Only one-way operation of the automatic control circuit of the motor
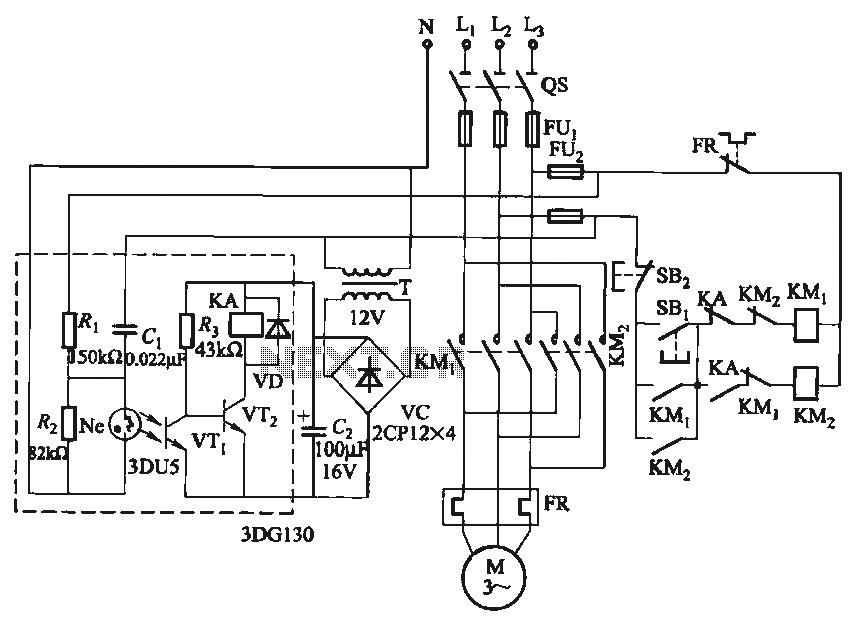
In certain applications, it is crucial to allow a motor to operate in only one specific direction, even when the power supply phase sequence is incorrect. This situation may arise due to external factors, such as incorrect wiring after maintenance. To prevent damage to both the motor and associated equipment, it is essential to control the phase sequence. The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-90 addresses this requirement. When the power supply phase sequence is correct, meaning the U, V, W phases are in the proper order, the neon bulb (Ne) remains off, and the relay (KA) is activated. When the start button (SBi) is pressed, the contact (KMi) engages, allowing the motor to start running in the forward direction. Conversely, if the power supply phase sequence is incorrect, the neon bulb lights up, and relay (KA) is deactivated. Pressing the start button (SBi) in this situation causes relay (KMz) to engage, allowing the motor to continue running in the forward direction despite the incorrect phase sequence.
The described circuit employs a phase sequence detector to ensure that the motor operates correctly under varying conditions. The neon bulb serves as an indicator of the phase sequence status; when it is illuminated, it signifies that the phase sequence is incorrect. The relay (KA) acts as a safety mechanism, preventing the motor from starting if the phase sequence is not as required. The use of two relays, KA and KMz, allows for a fail-safe operation: KA ensures that the motor does not start under incorrect conditions, while KMz provides a means to maintain motor operation even when the phase sequence is altered.
This circuit can be particularly beneficial in industrial settings where motors are frequently subjected to changes in power supply conditions. By implementing this phase sequence control mechanism, the risk of equipment damage is significantly reduced, and operational reliability is enhanced. The design should ensure that all components, such as relays and indicators, are rated for the specific voltage and current levels associated with the motor and power supply to maintain safety and efficiency. Proper installation and regular maintenance of this circuit will contribute to its longevity and the overall safety of the motor operation.In some places, allowing only a specific direction by the motor running, even when the power supply phase sequence for some reason (such as outside line after overhaul wrong) while inverted, but also to ensure that the motor running in the specified direction. Otherwise, it will cause physical and equipment do so. The phase sequence can be used for this determination is to be controlled. Circuit shown in Figure 3-90. When the power supply phase sequence is correct, that is, U, V, W phase sequence when, Ne neon bulb does not light, relay device KA pull, press the start button SBi, contact KMi pull the motor starts running forward.
If the power supply phase sequence right, Ne shiny, KA released. Press SBi, KMz suction units, the motor will change the phase sequence followed by people power, the motor still running forward start.
The described circuit employs a phase sequence detector to ensure that the motor operates correctly under varying conditions. The neon bulb serves as an indicator of the phase sequence status; when it is illuminated, it signifies that the phase sequence is incorrect. The relay (KA) acts as a safety mechanism, preventing the motor from starting if the phase sequence is not as required. The use of two relays, KA and KMz, allows for a fail-safe operation: KA ensures that the motor does not start under incorrect conditions, while KMz provides a means to maintain motor operation even when the phase sequence is altered.
This circuit can be particularly beneficial in industrial settings where motors are frequently subjected to changes in power supply conditions. By implementing this phase sequence control mechanism, the risk of equipment damage is significantly reduced, and operational reliability is enhanced. The design should ensure that all components, such as relays and indicators, are rated for the specific voltage and current levels associated with the motor and power supply to maintain safety and efficiency. Proper installation and regular maintenance of this circuit will contribute to its longevity and the overall safety of the motor operation.In some places, allowing only a specific direction by the motor running, even when the power supply phase sequence for some reason (such as outside line after overhaul wrong) while inverted, but also to ensure that the motor running in the specified direction. Otherwise, it will cause physical and equipment do so. The phase sequence can be used for this determination is to be controlled. Circuit shown in Figure 3-90. When the power supply phase sequence is correct, that is, U, V, W phase sequence when, Ne neon bulb does not light, relay device KA pull, press the start button SBi, contact KMi pull the motor starts running forward.
If the power supply phase sequence right, Ne shiny, KA released. Press SBi, KMz suction units, the motor will change the phase sequence followed by people power, the motor still running forward start.