phono preamp

Contents Introduction Two Versions RF Pickup Component Selection and Noise Sound Photo Gallery Introduction In support of the LM4562 op-amp, National Semiconductor published Application Note AN-1651, which discusses the growing requirements of high-performance audio. The author, Joe Curcio, provided designs for two phonostages and an electrostatic headphone driver. The second phonostage design was constructed.
The LM4562 operational amplifier is a high-performance audio op-amp known for its low noise and distortion characteristics, making it suitable for audio applications. The application note AN-1651 outlines various circuit designs that leverage the capabilities of the LM4562, specifically targeting high-fidelity audio performance.
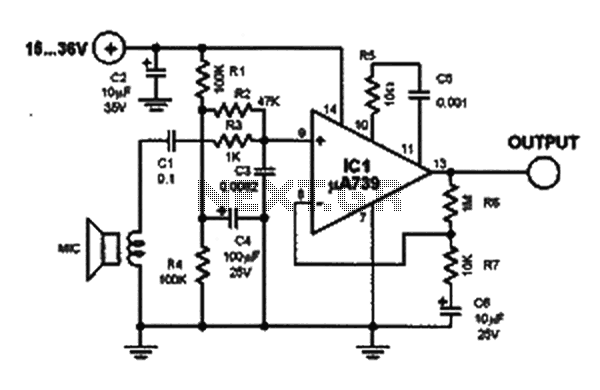
The first design presented is a phonostage amplifier, which is crucial for amplifying the low-level signals from a turntable. This circuit typically includes a differential input stage that utilizes the LM4562 to maintain high common-mode rejection and low noise levels. The selection of resistors and capacitors in this stage is critical to ensure that the frequency response is flat across the audible spectrum, minimizing any coloration of the audio signal.
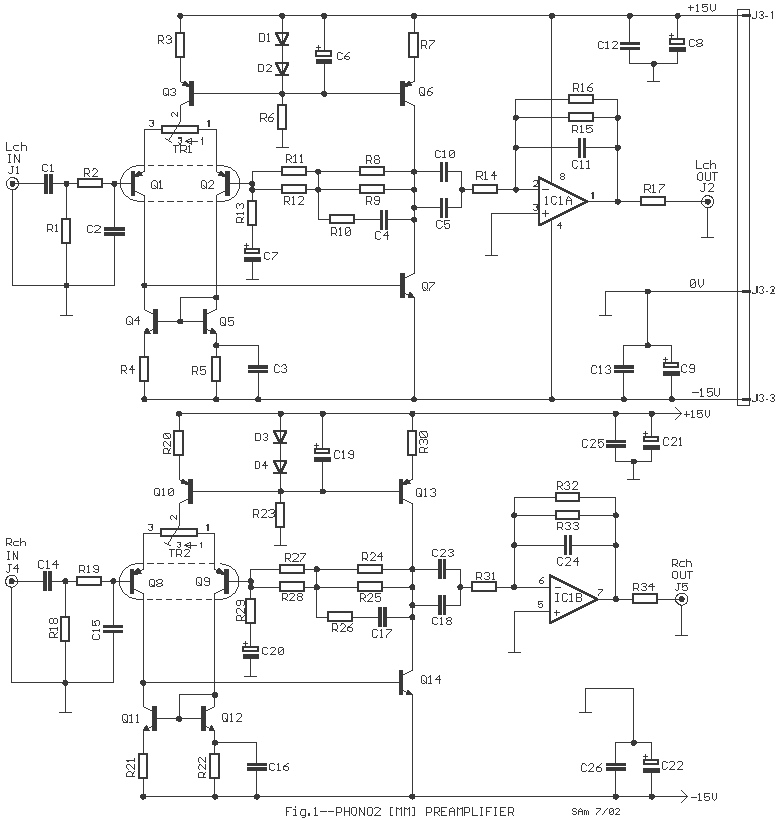
The second phonostage design, which was constructed, features an enhanced layout for improved signal integrity and reduced electromagnetic interference. This design may incorporate additional filtering stages to suppress RF noise, which is essential for maintaining audio clarity in environments with high RF emissions. Critical components such as film capacitors and precision resistors are recommended to maintain the integrity of the audio signal.
The application note also discusses the selection of components for optimal performance, emphasizing the importance of using low-noise resistors and high-quality capacitors to minimize signal degradation. The layout of the PCB should be designed to minimize trace lengths and avoid ground loops, which can introduce unwanted noise into the audio path.
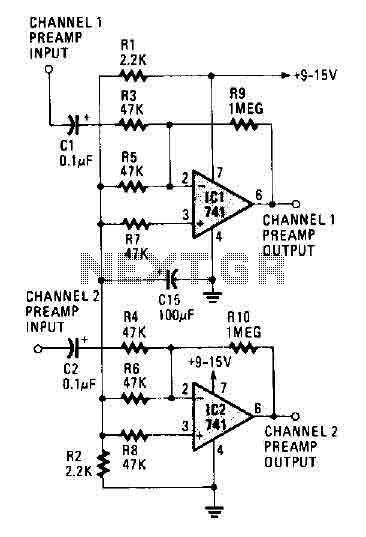
In addition to the phonostage designs, the application note includes a section on an electrostatic headphone driver, which requires a different approach due to the unique characteristics of electrostatic headphones. The driver circuit must provide high voltage while maintaining low distortion, and the LM4562 can be utilized in this application as well.
Overall, the insights provided in AN-1651 serve as a valuable resource for audio engineers and hobbyists looking to create high-performance audio equipment using the LM4562 op-amp, with detailed guidelines on circuit design, component selection, and layout considerations to achieve optimal audio fidelity.Contents Introduction Two Versions RF Pickup Component Selection and Noise Sound Photo Gallery Introduction In support of the LM4562 opamp, National Semiconductor published Application Note AN-1651, Keeping Up with the Expanding Demands of High-Performance Audio. The author, Joe Curcio, showed designs for two phonostages and an electrostatic headphone driver. I built the second phonostage design,.. 🔗 External reference
The LM4562 operational amplifier is a high-performance audio op-amp known for its low noise and distortion characteristics, making it suitable for audio applications. The application note AN-1651 outlines various circuit designs that leverage the capabilities of the LM4562, specifically targeting high-fidelity audio performance.
The first design presented is a phonostage amplifier, which is crucial for amplifying the low-level signals from a turntable. This circuit typically includes a differential input stage that utilizes the LM4562 to maintain high common-mode rejection and low noise levels. The selection of resistors and capacitors in this stage is critical to ensure that the frequency response is flat across the audible spectrum, minimizing any coloration of the audio signal.
The second phonostage design, which was constructed, features an enhanced layout for improved signal integrity and reduced electromagnetic interference. This design may incorporate additional filtering stages to suppress RF noise, which is essential for maintaining audio clarity in environments with high RF emissions. Critical components such as film capacitors and precision resistors are recommended to maintain the integrity of the audio signal.
The application note also discusses the selection of components for optimal performance, emphasizing the importance of using low-noise resistors and high-quality capacitors to minimize signal degradation. The layout of the PCB should be designed to minimize trace lengths and avoid ground loops, which can introduce unwanted noise into the audio path.
In addition to the phonostage designs, the application note includes a section on an electrostatic headphone driver, which requires a different approach due to the unique characteristics of electrostatic headphones. The driver circuit must provide high voltage while maintaining low distortion, and the LM4562 can be utilized in this application as well.
Overall, the insights provided in AN-1651 serve as a valuable resource for audio engineers and hobbyists looking to create high-performance audio equipment using the LM4562 op-amp, with detailed guidelines on circuit design, component selection, and layout considerations to achieve optimal audio fidelity.Contents Introduction Two Versions RF Pickup Component Selection and Noise Sound Photo Gallery Introduction In support of the LM4562 opamp, National Semiconductor published Application Note AN-1651, Keeping Up with the Expanding Demands of High-Performance Audio. The author, Joe Curcio, showed designs for two phonostages and an electrostatic headphone driver. I built the second phonostage design,.. 🔗 External reference