Negative Voltage Supply Circuit

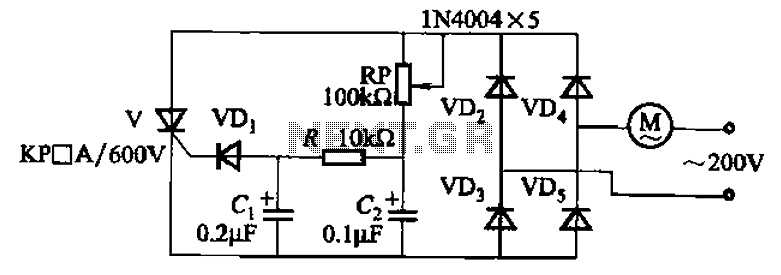
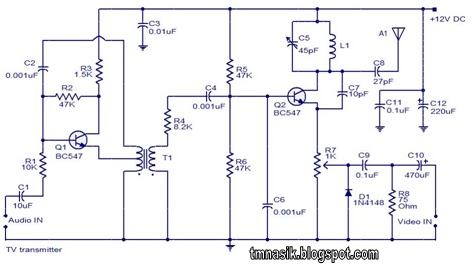
The combination of a Hartley oscillator and a step-up transformer can generate significant negative high voltage, particularly when the voltage output of the transformer is multiplied by the circuit.
The Hartley oscillator is a type of LC oscillator that utilizes an inductor-capacitor (LC) circuit to produce oscillations. It typically consists of two inductors and one capacitor, arranged in a feedback loop. The oscillator operates by charging and discharging the capacitor through the inductors, generating an alternating current (AC) output. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of the inductors and capacitor used in the circuit.
In this configuration, the step-up transformer plays a crucial role in amplifying the output voltage generated by the Hartley oscillator. The transformer consists of two coils of wire wound around a magnetic core. When an AC current flows through the primary coil, it creates a magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary coil. The turns ratio between the primary and secondary coils determines the multiplication factor of the voltage output.
When the Hartley oscillator's output is fed into the primary winding of the transformer, the resulting AC signal is transformed into a higher voltage in the secondary winding. This increased voltage can be utilized for various applications, including powering high-voltage devices or circuits that require a significant negative voltage supply.
The design considerations for this circuit include selecting appropriate values for the inductors and capacitor to achieve the desired frequency of oscillation, as well as determining the turns ratio of the transformer to ensure that the output voltage meets the requirements of the intended application. Additionally, attention must be given to component ratings, thermal management, and circuit layout to ensure reliable operation and prevent damage to sensitive components.
Overall, the combination of a Hartley oscillator with a step-up transformer is an effective method for generating significant negative high voltage, with the potential for various practical applications in electronics. The combination Hartley oscillator/step-up transformer shown in A can generate significant negative high voltage, especially if the voltage output of the transformer is multiplied by the circuit.
The Hartley oscillator is a type of LC oscillator that utilizes an inductor-capacitor (LC) circuit to produce oscillations. It typically consists of two inductors and one capacitor, arranged in a feedback loop. The oscillator operates by charging and discharging the capacitor through the inductors, generating an alternating current (AC) output. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the values of the inductors and capacitor used in the circuit.
In this configuration, the step-up transformer plays a crucial role in amplifying the output voltage generated by the Hartley oscillator. The transformer consists of two coils of wire wound around a magnetic core. When an AC current flows through the primary coil, it creates a magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary coil. The turns ratio between the primary and secondary coils determines the multiplication factor of the voltage output.
When the Hartley oscillator's output is fed into the primary winding of the transformer, the resulting AC signal is transformed into a higher voltage in the secondary winding. This increased voltage can be utilized for various applications, including powering high-voltage devices or circuits that require a significant negative voltage supply.
The design considerations for this circuit include selecting appropriate values for the inductors and capacitor to achieve the desired frequency of oscillation, as well as determining the turns ratio of the transformer to ensure that the output voltage meets the requirements of the intended application. Additionally, attention must be given to component ratings, thermal management, and circuit layout to ensure reliable operation and prevent damage to sensitive components.
Overall, the combination of a Hartley oscillator with a step-up transformer is an effective method for generating significant negative high voltage, with the potential for various practical applications in electronics. The combination Hartley oscillator/step-up transformer shown in A can generate significant negative high voltage, especially if the voltage output of the transformer is multiplied by the circuit.