NE555 triangular wave loading system, square wave generator circuit
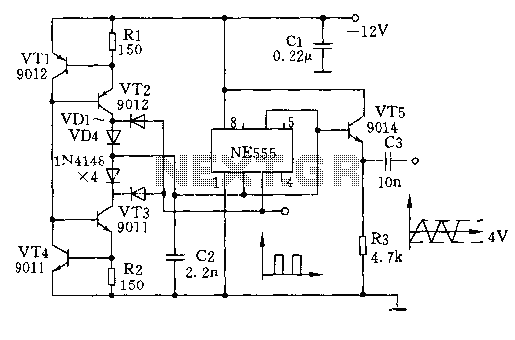
The circuit depicted involves transistors VT1, VT2, and resistor R1, which form a constant current source for charging capacitor C2 in a linear manner. Transistors VT3, VT4, and resistor R2 create a constant current source for discharging capacitor C2, also achieving linearity. Upon powering the circuit, the voltage across C2 is initially zero. The 555 timer IC's pins 2 and 6 are less than 1/3Vcc, causing pin 3 to output a high signal (approximately 10.8V), which forward-biases diode VD4 while reverse-biasing diode VD3. Diode VD1 is forward-biased, while VD2 is reverse-biased. The collector current from VT2 charges C2 through VD1. As the voltage across C2 increases linearly to 2/3Vcc (approximately 8V), the 555 timer triggers pin 6, causing pin 3 to output low (approximately 0V). At this point, diodes VD1 and VD4 are reverse-biased, while VD2 and VD3 are forward-biased, allowing the charge on capacitor C2 to discharge through the collector of VT3. When the voltage across C2 decreases linearly to 1/3Vcc (approximately 4V), the 555 timer triggers pin 2, resetting pin 3 to output high. This cycle can repeat, producing a highly linear triangular wave at pins 2 and 6, and a square wave with a 50% duty cycle at pin 3. The frequency of the circuit can range from 0 to over 200 kHz, demonstrating high stability. The frequency can be calculated as F = 0.1375 / ((R1 + R2) * C2), where the values of R1 and R2 can yield a frequency of approximately 208 kHz. The output buffer stage is provided by VT5, which removes the triangular wave from VT5 and stabilizes the output at around 4V. The circuit can be adjusted by changing the values of R1 or R2 to alter the rise or fall time of the triangular wave, which in turn affects the duty cycle of the square wave. Additionally, controlling the voltage at pin 5 of the 555 timer can modify the frequency of the square wave output at pin 3.
The described circuit utilizes a 555 timer IC in astable mode to generate a triangular wave and a corresponding square wave. The configuration allows for precise control over the frequency and duty cycle of the output signals. The constant current sources created by the transistors and resistors ensure that the charging and discharging of capacitor C2 occur in a linear fashion, which is crucial for maintaining the desired waveform characteristics.
The circuit's operation begins with the initial state where capacitor C2 is uncharged. As the circuit is powered, the 555 timer's output transitions based on the voltage levels across C2. The linear charging phase is facilitated by the constant current source formed by VT1, VT2, and R1, while the discharging phase is managed by VT3, VT4, and R2. This configuration allows for the generation of a triangular waveform, which is an essential feature for various applications, including signal processing and waveform generation.
The output frequency, determined by the resistors R1 and R2 and the capacitor C2, can be fine-tuned to meet specific requirements. The high-frequency capability of the circuit, extending up to 200 kHz, makes it suitable for applications that require rapid signal changes. Furthermore, the circuit's stability ensures reliable performance across its operational range.
In summary, this circuit serves as an effective waveform generator, leveraging the properties of the 555 timer and transistor current sources to produce stable and adjustable triangular and square waveforms, suitable for a variety of electronic applications.How it works: the circuit as shown in FIG. VT1, VT2 and resistor R1 constitute a constant current source for charging the capacitor C2 for linear; VT3, VT4 and resistor R2 constitute a constant current source for discharging the capacitor C2 to achieve linear. Circuit is first turned on, the voltage on C2 is zero, 555 IC 2,6 feet less than 1 / 3Vcc, its 3 feet high output (approximately 10.8V), forward-biased diode VD4, VD3 reverse bias; VD1 positive partial, VD2 reverse bias. VT2 collector current charging C2 through VD1, when the voltage on C2 linear growth 2 / 3Vcc (ie 8V) when the 555 trigger 6 feet, 3 feet so that output low (approximately 0V).
At this time VD1, VD4 reverse bias, and VD2, VD3 forward biased, the charge on the capacitor C2 through VT3 collector discharge, when the voltage on C2 linearly down to 1 / 3Vcc (ie 4V), the trigger 555 2 feet, leaving 3 pin reset output high, again and again, in 555 feet of 2,6 can get very high linearity of the triangular wave, and in 3 feet can get 50% duty cycle square wave. The frequency of this circuit is 0 ~ 200kHz and above range, and high stability. Frequency of the circuit by calculation:. F F0.1375 / (R1 + R2) C2 given by the circuit R1, R2 value, f F208kHz. Schematic VT5 high B output buffer stage, triangle pole removed from VT5 shot, by about 4V at the same time, the circuit can work application: change R1 or size R2, you can change the triangle wave rise or fall time, a corresponding change in the square wave duty cycle, or the control voltage 555 5 feet, 3 feet square wave can change the frequency (linear change).
The described circuit utilizes a 555 timer IC in astable mode to generate a triangular wave and a corresponding square wave. The configuration allows for precise control over the frequency and duty cycle of the output signals. The constant current sources created by the transistors and resistors ensure that the charging and discharging of capacitor C2 occur in a linear fashion, which is crucial for maintaining the desired waveform characteristics.
The circuit's operation begins with the initial state where capacitor C2 is uncharged. As the circuit is powered, the 555 timer's output transitions based on the voltage levels across C2. The linear charging phase is facilitated by the constant current source formed by VT1, VT2, and R1, while the discharging phase is managed by VT3, VT4, and R2. This configuration allows for the generation of a triangular waveform, which is an essential feature for various applications, including signal processing and waveform generation.
The output frequency, determined by the resistors R1 and R2 and the capacitor C2, can be fine-tuned to meet specific requirements. The high-frequency capability of the circuit, extending up to 200 kHz, makes it suitable for applications that require rapid signal changes. Furthermore, the circuit's stability ensures reliable performance across its operational range.
In summary, this circuit serves as an effective waveform generator, leveraging the properties of the 555 timer and transistor current sources to produce stable and adjustable triangular and square waveforms, suitable for a variety of electronic applications.How it works: the circuit as shown in FIG. VT1, VT2 and resistor R1 constitute a constant current source for charging the capacitor C2 for linear; VT3, VT4 and resistor R2 constitute a constant current source for discharging the capacitor C2 to achieve linear. Circuit is first turned on, the voltage on C2 is zero, 555 IC 2,6 feet less than 1 / 3Vcc, its 3 feet high output (approximately 10.8V), forward-biased diode VD4, VD3 reverse bias; VD1 positive partial, VD2 reverse bias. VT2 collector current charging C2 through VD1, when the voltage on C2 linear growth 2 / 3Vcc (ie 8V) when the 555 trigger 6 feet, 3 feet so that output low (approximately 0V).
At this time VD1, VD4 reverse bias, and VD2, VD3 forward biased, the charge on the capacitor C2 through VT3 collector discharge, when the voltage on C2 linearly down to 1 / 3Vcc (ie 4V), the trigger 555 2 feet, leaving 3 pin reset output high, again and again, in 555 feet of 2,6 can get very high linearity of the triangular wave, and in 3 feet can get 50% duty cycle square wave. The frequency of this circuit is 0 ~ 200kHz and above range, and high stability. Frequency of the circuit by calculation:. F F0.1375 / (R1 + R2) C2 given by the circuit R1, R2 value, f F208kHz. Schematic VT5 high B output buffer stage, triangle pole removed from VT5 shot, by about 4V at the same time, the circuit can work application: change R1 or size R2, you can change the triangle wave rise or fall time, a corresponding change in the square wave duty cycle, or the control voltage 555 5 feet, 3 feet square wave can change the frequency (linear change).