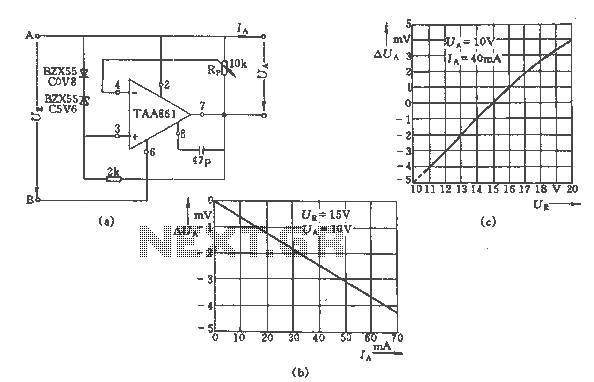
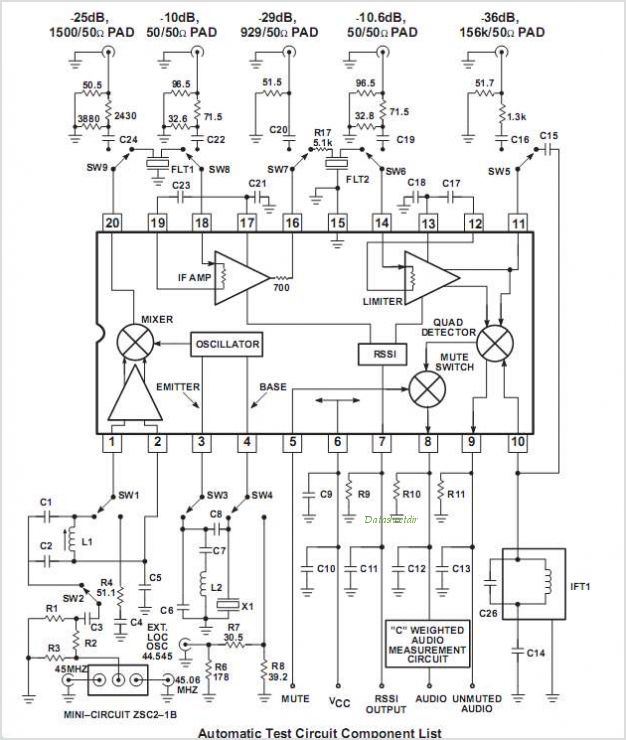
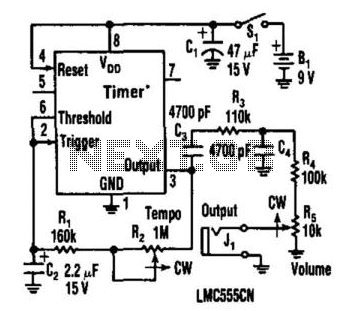
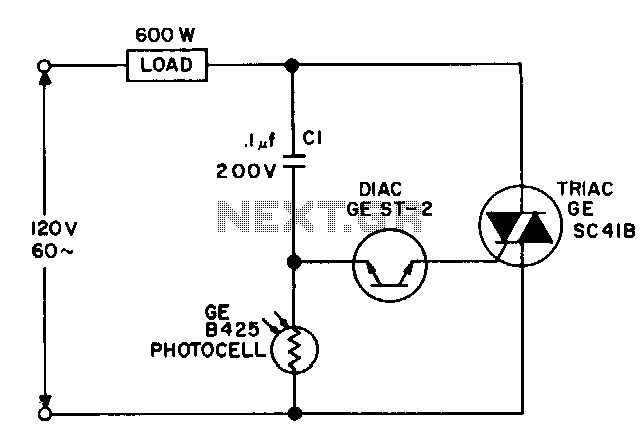
PFC Switching Power Supply

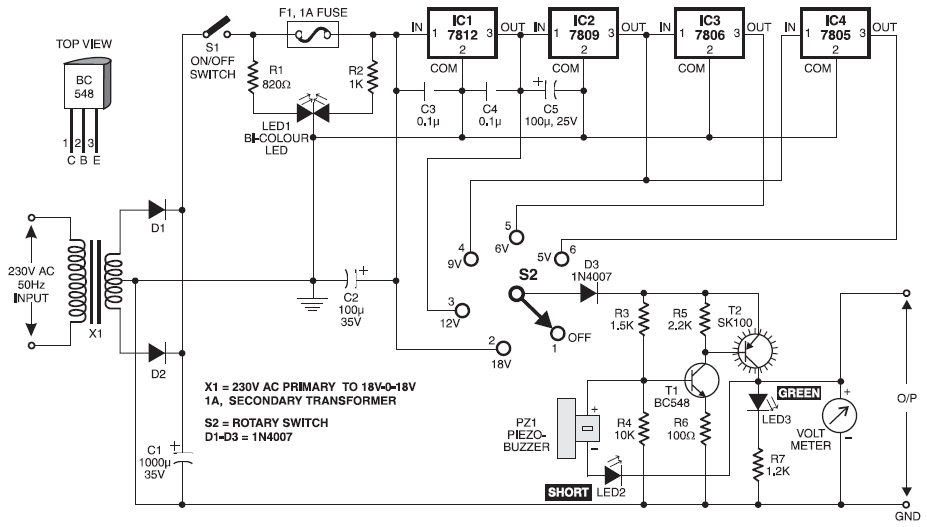
The following circuit illustrates a Power Factor Correction (PFC) Switching Power Supply Circuit Diagram. Features include suitability for 1U (1.75-inch) form factor and minimization of input harmonics.
The PFC Switching Power Supply Circuit is designed to enhance the efficiency of power conversion while reducing harmonic distortion at the input stage. This circuit typically employs a PFC controller, which regulates the input current to follow the input voltage waveform, thereby improving the power factor towards unity.
The circuit can be implemented using a boost converter topology, where the input AC voltage is rectified to DC and then boosted to a higher DC voltage level. The PFC controller continuously monitors the input voltage and adjusts the duty cycle of the switching element, usually a MOSFET, to maintain the desired power factor.
Key components of the circuit include:
1. **Rectifier**: Converts AC input voltage to pulsating DC. Often a bridge rectifier is used to handle both halves of the AC waveform.
2. **Boost Converter**: Comprises an inductor, a diode, a switch (MOSFET), and a capacitor. The inductor stores energy when the switch is closed and releases it when the switch is open, boosting the voltage.
3. **PFC Controller**: This integrated circuit (IC) monitors the input voltage and adjusts the switching duty cycle to achieve a sinusoidal input current that is in phase with the input voltage.
4. **Filter Capacitor**: Smooths the output voltage to reduce ripple, ensuring stable operation of downstream components.
5. **Feedback Loop**: Provides real-time adjustments to the PFC controller based on the output voltage and current, contributing to overall circuit stability.
The design is particularly suited for applications requiring compact form factors, such as 1U rack-mounted systems, where space is limited. Additionally, the minimization of input harmonics is crucial for compliance with regulations such as IEC 61000-3-2, which governs harmonic emissions in electrical equipment.
Overall, this circuit design not only enhances energy efficiency but also contributes to a cleaner power supply, reducing the environmental impact of electronic devices.The following circuit shows about PFC Switching Power Supply Circuit Diagram. Features: suited for 1U (1.75-inch), minimise input harmonic .. 🔗 External reference
The PFC Switching Power Supply Circuit is designed to enhance the efficiency of power conversion while reducing harmonic distortion at the input stage. This circuit typically employs a PFC controller, which regulates the input current to follow the input voltage waveform, thereby improving the power factor towards unity.
The circuit can be implemented using a boost converter topology, where the input AC voltage is rectified to DC and then boosted to a higher DC voltage level. The PFC controller continuously monitors the input voltage and adjusts the duty cycle of the switching element, usually a MOSFET, to maintain the desired power factor.
Key components of the circuit include:
1. **Rectifier**: Converts AC input voltage to pulsating DC. Often a bridge rectifier is used to handle both halves of the AC waveform.
2. **Boost Converter**: Comprises an inductor, a diode, a switch (MOSFET), and a capacitor. The inductor stores energy when the switch is closed and releases it when the switch is open, boosting the voltage.
3. **PFC Controller**: This integrated circuit (IC) monitors the input voltage and adjusts the switching duty cycle to achieve a sinusoidal input current that is in phase with the input voltage.
4. **Filter Capacitor**: Smooths the output voltage to reduce ripple, ensuring stable operation of downstream components.
5. **Feedback Loop**: Provides real-time adjustments to the PFC controller based on the output voltage and current, contributing to overall circuit stability.
The design is particularly suited for applications requiring compact form factors, such as 1U rack-mounted systems, where space is limited. Additionally, the minimization of input harmonics is crucial for compliance with regulations such as IEC 61000-3-2, which governs harmonic emissions in electrical equipment.
Overall, this circuit design not only enhances energy efficiency but also contributes to a cleaner power supply, reducing the environmental impact of electronic devices.The following circuit shows about PFC Switching Power Supply Circuit Diagram. Features: suited for 1U (1.75-inch), minimise input harmonic .. 🔗 External reference