supply, which is essential for the operation of the alarm. The alarm will remain active as long as moisture is detected. To turn off the alarm, the DC power supply must be disconnected, which interrupts the power flow to the circuit and silences the horn.
For practical implementation, the circuit may include additional features such as a resistor to limit current flow, a diode for reverse polarity protection, and possibly a transistor to amplify the signal for the alarm. The spacing of the wires can be adjusted based on the application requirements, allowing for sensitivity tuning to detect varying levels of moisture. Furthermore, the entire assembly can be enclosed in a protective housing to prevent false alarms from environmental factors such as dust or debris while ensuring reliable operation in intended conditions.
Overall, this moisture detection system is straightforward and can be easily integrated into various applications, including agricultural monitoring, home safety systems, or industrial environments where moisture levels need to be controlled.The detector is made of fine wires spaced about one or two inches apart. When the area between a pair of wires becomes moistened, the horn will sound To turn it off, dc power must be disconnected.
The described moisture detector employs a simple yet effective design utilizing fine wires arranged in parallel with a specified spacing. This configuration allows for the detection of moisture between the wires, which serves as the primary sensing mechanism. When moisture bridges the gap between any two wires, it completes an electrical circuit, triggering an alarm system, typically in the form of a horn or buzzer.
The circuit can be powered by a DC power supply, which is essential for the operation of the alarm. The alarm will remain active as long as moisture is detected. To turn off the alarm, the DC power supply must be disconnected, which interrupts the power flow to the circuit and silences the horn.
For practical implementation, the circuit may include additional features such as a resistor to limit current flow, a diode for reverse polarity protection, and possibly a transistor to amplify the signal for the alarm. The spacing of the wires can be adjusted based on the application requirements, allowing for sensitivity tuning to detect varying levels of moisture. Furthermore, the entire assembly can be enclosed in a protective housing to prevent false alarms from environmental factors such as dust or debris while ensuring reliable operation in intended conditions.
Overall, this moisture detection system is straightforward and can be easily integrated into various applications, including agricultural monitoring, home safety systems, or industrial environments where moisture levels need to be controlled.The detector is made of fine wires spaced about one or two inches apart. When the area between a pair of wires becomes moistened, the horn will sound To turn it off, dc power must be disconnected.