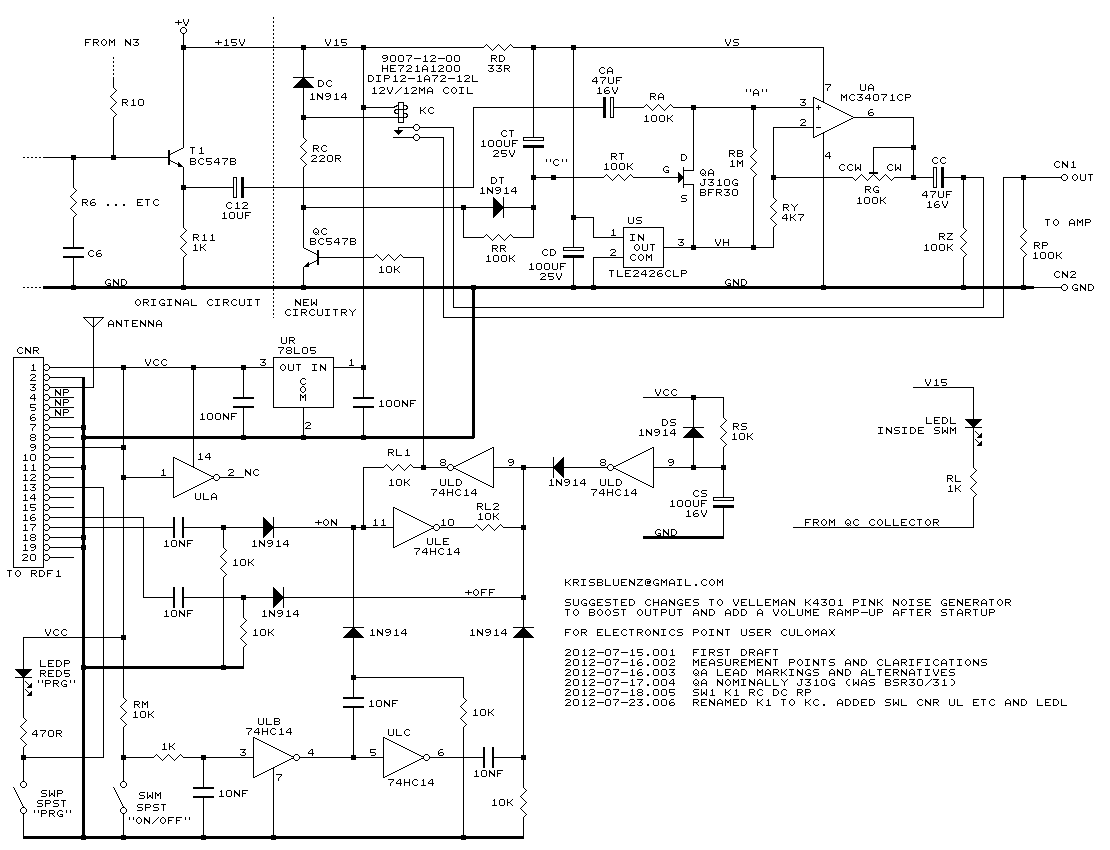
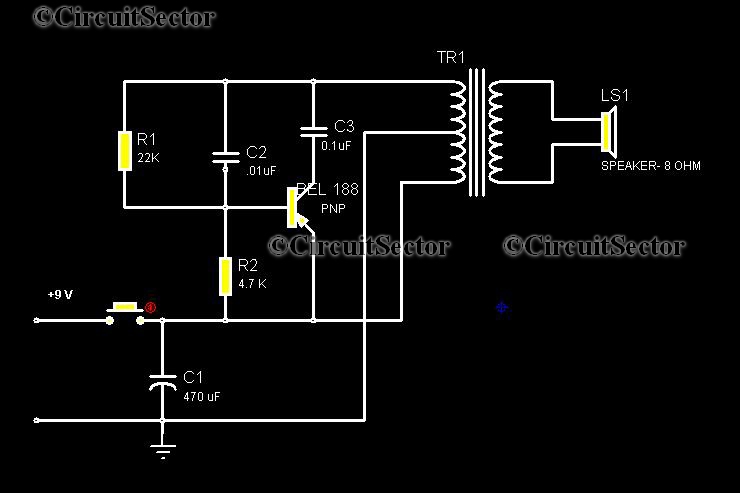
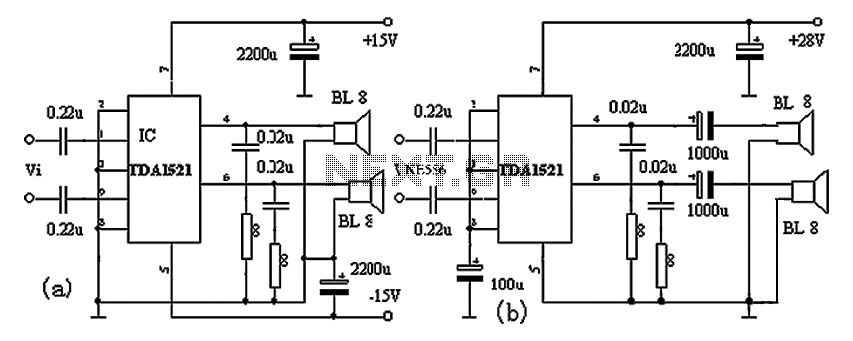
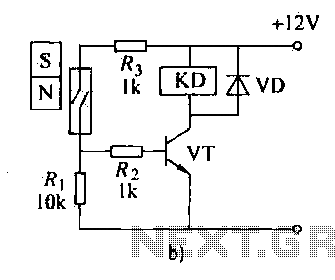
Binary circuit diagram box
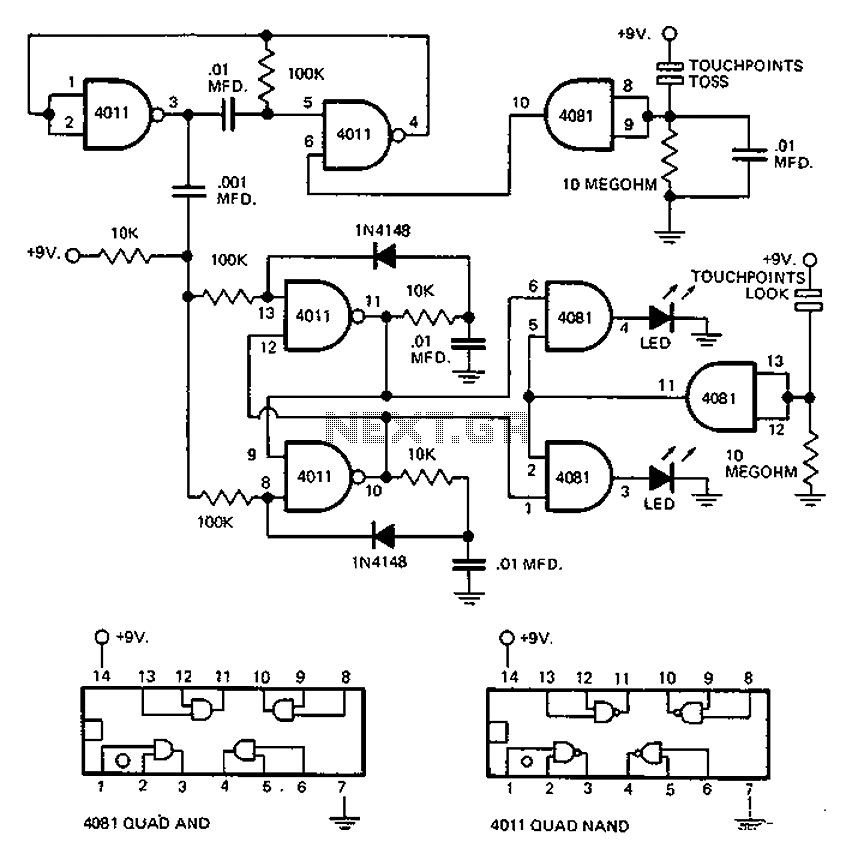
This circuit employs an astable multivibrator to alter the state of a signal based on specific conditions. It also incorporates a flip-flop, which retains the state of the output once a change is detected, completing a cycle of the oscillator.
The circuit utilizes an astable multivibrator, which is a type of oscillator that continuously switches between its high and low states without requiring any external triggering. The multivibrator generates a square wave output, which can be used to drive other components or systems. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the resistors and capacitors connected to the multivibrator.
In conjunction with the astable multivibrator, a flip-flop is employed to store the state of the output signal. The flip-flop can be configured to respond to the transitions of the multivibrator's output, effectively capturing the signal state at specific intervals. This capability allows for the retention of the signal's state even after the triggering event has passed, making it useful in applications where the state needs to be preserved for further processing or control.
The combination of the astable multivibrator and the flip-flop creates a robust circuit that can be utilized in various applications, such as timing circuits, pulse width modulation, or as a basic memory element in digital systems. The design flexibility allows for adjustments in frequency and output characteristics, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic projects. Proper selection of components and configuration will ensure optimal performance and reliability of the circuit. Circuit Description: This circuit uses an astable multivibrator to change the face-up or facing negative circumstances, also uses a flip-flop, flip-flop state that there had be en a change is to be stored by multivibrator complete cycle of each of the oscillator.
The circuit utilizes an astable multivibrator, which is a type of oscillator that continuously switches between its high and low states without requiring any external triggering. The multivibrator generates a square wave output, which can be used to drive other components or systems. The frequency of oscillation is determined by the resistors and capacitors connected to the multivibrator.
In conjunction with the astable multivibrator, a flip-flop is employed to store the state of the output signal. The flip-flop can be configured to respond to the transitions of the multivibrator's output, effectively capturing the signal state at specific intervals. This capability allows for the retention of the signal's state even after the triggering event has passed, making it useful in applications where the state needs to be preserved for further processing or control.
The combination of the astable multivibrator and the flip-flop creates a robust circuit that can be utilized in various applications, such as timing circuits, pulse width modulation, or as a basic memory element in digital systems. The design flexibility allows for adjustments in frequency and output characteristics, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic projects. Proper selection of components and configuration will ensure optimal performance and reliability of the circuit. Circuit Description: This circuit uses an astable multivibrator to change the face-up or facing negative circumstances, also uses a flip-flop, flip-flop state that there had be en a change is to be stored by multivibrator complete cycle of each of the oscillator.